A new jargon , JAM Trinity,Jan Dhan Yojana, Aadhar, Mobile numbers, has become the Indian’s finance buzzword since it found place in two important documents recently, The Economic Survey 2014-15 and the Union Budget 2015-16. According to the Economic Survey of 2014, there are about 125.5 million Jan Dhan bank accounts,17,757 million Aadhaar numbers, and 904 million mobile phones. This article explains in detail the JAM Trinity : Jan Dhan Yojana, Aadhar, Mobiles in India.
Table of Contents
JAM Trinity and Subsidies
JAM is an abbreviation for Jan Dhan Yojana, Aadhaar and Mobile number. It was coined by Chief Economic Advisor, Arvind Subramanian, and was first used for Economic Survey on 28th Feb 2015. It is supposed to be a game changing reform that will allow transfer of benefits in a leakage-proof, well-targeted and cashless manner. Let’s go through the various components of JAM.
Jan Dhan Bank Accounts
In India around 40 per cent of the population is unbanked. To bring banks to the people Pradhan Mantri Jan-Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) was launched in Aug 2014. Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojna account can be opened in any bank branch or Business Correspondent (Bank Mitr) outlet. PMJDY accounts are opened with Zero balance. However, if the account-holder wishes to get cheque book, he will have to fulfill minimum balance criteria.
Features of Bank accounts under PMJDY Scheme are
- No Minimum Balance.
- Interest on deposit. Interest is presently at 4 % in most of the banks.
- RuPay Debit Card. Rupay Debit Card provides accidental insurance cover upto Rs.1.00 lakh without any charge to the customer. To get benefit of Accidental Insurance Cover, RuPay Debit Card must be used at least once in 45 days.
- Life insurance cover of Rs. 30,000. Only one person in the family will be covered in the Bima Scheme and in case of the person having multiple cards / accounts the benefit will be allowed only under one card i.e. one person per family will get a single cover of Rs.30,000, subject to the eligibility conditions.The life cover of Rs 30,000 under the scheme will be initially for a period of 5 years, i.e. till the close of financial year 2019-20. Thereafter, the scheme will be reviewed and terms and condition of its continuation, including the issue of future payment of premium by the insured thereafter, would be suitably determined.
- Overdraft facility upto Rs 5000 is available in only one account per household, preferably lady of the household. It is permitted only after satisfactory operation of the account for 6 months
- Beneficiaries of Government Schemes will get Direct Benefit Transfer in these accounts.
- Who Cannot open: Persons whose income is taxable under I.T. Act 1961 or are filing the yearly Income Tax return or in whose case TDS is being deducted from the income, and their families
Pradhan Mantri Jan-Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) is National Mission for Financial Inclusion to ensure access to financial services, namely, Banking or Savings & Deposit Accounts, Remittance, Credit, Insurance, Pension in an affordable manner. As many as 11.5 crore bank accounts have been opened under the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana, exceeding the enhanced target of 10 crore and covering 99.74 per cent of households. Rs 9,000 crore has been deposited in the Jan Dhan accounts. Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced the financial inclusion scheme in his first Independence Day speech on 15 Aug 2014. It was launched in August with a target to open bank accounts for 7.5 crore poor persons by January 26, 2015. The target was later increased to 10 crore accounts. The achievement,under Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana, was recognised by the Guinness Book of World Records on 20th January 2015.
In its citation, the Guinness Book said: “Most bank accounts opened in one week as part of the Financial Inclusion Campaign is 18,096,130 and was achieved by the Department of Financial Services, Government of India from August 23 to 29, 2014.”
Reference: Offical Pradhan Mantri Jan-Dhan Yojana Website Wikipedia Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojna
Aadhaar
Aadhaar , which means foundation, is a unique 12-digit Identification number issued to individuals for the purpose of establishing unique identification of every single person. It’s purpose is to eliminate the fake identities and documents from the government records. Aadhaar Card serves as an Address Proof and an identity proof, especially for those who do not have a passport or a driving license. As many as 76.83 crore Aadhaar numbers,out of a total population of 121.01 crore (Census 2011), have been generated as on February 15,2015 and about Rs 5,512.18 crore has been spent until January 2015 on the project. The government has approved an outlay of Rs 13,663.22 crore for the period 2009-17.
- In Aadhaar uniqueness is determined through the biometric (fingerprints, iris scan, photograph) and demographic (residential address) details of the individuals.
- Any resident of India including infants can enrol for Aadhaar. Even NRIs and foreign citizens residing in India can also enrol for Aadhaar.
