For person earning income from Salary , documents Form 16, and Form12BA provided by employer are needed.Understanding Form 16: Tax on income we looked into details of Form 16. Form 12BA give details of Perquisites given by the employer to employee in the financial year. Before we look at Form 12BA lets try to understand Perquisites, also known as perks.
Table of Contents
What are Perquisites?
Perquisites are benefits provided by the employers in addition to the normal salary at a free of cost or concession rates. Income tax act defines Perquisite as any casual emolument or benefit attached to an office or position in addition to salary or wages. Value of these perquisites is added to the income of employees. Hence Perquisites are taxable. There are rules for valuation of perquisites. Some of the perquisites are given below:
|
1
|
Accommodation
|
|
2
|
Cars/Other automotive
|
|
3
|
Sweeper, gardener, watchman or personal attendant
|
|
4
|
Gas, electricity, water
|
|
5
|
Interest free or concessional loans
|
|
6
|
Holiday expenses
|
|
7
|
Free or concessional travel
|
|
8
|
Free meals
|
|
9
|
Free Education
|
|
10
|
Gifts, vouchers etc.
|
|
11
|
Credit card expenses
|
|
12
|
Club expenses
|
|
13
|
Use of movable assets by employees
|
|
14
|
Transfer of assets to employees
|
|
15
|
Value of any other benefit/amenity/service/privilege
|
|
16
|
Stock options (non-qualified options)
|
|
17
|
Other benefits or amenities
|
A perquisite can be provided both by way of a
- Monetary payment : Employer either reimburses the expenses incurred by the employee for such facilities or pays on behalf of the employee. Ex:personal gas bills of the employee are in the name of employee and the employer reimburses the amount of such gas bills to him or pays on his behalf to the gas agency, it is in monetary terms and taxable in case of all employees; on the other hand, if such bills are in the name of employer, it will be perquisite in case of specified employee only.
OR
- Non-monetary payment/benefit : Payments which can be called non-monetary payments are car facility, benefit on account of interest-free loans, rent-free accommodation, furniture provided to employees etc.
As defined earlier, Perquisite as any casual emolument or benefit attached to an office or position in addition to salary or wages, Mostly perquisites are associated with position or office. Often distinition is made between employees and specified employees. A Specified employee is the one who satisfies any of the following cases:
- He is a director of the company,
- He has a substantial interest in the company, ie he is the beneficial owner of equity shares carrying 20% of voting power in the employer company.
- His monetary income under the head “Salaries” for the year exceeds Rs.24,000. The amount considered here includes amounts due from, paid or allowed by one or more employers. It excludes all non-monetary benefits.
For example Salary details and perquisites for the directors of Reliance Industries, from their annual report downloadable from RIL website ,is given below:
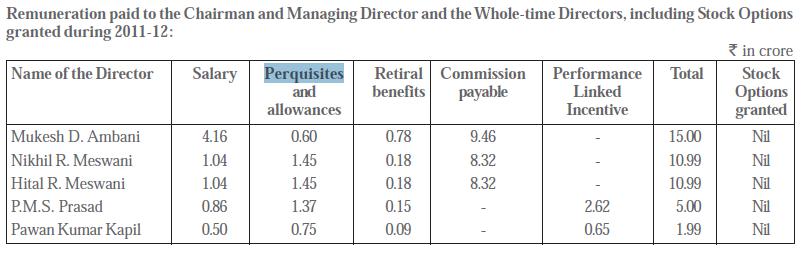
Details of Perquisites for Nikhil R. Meswani and Pawan Kumar Kapil , on Pg 18 of annual report, are as follows:
The perquisites and allowances, as aforesaid, shall include accommodation (furnished or otherwise) or house rent allowance in lieu thereof; house maintenance allowance together with reimbursement of expenses and / or allowances for utilisation of gas, electricity, water, furnishing and repairs; medical reimbursement; leave travel concession for self and family including dependents; medical insurance and such other perquisites and / or allowances.
Perquisites and Indian Income tax Act
Definition of Perquisites: Perquisites are defined in the section 17(2) of the Indian Income-tax Act of 1961.
Section 10(10CC) – Exemption on Non monetary perquisites: With effect from 01.06.2002, employer has given a option to deposit the tax on non monetary perquisites on behalf of employee without deducting the same from the employee {section 192(1A) &192(1b)} As per section 10(10CC), the amount of tax actually paid by an employer, at his option, on non-monetary perquisites on behalf of an employee, is not taxable in the hands of the employee. Such tax paid by the employer shall not be treated as an allowable expenditure in the hands of the employer under section 40. The tax so paid by the employer shall be deemed to be TDS made from the salary of the employee. Details at simpletaxindia:Tax on perquisites(jan 2012)
Statement of Perquisites: 192 (2C) lays down employer, shall furnish to employee a statement giving correct and complete particulars of perquisites or profits in lieu of salary provided to him and the value thereof in form no. 12BA. The form and manner of such particulars are prescribed in Rule 26A, Form 12BA and Form 16 of the Income-tax Rules . Information relating to the nature and value of perquisites is to be provided by the employer in Form no. 12BA in case of salary paid or payable is above Rs.1,80,000/-. In other cases, the information would have to be provided by the employer in Form 16 itself.
