The Rupee is the common name for the currency of India. The word rupee is derived from the Sanskrit word rupya, which means silver. Which was the first rupee? When was the Rupee Symbol introduced? Countries which have Rupee has Currency, History of Rupee
Table of Contents
Indian Rupee, Notes and Coins
The Indian rupee (sign: ₹; code: INR) is the official currency of India. The rupee is subdivided into 100 paise (singular paisa), though as of 2018, coins of denomination of 50 paise is the lowest value in use. The issuance of the currency is controlled by the Reserve Bank of India
The contemporary Indian notes are Rs 10, Rs 20, Rs 50, Rs 100, Rs 200, Rs 500 & Rs 2000. These notes show the portrait of Mahatma Gandhi on the face & hence is called a Mahatma Gandhi series.
The pictures on the back of Indian notes reflect our culture, our history, our progress. Our article, Monuments on The Indian Notes: Konark Temple, Mangalyaan Mission, discusses it in detail.
Notes have two sides, the side which has the face of Mahatma Gandhi is called as Obverse & the other side is called Reverse.
On 8 Nov 2016, the Government of India announced the demonetisation of ₹500 and ₹1000 banknotes with effect from midnight of the same day, making these notes invalid. Our article Demonetization in India 2016: Success or Failure covers Demonetization in detail.

Rupee Symbol
On 5th March 2009, a contest was announced. President Mr.Pranab Mukherjee said, “New Indian rupee symbol should reflect our Indian culture And ethos.”
Out of 3000 designs, 5 were shortlisted, shown in the image below
Cabinet selected the definite symbol on 15 JULY 2010. The winner was Mr Udaya Kumar, Assistant Professor at IIT Guwahati. He was awarded 2.5 lakh. The design is based on the Tricolour, with two lines at the top and white space in between. Rupee symbol represents the Indian flag. It is a blend of Indian and Roman letters: a capital ‘R’, and Devanagari ‘ra’, which represent rupya.

Countries which have Rupee has Currency
The rupee is the common name for the currencies of India, Pakistan, Indonesia, Maldives, Mauritius, Nepal, Seychelles, Sri Lanka. In the Maldives, the unit of currency is known as the Rupiah, which is a cognate of the Sanskrit rupya.
Basically, the Indian rupee is referred to as simply a rupee, whereas for other countries it is mandatory for them to introduce their county name before rupee. i.e. Pakistani rupee, Nepalese rupee, Mauritius rupee, Sri Lankan rupee etc.
- The Indian rupees (₹) and Pakistani rupees (₨) are subdivided into one hundred paise (singular paisa) or pice.
- The Mauritian and Sri Lankan rupees subdivide into 100 cents.
- The Nepalese rupee subdivides into one hundred paisas (both singular and double) or four sukas or two mohors.
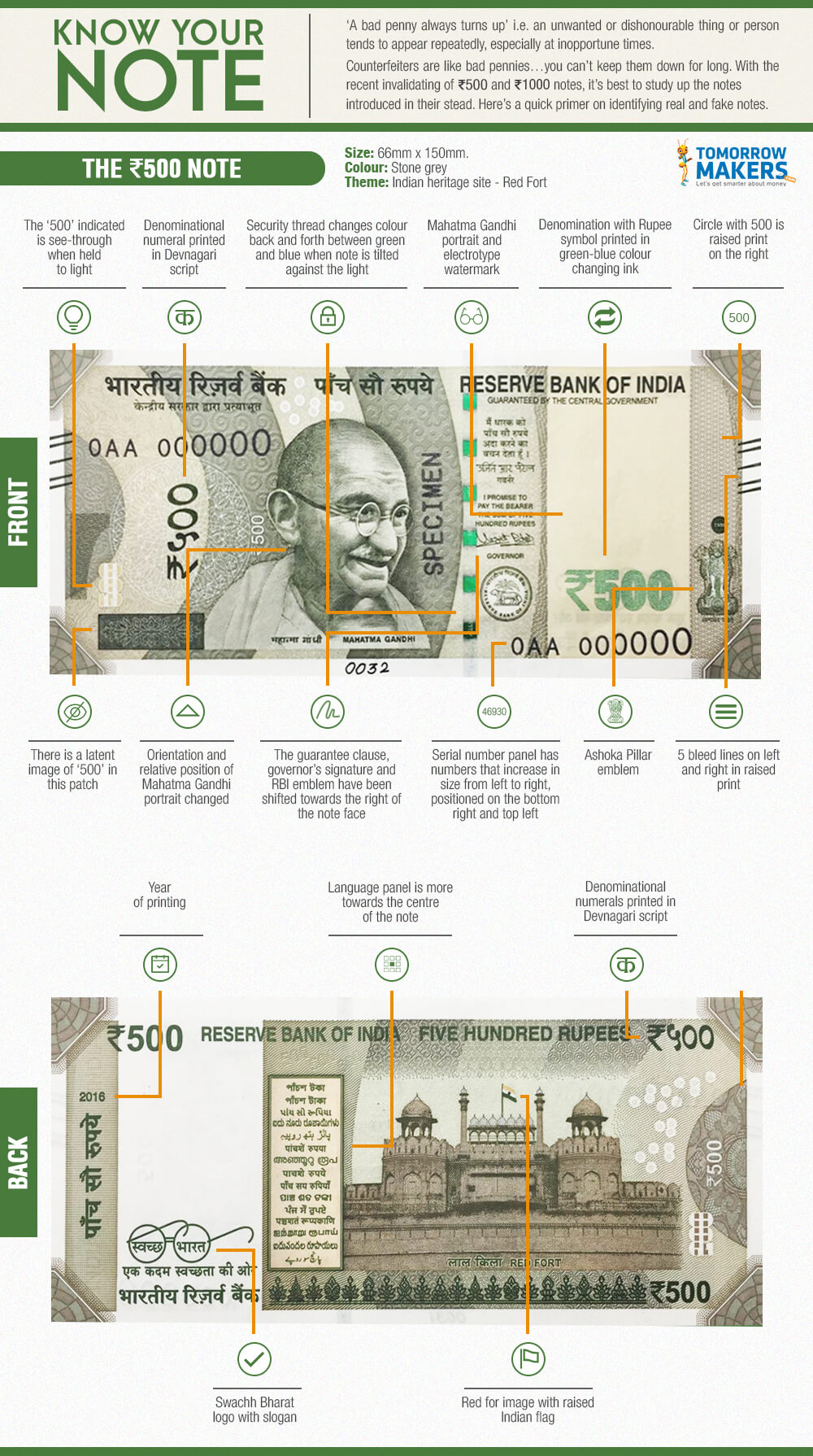
Security Features of Indian Notes
Counterfeiting is a major problem in banknotes. To prevent counterfeiting every country includes various types of security features in their banknotes. The infographic below explains the various security features in Indian Notes. More details in our article Security Features in Indian Notes, International Notes
The First Rupee
The first rupee is believed to have been introduced by king Sher Shah Suri (1486–1545). Sher Khan was an Afghan emperor who founded the Suri dynasty with its capital at Delhi in India. He became a commander in the Mughal Army under Babur. In 1537, when Babur’s son Humayun was on an expedition, Sher Khan established the Suri Empire.

