An Indian family has common goals such as buying a car,having a house,going for foreign trip, education of kids,marriage of kids and retirement. One of the first big investments that one makes after starting a job getting bugged by commute on public transport system or haggling with the auto rickshaws is buying a car. Okay so one fine day you say I want to buy a car. You have an idea what you like but you want to check out. When google devta is around,all you need to do is click and Voila you are inundated with so many choices. You check out the website dedicated to take you closer to choosing a dream car and you are bombarded with information and questions. Should you go for a hatchback or sedan, what is wheelbase, track,is 67 PS@5500RPM better than car with 65PS@6200RPM, what about airbags or ABS. ( i wanted a car with airbags till I found out that is a security feature useful during accident), what about the car segments surely A1,C1 segment stand for something. This article tries to clarify some basic terms related to car to help you in buying car.
Table of Contents
Classification of Car based on Body Shape
A car has broadly three areas such as engine area, passenger area and luggage area. Depending on how physically they are put together car is classified as one-box car,two box car, three box car as shown in image below.
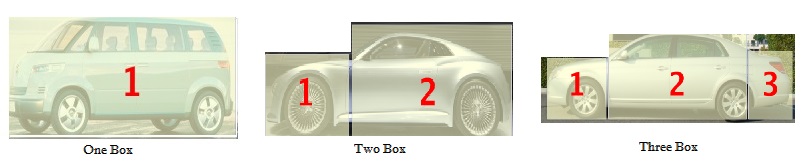
- One Box (VAN/MPV) : Engine area, Passenger area & boot space (space for luggage popularly called as dikki) are all in one box, there are no separate compartments. For eg. Omni, Ace Magic, Versa
- Two Box popularly called as Hatchback : Engine area is a separate compartment while Passenger area and luggage area are together, For example in Maruti 800, Alto, Santro, i10, A Star, Swift etc.
- Three box or Sedan or Saloon or Notchback – Engine area, Passenger area & luggage area have different compartments For ex : SX4, City, Fiesta, Dzire, Ambassador, Indigo CS etc. In cars sedan is synonymous to luxury.Some Variations
- SEMI NOTCHBACK – Its a sedan whose boot door can be opened like a hatchback (wagon r, swift), where the rear wind sheild too opens along with the boot door. Unlike sedan whose rear wind sheild is always fixed. There are only few examples for SEMI NOTCHBACK – Skoda Octavia, Accent Viva.
- ESTATE or STATION WAGON – Its nothing but sedan whose roof is extended till the rear to create more boot space. For eg. Indigo Marina, Octavia Combi, etc.
- Multi Utility Vehicle (MUV) is a type of vehicle designed like a shape of van but is meant for personal use which can be used for both passengers and luggage. For example Toyota Innova, Tata Sumo,Mahindra Bolero etc
- Sport Utility Vehicle (SUV) stands for meant for usage in all road conditions like level road,uneven roads,hilly areas, etc. The engine area is separate, but the passenger & luggage area are enclosed together These vehicles have large tyres, higher seating, higher ground clearance.It looks like a station wagon. It means that is has a mini truck kind of platform. Example Skoda Yeti,Mahindra XUV 500 etc.
Terms related to Car
Some terms that one comes up in reading description of cars are as follows
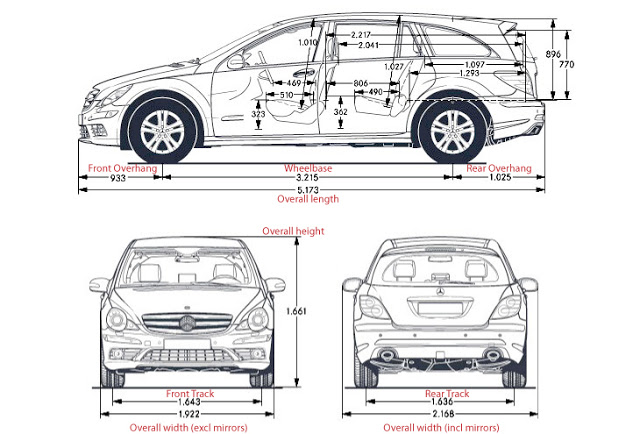
Dimensions of Car
- Wheelbase is the distance between the centre lines of the vehicle’s front and rear axles.
