The world of cryptocurrencies and virtual digital assets (VDA) has gained significant popularity in recent years. As governments seek to regulate these assets, India’s Income Tax Act introduced Section 115BBH, which became effective from April 1, 2022. This section aims to explain tax on cryptocurrency, income from VDAs, TDS, How to show in ITR etc.
Table of Contents
Overvide of Tax on Cryptocurrency and Virtual Digital Assets
- Section 115BBH of the Income Tax Act, effective from April 1, 2022, taxes income from Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs), including cryptocurrencies and NFTs.
- VDAs encompass cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and other digital assets notified by the central government.
- Income from cryptocurrency can fall under capital gains or business income, depending on whether it’s held for investment or trading purposes.
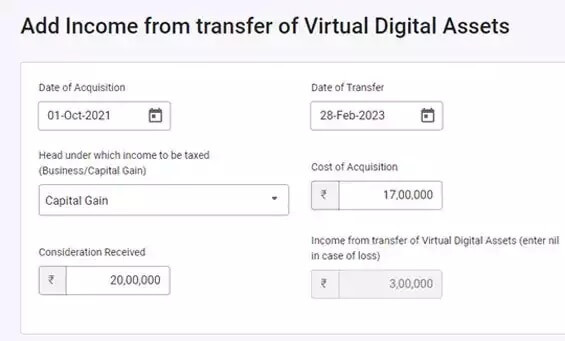
- Capital gains on VDA transfers should be calculated as Selling Price – Purchase Price, with no deductions or indexation benefits.
- TDS at 1% is applicable on VDA transfers exceeding INR 10,000 (INR 50,000 for specified persons).
- Report this income in ‘Schedule VDA’ of ITR-2 or ITR-3.
- ITR-1 or ITR-4 are not suitable for reporting cryptocurrency income.
- If the exchange is located outside India, you need to report the same under Foreign Assets
- Taxpayers must pay a flat rate of 30% on income from VDA transfers.
- Deductions are allowed only for the cost of acquisition (purchase price).
- Loss from VDA transfers cannot be set off against other income or carried forward to future years.
- Gifting cryptocurrency or VDAs is taxable for the receiver.
- The Income Tax Department has sent notices to taxpayers who didn’t report crypto trading income in previous ITRs.
- The applicability of GST on cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and VDAs is still unclear, awaiting a clarification from the GST Council.
What Qualifies as a Virtual Digital Asset (VDA)?
According to Section 2(47)(A) of the Income Tax Act, a VDA encompasses cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and any other digital assets officially notified by the central government. This broad definition encompasses various digital assets used for investment and trading purposes.
Understanding Section 115BBH of the Income Tax Act
If a taxpayer earns income from the transfer of VDA, they are required to pay income tax at a flat rate of 30%. However, there are specific provisions and restrictions that taxpayers need to be aware of:
1. Deductions on Transfer of VDA:
– The taxpayer cannot claim any expense or allowance against the income from VDA.
– The taxpayer can, however, claim the cost of acquisition (i.e., purchase price) as a deduction from the income.
– Thus, the taxable income is calculated as Selling Price – Purchase Price.
2. Loss from Transfer of VDA:
– The taxpayer cannot set off the loss from the transfer of one VDA against the profit from the transfer of another VDA.
– Loss from VDA cannot be set off against any other income or carried forward to future years.
– Similarly, losses under any other head of income cannot be set off against the profit from the transfer of VDA.
3. Gift of Crypto Investment:
– Gifting cryptocurrency, NFTs, or other VDAs is taxable in the hands of the receiver.
Reporting of Crypto Income & how to prepare data
Important things to consider when reporting the Crypto Income for income tax filing. Also refer the below table to understand who should file taxes from the perspective of crypto income or activity.
- Jurisdiction: Determine whether the exchange is in India or outside India? You may check based on the registered office of the company / firm.
- Tax Residency Status: Determine whether you are a tax resident of India or NRI?
- Trading Data: Get the Trade History * (Transaction Statement) from the Exchange website for FY 2022-23 (from 1st Apr 2022 to 31st Mar 2023).
Calculation of Capital Gain Tax on Cryptocurrency Transfer
To calculate capital gains on the transfer of VDA, consider the following:
Capital Gain = Selling Price – Purchase Price
No deduction is allowed for transfer expenses or cost of improvement.
Indexation benefit is not available.
No capital gain exemption is allowed under Section 54 to 54F.
No deduction under chapter VI-A can be claimed on such income.
How gains on CryptoCurrency are calculated – an example?
Below is a scenario one traded on Ethereum INR at the same exchange on the same day. Example narrates how the profit gets calculated.
| Crypto Name | Event Type | Event Date | Quantity | Rate | Total Amount | Profit / Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETHINR | Buy | 2022-10-01 09:00 | 10 | 1200 | 12000 | – |
| ETHINR | Sell | 2022-10-01 10:00 | 10 | 1400 | 14000 | 2000 |
| ETHINR | Buy | 2022-10-01 11:00 | 20 | 3000 | 60000 | – |
| ETHINR | Sell | 2022-10-01 13:00 | 20 | 2500 | 50000 | -10000 |
| W.e.f FY 2022-23, one cannot set off his Rs 2000 profit with Rs 10,000 loss. He needs to pay 30% tax on Rs 2000 i.e, 600 and the Rs 10,000 loss cannot be set off or carry forward. |
||||||
When to report Crypto income under Foreign Assets?