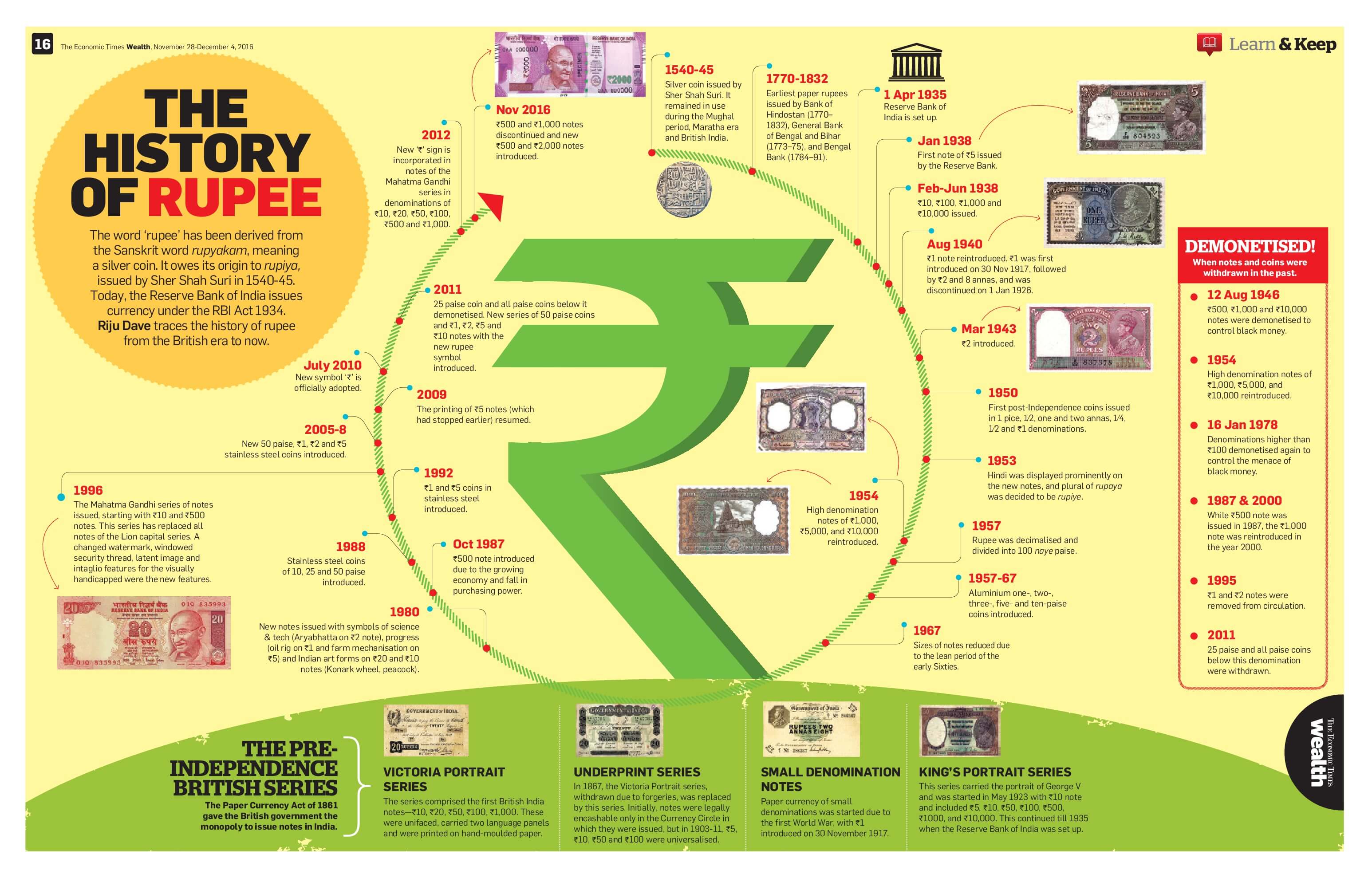
History of Rupee Infographic
The infographic from Economic Times traces the History of Rupee. Click on the image to see the bigger view.
Bank notes in the Ashoka Pillar watermark series in Rs 10 denomination were issued between 1967 and 1992, Rs 20 in 1972 and 1975, Rs 50 in 1975 and 1981 and Rs 100 between 1967-1979. The banknotes issued during this period contained the symbols representing science and technology, progress and orientation to Indian art forms.
In the year 1980, the legend Satyameva Jayate — ‘truth alone shall prevail’ — was incorporated under the national emblem for the first time.
In October 1987, the Rs 500 banknote was introduced with the portrait of Mahatma Gandhi and Ashoka Pillar watermark.
The Mahatma Gandhi banknote series – 1996 were issued in the denominations of Rs 10, Rs 100 (June 1996), Rs 50 (March 1997), Rs 500 (October 1997), Rs 1,000 (November 2000), Rs 20 (August 2001), and Rs 5 (introduced in November 2001).
The Mahatma Gandhi Series – 2005 banknotes were issued in the denomination of Rs 10, Rs 20, Rs 50, Rs 100, Rs 500 and Rs 1,000 and contained some additional/new security features as compared to the 1996 series.
The Rs 50 and Rs 100 banknotes were issued in August 2005, followed by Rs 500 and Rs 1,000 denominations in October 2005 and Rs 10 and Rs 20 in April 2006 and August 2006,
Video on History of Rupee
This video in Hindi shows the complete history of Indian currency notes from the beginning to the present day. The first currency note that was introduced in India.
When the European companies came to India for business, they established a private bank here for their convenience. They introduced paper currency started replacing silver and gold currency. And India’s first paper currency was issued by the Bank of Hindostan of Calcutta in the year 1770. Infographic History of Rupee also shown in an image later in the article.