- Track is the distance between the centre lines of the left and right tyres.
- Ground Clearance or simply clearance is the amount of space between the base of an automobile tire and the underside of the chassis; or, more properly, to the shortest distance between a flat, level surface, and any part of a vehicle other than those parts designed to contact the ground (such as tires, tracks, etc.). Ground clearance for cars, is usually given with no cargo or passengers. Given the bad roads in India, ground clearance is an important factor.
- Mercedes factory diagram labelled using terms fromVehicle Dimensions
Engine
Purpose of a car engine is to convert fuel into motion by burning the fuel inside an engine,ignited by an electric spark,which releases an incredible amount of energy in the form of expanding gas. This makes the crankshaft rotate and ultimately causes the wheels to turn.Therefore, a car engine is an internal combustion engine — combustion takes place internally. Almost all cars currently use what is called a four-stroke combustion cycle to convert fuel into motion. The core of the engine is the cylinder, with the piston moving up and down inside the cylinder. Most cars have more than one cylinder (four, six and eight cylinders are common). In a multi-cylinder engine, the cylinders usually are arranged in one of three ways: inline, V or flat boxer. Details at How Car Engines Work
- Engine capacity – The total volume of all the cylinders in a car’s engine added together and expressed in cubic centimetres (cc) or more frequently litres . So, an engine with a capacity of 1598cc will be referred to as a 1.6-litre unit. Generally, the bigger an engine’s capacity, more the performance
- Torque and HorsePower :Torque is a measure of the ability of an engine to do work. Horse power of the engine is the rate at which work can be done. Difference between Horse Power and TorqueWhat’s the difference between horsepower and torque?
- HorsePower is expressed in PS which stands for German pferdestrake. It is equivalent of Brake Horse power (BHP) 100PS@5500rpm means the vehicle delivers 100 PS of max power when the engine runs at 5500 rpm(revolutions per minute). 1HP = 746Watts = 1.01387PS
- Newton meter(NM) or Kilogram meter (KGM) are units of torque. 130NM@2000rpm means the vehicle delivers max torque of 130 NM at 2000 rpm.
- When you buy a new car or bike, for Power see the vehicle in which PS is high/RPM is low, For torque vehicle in which NM is high/RPM is low. For example Choosing which Vehicle is better in terms of Power and Torque
| Vehicle | 1 | 2 |
| Power | 67 PS@5500RPM | 65 PS@6200RPM |
| Torque | 99NM@2800RPM | 84NM@3500RPM |
| 67/5500 =.01299/2800= .035 | 65/6200=.01084/3500= .024 | |
| Vehicle 1 is better than Vehicle 2 | ||
Fuel
- Fuel Type :There are several fuel types – Petrol, Diesel, CNG,Electric,LPG,Hybrid
- Fuel efficiency answers the question Kitna Deti hai is a ratio of distance to amount of fuel used. Fuel economy is recorded in kilometers per liter, KMPL or KPL. The higher the ratio, the more efficiently the vehicle uses gas. In other countries it is measured in miles per gallon, MPG or liters per 100 kilometers, abbreviated L/100km
Transmission: Explains how gears get changed to drive at different speeds. Types of automobile transmissions include manual, automatic.
- Manual transmission cars allow the driver to change the gears by using a manual clutch pedal while changing gears.
- Automatic transmission gears change automatically depending on the vehicle speed and engine speed, there is no clutch pedal.
- Carblog Should I Buy Manual Transmission Or Automatic Transmission Car? explains pros and cons of the type of transmission
Comfort and Convenience
- Power Steering : is a motorized mechanism which allows you to easily turn your steering wheel.
- Power Windows : windows which can be raised and lowered by pressing a button or switch, as opposed to using a hand-turned crank handle.