- Aadhaar is not a card or a smart card rather it is a number which is unique for every beneficiary of it.
- No fee will be charged at any stage under this scheme
- Aadhaar number will remain valid for life.
- Aadhaar number will help you provide access to services like banking, mobile phone connections and other Govt and Non-Govt services in due course.
- The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) is the regulatory body on the behalf of government.
For more details one can read UIDAI’s FAQ on Aadhar.
Aadhaar program was launched in 2009 with a main objective to give universal identity to every resident Indian. Initially people faced lot of difficulties during enrolment such as technical snags, incorrect data displayed etc. Also the importance of Aadhaar card was unclear. With the passage of time, importance of Aadhar card has greatly increased as compared to what it was meant for at the time of its inception. With the new government’s willingness to continue the previous government’s ambitious Aadhaar project, the value of Aadhaar has drastically increased. Aadhaar card will be identity proof of every individual in future. Since the details of Aadhar card holder are kept at secure online servers, the bio-metrically verified identity of an individual can be used to confirm the identity of its holder. The Supreme Court of India passed an interim order on 23 September 2013 that no public services such as LPG can be denied to public due to lack of Aadhaar. Let’s look at Where all is Aadhaar being used.
LPG Subsidy – Government has started the PAHAL Scheme under which the subsidy amount of LPG cylinder is directly transferred into the Aadhaar number linked bank account of the consumer.Well one can avail LPG Subsidy without Aadhar also.
Passport : Aadhar card is necessary for issuance of new Passport.The Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) will now be using Aadhar Card for identification of the applicant and on the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) database for validation of one’s criminal antecedents. If you have an Aadhaar card, you can get passport in just 10 days. Under this format, police verification will be done at a later date as opposed to the previous rule requiring police verification which used to be time consuming.
Buying new vehicle and Driving License – Andhra Pradesh government made Aadhaar card mandatory for registering new vehicles and obtaining driving licence. It has also decided to link all existing vehicle owners and driving licence holders with Aadhaar number.
Bank Account: The guiness world record holder scheme Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) accepts Aadhaar card/number as the only document sufficient to open the bank account.
Voter Card Linking: Starting 9th March 2015, Aadhaar card UIDAI number would be linked to the voter ID’s. This will eliminate bogus voters. The deadline for linking Aadhaar with voter ID card is Aug 2015. By May, the Southern states of Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Kerala and Goa will complete the linking.
Monthly Pension: The Indian Government has launched an Aadhaar-based digital life certificate called Jeevan Pramaan for pensioners, to make the process of pension payments simpler. This will do away with the requirement of a pensioner to submit a physical life certificate in November each year, in order to ensure the continuity of pension being credited into his or her account. Currently, 50 lakh individuals draw pension from the central government alone. A similar number draw pension from state and Union Territory governments. Several state-run companies also provide pension benefits and over 25 lakh retired personnel draw pension from the armed forces.
New SIM Card : The SIM purchaser has to give his or her Aadhaar number at the time of purchase and give the digital impression of fingers by pressing them on a machine. The pilot project kicked start from March 4, 2015 in metros like Delhi, Kolkata, Lucknow and Bangalore that have nearly full Aadhaar penetration and will run for six weeks. Vodafone was the first operator to roll out new amendment about new mobile sim activation, recommended by Department of Telecom (DOT) India.
Digital Locker : Digital Locker is Dedicated personal storage space, linked to each resident’s Aadhaar number. DigiLocker can be used to securely store e-documents as well as store Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) link of e-documents issued by various issuer departments. Each digital locker gives 10MB of free space to store documents. The e-Sign facility provided as part of DigiLocker system can be used to digitally sign e-documents. A beta version was released on 10.02.2015 by the Department of Electronics and Information Technology (DeitY) It can be accessed through the website www.digilocker.gov.in
Provident Fund: Similar to pension, provident fund money will be given to the account holder who’ve registered their Aadhaar number with employee provident fund organization (EPFO).
Attendance of Government Employees – The union government is asking its employees to use biometric attendance system, based on Aadhaar.The Biometric Attendance System Dashboard ,www.attendance.gov.in, gets updated realtime. It has thrown up some interesting statistics. Central Government employees seem to be on their toes and are spending extra time in their offices ever since the Aadhaar enabled Biometric Attendance System (AEBAS) was launched in September 2014.

Considering the increasing acceptance of Aadhaar card it is must for everyone to get it issued. It is believed that the card will further be given more importance as more and more government schemes are being launched requiring it as a mandatory document.