Type of perquisites, valuation of perquisites are defined in every Finance Act (popularly known as Budget presented by Finance Minister).
Valuation of Perquisites
Perquisites are taxable in the hands of employees. There are rules for valuation of perquisites. Let’s look at some of the rules. Please note that these rules keeps changing and are notified by Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT). For the financial year 2011-12 or Assessment Year 2012-13 Circular No.08/2010 dated 13.12.2010. Details about the circular can be read at TaxGuru:TDS on Salary – Provisions Applicable for A.Y. 2012-13 / Financial Year 2011-12 along with format of Forms and Undertakings . Valuation of some of the perquisites are discussed below:
Accommodation :- For purpose of valuation of the perquisite accomdation is divided into various categories like: Rent free Unfurnished Accommodation, Rent-Free Furnished Accommodation, Concession in Rent etc. Taxable value of Rent-Free Unfurnished Accommodation is explained below:
| Description | Perquisite Value |
| Where Government provides the accommodation to a person holding an office or post in connection with the affairs of the Union or State or serving with any body or undertaking under the control of such Government on deputation. | Licence fee determined by Union or State Government in respect of accommodation in accordance with the rules framed by that Government. |
| Where any other employer provides such accommodation. | Where accommodation is owned by employer. Perquisite Value is –
Where accommodation is taken on lease or rent by the employer. Perquisite Value is least of the following –
|
Interested readers can find about more about Taxable value of Rent-Free Furnished Accommodation, Taxable value of Concession in Rent
Gift or Voucher or Token: [Rule 3(7)(iv)]: The value of any gift or voucher or token in lieu of which such gift may be received by the employee or by member of his household on ceremonial occasions or otherwise shall determined as equal to the amount of such gift.
However, where the value of such gift, voucher or token, as the case may be, is below Rs.5,000 in the aggregate during the previous year, the value of perquisite shall be taken as Rs.Nil.
Medical Reimbursement by the employer exceeding Rs. 15,000/- p.a. u/s. 17(2)(v) is to be taken as perquisites.
Links to details about other perquisites from website accounting-n-taxation are given below. IndiaInvest: Valuation of Perquisites also lists out details.
- Domestic Servant New Rule 3(3), Gas, Electric Energy and Water New Rule 3(4),
- Perquisite Valuation of Motor Car Provided by the Employer, Taxable Perquisite Value of Conveyance Owned by the Employee,
- Perquisite Valuation of Educational Facilities, Perquisite Valuation of Transport Facility, Perquisites Value of Securities Option, Perquisites Valuation of Other Benefit or Amenity, Service, Right or Privilege,
- Perquisite Value of Interest Subsidy, Perquisite Valuation of Travelling, Touring, Accommodation And Any Other Expenses, Perquisite Valuation of Food, Perquisite Valuation of Expenses charged to Credit Cards, Perquisite Valuation of Club Facilities, Perquisite Valuation of Use of Movable Asset, Perquisite Valuation of Transfer of any Movable Asset
Exempted Perquisites
Some of the perquisites are exempted from income tax (free) such as:
- Tea, coffee(non-alcoholic beverages), snacks provided during working hours.
- Free Meals provided at the office or business premises during office hours or through paid non-transferable vouchers usable only at eating joints. If the value is up to Rs.50 per meal, it is not taxable. Otherwise, taxable. Assuming 2 meals per day and 22 working days in a month, it works out to Rs. 2200/- p.m which at times is given in form food coupons or Sodexo coupons. kirandhanwada: Sodexo coupons invalid business model has details on Sodexo coupons.
- Recreational facilities provided.
- Good manufactured by employer and sold by him to employees at the concessional(not free) rates. Ex: Motorola providing his employees Motorola mobiles at less than market value or Hindustan Lever giving its products(Surf, Knorr soup) at lesser than market value.
- Amount spent on training of employee including the boarding and lodging expenses of the employees on such a training.
- Telephone and mobile phone facility.
- Computer or laptop whether to use at home or office (ownership is not transferred to employee)
- Loan given at nil or concessional rate of interest by the employer provided the aggregate amount of loan does not exceed 20,000.
- Health club, sports facility.