- Central Locking : The central lock is the system which allows you close simultaneously to close (open) all doors of the car using remote control.
Security Features :
- ABS means anti-lock braking a system that prevents brakes from locking up on slippery surfaces so car can still be steered in emergency braking under adverse conditions.
- AirBags An airbag is a vehicle safety device. It is basically a cushion designed to inflate rapidly during an automobile collision in the space between the passenger and the body of the car such as steering wheel or dash board to prevent crash injuries. Airbags are only useful when wearing seatbelts.Without seatbelts you’ll get a punch in the face before slamming into the windshield. For more details on AirBags read Chandigarh police AirBags or Wikipedia Airbag
Make, Model, Variants
- Make or Brand is the company that made the car for ex :Maruti, Hyundai,Chevrolet, Ford, Honda or Toyota,
- Models are the cars a car company sells: ex Maruti sells Alto,Ritz,Swift models while Hyudai sells i10, Accent etc.
- Variants or Trim Levels : they further identify a model of company by its particular set of special features. For every model of a car there is an entry-level model or base model. And then different configurations of equipment and amenities are added for ex the base model or trim may have only basic features (wheel covers, cloth seats) compared to the top-of-the-line model (alloy wheels, leather upholstery). For example Hyudai i10 comes in following variants Era,Magna,Sportz. It similar to clothes with size S,M,L, Xl etc.For example in MARUTI we come across three letter variants LXi,VXi, ZDi which stands for <Level of Variant : Ex L,V,Z> <Petrol type Xi for Petrol, Di for Diesel> <Special Feature ex ABS<>
- LXi is Basic lower end, using petrol, no added features ex No power windows
- VXi :-next level ,using petrol, few added features not all,example it power windows, power steering
- ZDi – high end cars, using diesel, fully loaded ex it has ABS, built in music player, alloy wheels
Specifications of Honda Amaze,BRIO are given below (just a random selection of car for specification)

Car segment
Cars are classified into various segments to identify other similar vehicles for consumers to compare against, to help make the car-buying process much easier .Vehicle segments in India are defined by are defined by Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers (SIAM), apex Industry body representing leading vehicle and vehicular engine manufacturers in India. Vehicles are are classified as Passenger Vehicles, Commerical Vehicles, Two Wheelers,Three Wheelers .Passengers Cars are further classified in various segments. Earlier classification of segment was done on the basis of the length of the vehicle
| Segment | Length | Examples |
| A1 Segment | Up to 3400mm | Maruti 800, Nano |
| A2 Segment | 3401 to 4000mm | Alto, WagonR,i10,A-star,Swift,i20,palio,indica etc |
| A3 Segment | 4001 to 4500mm | City, Sx4, Dzire, Logan, Accent, Fiesta, Verna |
| A4 Segment | 4501 to 4700mm | Corolla, civic, C class, Optra, Octavia |
| A5 Segment | 4701 to 5000mm | Camry, E class, Accord, Sonata, Laura, Superb etc |
| A6 Segment | Above 5000mm | Mercedes S class, 5 series etc |
| B1 Segment | Vans | Omni, Versa, Magic etc |
| B2 Segment | MUV/MPV | Innova, Tavera, Sumo |
| SUV Segment | SUV | CRV, Vitara |
In 2011 SIAM classified Cars into Micro, Mini, Compact, C1, C2, D, E and F classes based on their engine size and dimensions.