Biggest Indian Note ever printed
The highest denomination currency note ever printed by the Reserve Bank of India is a ₹10,000 note during the British Raj in 1938. The note was demonetised in 1946.
But a new version of the note was introduced in 1954. However, the ₹10,000 note along with ₹1,000 and ₹5,000 notes were demonetised by the then PM Morarji Desai in 1978.

RBI Museum
RBI Monetary Museum aims at documenting and preserving this heritage. The Museum has exhibits of the representative coinage of India, paper currency, gold bars as well as financial instruments and curiosities down the ages.
You can visit it online at RBI website here
You can also visit RBI Museum in Mumbai and Kolkata.
Where does the Word Rupee come from?
Related Articles
- History of Money: How Money has evolved from Barter to Bitcoins
- What is Currency? Why does Currency Value change?
- Currencies of the World, Tricks to Remember Currencies
- What are Central Banks,What is RBI? What do they do?
- Monuments on The Indian Notes: Konark Temple, Himalayas, Manglayan Mission
- Coin: Anatomy, Indian coins, Motto, History, Mint Marks
- The National and Official Languages of India: Hindi, English, Banknotes

2 responses to “Rupee: Indian Currency and Other Countries, Rupee Symbol”
[…] face of Mahatma Gandhi is called as Obverse & the other side is called Reverse. Our article Rupee: Indian Currency and Other Countries, Rupee Symbol goes into detail of Which was the first rupee? When was the Rupee Symbol introduced? Countries […]
[…] Rupee: Indian Currency and Other Countries, Rupee Symbol […]