Mobile and India
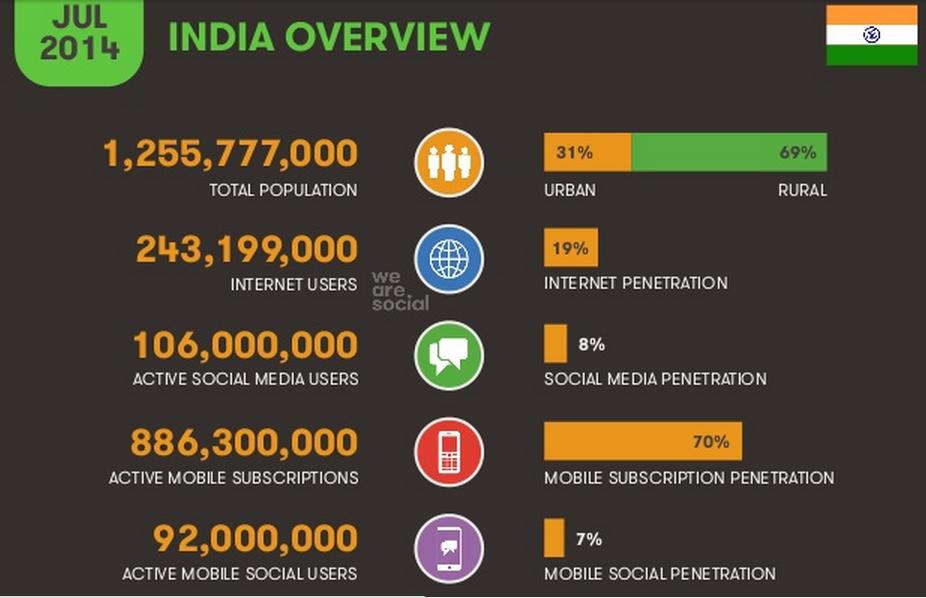
There are almost 900 million mobile phone users in India. Telecom industry in India has come a long way from Dhirubhai Ambani pioneer offer in 2000, which envisioned a mobile handset in every Indian household. Today, after 14 years, we have more mobile phones than toilets. The falling cost of handsets, coupled with improved usability and increasing network coverage, are factors that are making mobile technology a global phenomenon. By 2020, 90% of the world population over 6 years old will have a mobile phone, with number of smartphones reaching 6.1 billion.
Mobile is no longer just a mode of communication. There is an increased convergence of wireless and mobility as industry moves from connectivity to applications.With the advent of new technologies, telecom is now enabling healthcare, education, financial inclusion and much more. It has the capacity to be a connecting platform between the government and citizens as well. For example, a fisherman who was previously clueless about the sales and demand of his fishes can now call from the sea for this information, and knows well in advance where he needs to deliver the products to maximize profits. As India adds more internet consumers buying online will increase. Majority of the transactions (if not everything) will be on mobile sets and from the middle class. They are the targeted customers of e-commerce companies and getting more comfortable buying on mobile sets (and online shopping). Remote areas are now getting access to courses from all across the globe through internet and mobile. The consumption of video content is witnessing a massive growth and is one of the major enablers in e-learning sector. Telecom industry is going to be a key driver for India’s economic growth. But An average Indian spends almost 5 hours accessing internet and out of the 3 hours spent on mobile internet, only 45 minutes are spent doing any other work apart from social media.Our articles What is Mobile Banking? What are Mobile Wallets or Digital Wallets A snapshot of Social, Digital & Mobile in India 2014
Related Articles:
- Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana,Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana and Atal Pension Yojna
- LPG Subsidy and Direct Benefit Transfer Scheme
- Pay and perks of Indian MP, MLA and Prime Minister
- What does Bharat Ratna winner get?
- When you loose your mobile : What to do?
Do you think Jan Dhan Yojana, Aadhaar and Mobile combination will serve it’s purpose? Do you have a Aadhaar card? What are your views on Jan Dhan Yojna bank account? Will Aadhaar card importance keep on increasing? With the growing population and increasing smartphone penetration, India is going mobile and digital but what will Indians continue to make an online purchases ? What do you use your mobile for?

3 responses to “JAM Trinity: Jan Dhan Yojana, Aadhaar and Mobile number”
my adhar card no.like
adhar card no. 448587830185
a/c 34540276721
My adhar no 761821291879,my a/c 34540276812
myaadhaar no 858252287021 a/c 34634303865 3926493298