- Mini:Seats upto-5, Length Normally <3600 mm, Body Style-Hatchback, Engine Displacement Normally upto 1.0 Litre
- Compact:Seats upto-5, Length Normally between 3600 – 4000 mm, Body Style-Sedan/Estate/Hatch/Notchback, Engine Displacement Normally upto 1.4 Litre
- Super Compact:Seats upto-5, Length Normally between 4000 – 4250 mm, Body Style-Sedan/Estate/Hatch/Notchback, Engine Displacement Normally upto 1.6 Litre
- Mid-Size:Seats upto-5, Length Normally between 4250 – 4500 mm, Body Style-Sedan/Estate/Hatch/Notchback, Engine Displacement Normally upto 1.6 Litre
- Executive:Seats upto-5, Length Normally between 4500 – 4700 mm, Body Style-Sedan/Estate/Notchback, Engine Displacement Normally upto 2 Litre
- Premium:Seats upto-5, Length Normally between 4700 – 5000 mm, Body Style-Sedan/Estates, Engine Displacement Normally upto 3 Litre
- B: Utility Vehicles/ Sports Utility Vehicles; 2×4 or 4×4 offroad capability ; Generally ladder on frame ; 2 box ; 5 Seats or more but upto 10 Seats
- UV1:Length <4400 mm, Price Upto Rs. 15 Lakh
- UV4:Price Between Rs. 15 to 25 Lakh
- C: Vans ; Generally 1 or 1.5 box; seats upto 5 to 10
- V1:Hard tops mainly used for personal transport, Price Upto Rs. 10 Lakh
Websites of Car and Cars Sold in India
Websites to help you choose the car
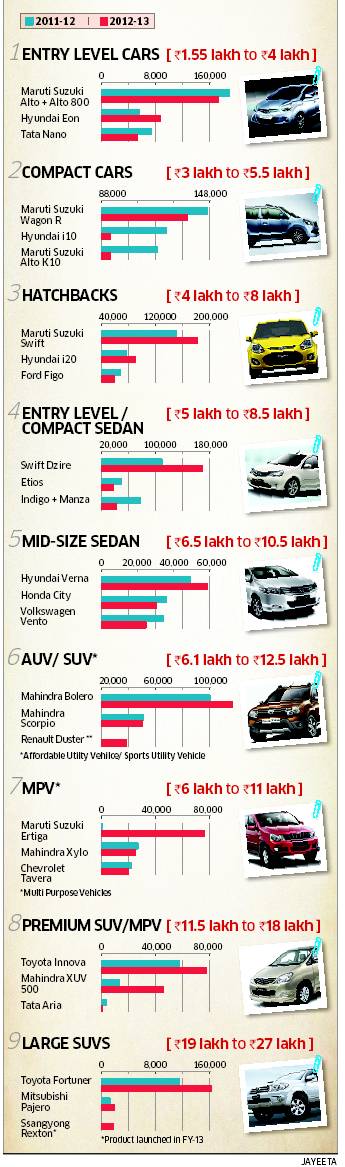
Various types of cars sold in India are given below Ref EconomicTimes.
Related Articles :
- Money awareness for 20s,30s : Job,Insurance,Income Tax,Loans,Credit Card
- Basics of Investing
[poll id=”48″]
What is ex-showroom price, car insurance, costs associated with car,chassis and more will be dealt in forthcoming articles. One needs to find a balance between what you want, what you can afford and what you can actually find in the dealer’s inventory. What features do you give importance to while buying a car – cost or price, engine,security features? How did you go about buying a car?

11 responses to “Understanding Car : Box,Segment,Specifications”
The Artice Was amazing .But i M Still Confused.can you please guide me the best car between 2l to 5l with as max feature as it can have.
Quite useful information! Congrats! It’s one of the best beginners’ guide in the world of cars i have come across recently.
Thanks for the great article.
I need your help for selecting the best family MUV Car. What is your view on Ertiga VDI. Is Ertiga price justified value for the Car?
Very well written and explained .
Thanks of lot for giving such a useful information .
Thanks a lot. Appreciate the comment. So why were you looking for the info ? And which car did you buy?
Very well written and clearly defined everything in detail that reader needs to know. Thanks for writing and sharing knowledge. Keep it up!!
Thanks Prasad for writing the comment. Its such an encouragement to us.
I read this piece of writing completely concerning the comparison of most up-to-date and previous technologies,
it’s amazing article.
Nice information of Maruti Alto on Car Box.
Thnaks for this very good informative article on Car Box.
Thnaks for this very good informative article on Car Box.