Example of Taxation of Perquisites
Illustrating valuation of perquisite and calculation of tax in the case of a male employee below age of sixty years of a private company in Mumbai who was provided accommodation in a flat at concessional rate for ten months and in a hotel for two months (With valid PAN furnished to employer).
|
S.No.
|
Particulars
|
Rupees
|
|
1
|
Salary
|
7,00,000
|
|
2
|
Bonus
|
1,40,000
|
|
3
|
Free gas, electricity, water etc. (Actual bills paid by company)
|
40,000
|
|
4(a)
|
Flat at concessional rate (for ten months). = Rs.3,60,00
|
3,60,000
|
|
4(b)
|
Hotel rent paid by employer (for two months)
|
1,00,000
|
|
4(c)
|
Rent recovered from employee.
|
60,000
|
|
4(d)
|
Cost of furniture.
|
2,00,000
|
|
5
|
Subscription to Unit Linked Insurance Plan
|
50,000
|
|
6
|
Life Insurance Premium
|
10,000
|
|
7
|
Contribution to recognized P.F.
|
42,000
|
|
8
|
Investment in long term infrastructure bonds (80CCF)
|
20,000
|
COMPUTATION OF TOTAL INCOME AND TAX PAID THEREON:
|
S.No.
|
Particulars
|
Rupees
|
|
|
1
|
Salary
|
7,00,000
|
|
|
2
|
Bonus
|
1,40,000
|
|
|
3
|
Total Salary for Valuation of (1+2):
Perquisites i.e. Rs.70,000 per month.
|
8,40,000
|
|
|
Valuation of perquisites
|
|||
|
4(a)
|
Perq. for flat:Lower of (15% of salary for ten months =Rs.1,05,000/-) and (actual rent paid=3,60,000)
|
1,05,000
|
|
|
4(b)
|
Perquisites for hotel : Lower of (24% of salary of 2 mths=33,600) and (actual payment=1,00,000)
|
33,600
|
|
|
4(c)
|
Perquisites for furniture(Rs.2,00,000) @ 10% of cost
|
20,000
|
|
|
4(c)(i)
|
Total of [4(a)+(b)+(c)] (1,05,000+ 33,600+ 20,000)
Less: rent recovered =
|
Rs.158,600
(-)Rs. 60,000
Rs. 98,600
|
|
|
4(d)
|
Add perq. for free gas, electricity, water etc. Rs.40,000 (+) 98,600
[4(c)(i)] =
Total perquisites
|
Rs 1,38,600
|
1,38,600
|
|
5
|
Gross Total Income (Rs.8,40,000 + 1,38,600)
|
9,78,600
|
|
|
6
|
Gross Total Income
|
9,78,600
|
|
|
7
|
Less: Deduction U/s 80C & 80CCF:
(i). Provident Fund (80C)
(ii). LIC (80C)
(iii). Subscription to Unit Linked Insurance Plan (80C)
(iv). Investment in Infrastructure Bond (80CCF)
Total
Restricted to Rs 1,00,000 u/s 80C and Rs 20,000 u/s 80CCF
|
:42,000
:10,000
:50,000/-
:20,000
= 1,22,000
|
(-)1,20,000
|
|
8
|
Total Income
|
8,58,600
|
|
|
9
|
Tax Payable
|
1,09,580
|
|
|
10
|
Add:
(i). Surcharge Nil
(ii). Education Cess @2%
(iii). Secondary and Higher Education Cess @1%
|
Nil
|
Nil
2,192
1,096
|
|
11
|
Total Income Tax payable
|
1,12,868
|
|
|
12
|
Rounded off to
|
1,12,870
|
|
Difference between Perquisite, Allowance and Fringe benfit
Allowance is defined as a fixed amount of money given periodically in addition to the salary for the purpose of meeting some specific requirements connected with the service rendered by the employee(ex:Conveyance allowance) or by way of compensation for some unusual conditions of employment. It is taxable on due/accrued basis whether it is paid in addition to the salary or in lieu thereon.
Fringe benefits: refer to various extra benefits provided to the employees, in addition to the compensation paid in the form of wage or salary. These benefits can be defined as any wage cost not directly connected with the employees productive effort, performance, service or sacrifice. Fringe Benefit Tax(FBT) was introduced as a part of the Finance Bill of 2005 and was set at 30% of the cost of the benefits given by the company, apart from the surcharge and education cess that also needed to be paid. FBT was scrapped in July 2009.
Related Posts:
- Income Tax Overview
- Understanding Form 16: Tax on income
- Basics of Tax Deducted at Source or TDS
- Salary, Net Salary, Gross Salary, Cost to Company: What is the difference
In this article we explained Perquisites. In next article we shall see Form 12BA which is statement provided by employer to employee with details of perquisites.

3 responses to “Understanding Perquisites”
This can be a topic which is close to my heart…
Best wishes! Where are yur dat though?
I want to know whether perquisites are admissible in case where the accommodation is not provided by the Employer, but sharing with retired father,not drawing H.R.A.and paying Licence Fee to the father’s allotting authority.Please enlighten me.Thanks.
[…] 12BA: give details of Perquisites given by the employer to employee. Understanding Perquisites, Understanding Form 12BA talks about Perquisites in […]