- If the exchange is located in India, there is no need to report under Foreign Assets for the holdings. Example: Zebpay
- If the exchange is located outside India, you need to report the same under Foreign Assets. Example: Binance.
- Following details needs to be reported under foreign assets
- Country in which exchange located.
- Nature of Asset as “Crypto/VDA”
- Date of Acquisition
- Cost of investment
- Income generated from such assets.
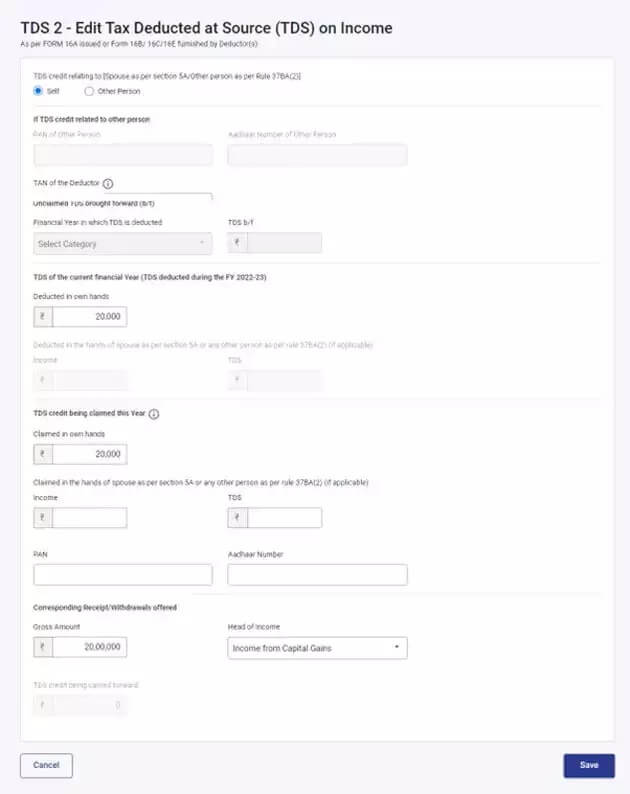
TDS on Transfer of Cryptocurrency and Other VDA
In addition to taxing cryptocurrency income at 30%, the government introduced Section 194S for the deduction of Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) on the transfer of cryptocurrency and other VDAs. TDS at the rate of 1% must be deducted if the aggregate transfer amount during the financial year exceeds INR 10,000.
- Budget 2022 has introduced the concept of TDS on Virtual Digital Assets (VDA) w.e.f July 01st 2022
- Buyer of VDA is required to pay TDS @ 1% on the total amount of consideration if the aggregate amount exceeds Rs 10,000 in a financial year. For specified persons, the limit is INR 50,000
- CBDT has released the guidelines for deduction of TDS on VDA
- Peer or Peer Transactions: Buyer is required to deduct TDS and file Form 26Q or 26QE
- Transfer of VDA through an exchange and VDA is owned by another person:
- Amount paid to Exchange by buyer directly or through a broker: Exchange is required to deduct TDS and file Form 26Q
- If the payment between exchange and the seller is through a broker(broker is not seller): Exchange and Broker are liable to deduct TDS. If there is a written agreement between the exchange and broker, the broker needs to deduct TDS and file Form 26Q. Exchange needs to file Form 26QF
- Transfer of VDA through an exchange and VDA is owned by such exchange.
- Amount paid to Exchange by buyer directly: Buyer is required to deduct TDS
- Amount paid to Exchange through a broker: Broker is required to deduct TDS.
- The sellers can claim the TDS deducted as a credit while filing their Income Tax Returns
Note:
- There is no clarity from the Income Tax department on TDS applicability if the sellers are outside India or foreign exchange is involved
- DTAA: Double taxation provisions are not yet clear. The crypto profits might be taxed in multiple countries and the provisions related to tax relief are not yet notified
Video on How to file Income Tax Return for Cryptocurrency
This video shows How to file Income Tax Return for Cryptocurrency
Income Tax Notice for Crypto Traders
The Income Tax Department has sent out notices to taxpayers who did not report their crypto trading income in previous years’ ITRs. These notices are sent under Section 148A of the Income Tax Act and provide an opportunity for taxpayers to respond and explain the non-reporting of income.
GST on Cryptocurrency, NFT, VDA
While the Income Tax Act addressed the income tax applicability on cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and VDAs, there is still no clarity on the applicability of Goods and Services Tax (GST) on these assets. It is expected that the sale of cryptocurrencies and other digital assets may be taxable under GST, as they may fall under the definition of goods as per the GST Act. However, a formal clarification from the GST Council is awaited.
Related articles:
- Tax and RSU of MNC
- ITR Forms for AY 2023-24 or FY 2022-23
- Declare ESPP,ESOP,RSU of MNC in ITR as Foreign Assets
- List of our videos on Income Tax
Conclusion
The introduction of Section 115BBH in the Income Tax Act marked a significant step towards regulating income from virtual digital assets and cryptocurrencies. Taxpayers dealing with VDAs need to be aware of the tax implications, capital gain calculations, and the potential for tax notices. As the cryptocurrency market continues to evolve, taxpayers must stay updated with the latest tax regulations and seek professional advice to ensure compliance with tax laws.

2 responses to “Understanding Tax on Cryptocurrency and Virtual Digital Assets”
Do I need to show capital gain on crypto Transactions that are done before July 2022 as TDS start to deduct from July 2022
Yes, you need to show capital gains on all transactions of the cryptos of the last financial year.
For those for which TDS was deducted you can claim TDS while filing ITR