Congratulations on your job. You have achieved one important milestone of your life. While in school, college every information was made available to you. In Job, your employer will make sure that you are trained to start contributing but you will be given a bunch of forms to sign without anyone explaining to you what you need. For example, your employer will ask you do declare tax saving and will ask you to submit proof towards Feb.
Table of Contents
What should you know as an employee?
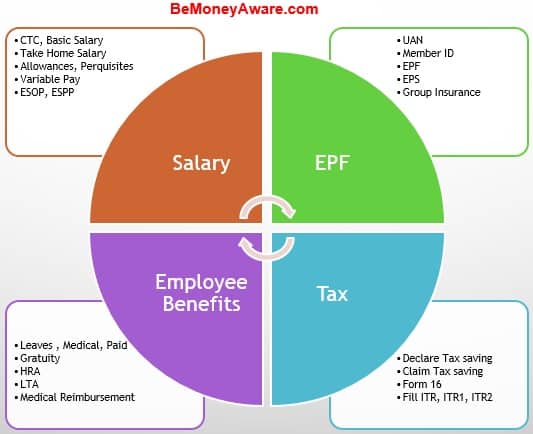
Companies on campus talk about what is called as cost to company (CTC), that is, the money they will spend on you. An employee needs to understand many things which are captured in the image below
- What is CTC, Net Salary, Gross Salary?
- What are the various allowances, like HRA, Transport Allowance, Medical Reimbursement
- What are the contributions towards long-term and retirement benefits such as Provident fund, superannuation fund, and, Gratuity?
- Variable payouts such as performance bonus, variable pay, and gratuity.
- Stock Options: ESOPs, or, Employee Stock Options are the other incentives offered. Here, the company provides you with an option to purchase some company’s stock at a fixed price (also called exercise price) on a future date.
- And then there is Form 16 and you have to pay Tax, even though your company has deducted TDS?
As a new employee do you understand this? Explore the section to learn about Salary, Employee Provident Fund and tax related to Salary.
About Income or Salary
Did you know? The word salary originates from the Latin word salarium. It was the quota of salt given to Roman soldiers in addition to their pay. When the officers found it cumbersome to transport and preserve the huge bulk of salt, they began offering a sum of money instead of the commodity. The money received was referred to as ‘salarium’ or salt-money which soon came to be known as ‘salary’ in modern English. Al
What are the components of Salary, How is take home salary calculated? What are different kinds of allowances, what is Dearness allowance, What is the salary of a Government employee, what is 7th pay commission? These articles try to answer these questions.
- Salary, Net Salary, Gross Salary, Cost to Company: What is the difference
- Salary,Allowances,Dearness Allowance,Government Salary, Pay Commission
- Understanding Variable Pay
- Understanding National Pension Scheme – NPS
- Casual Leave, Earned Leave, Sick Leave: Leaves in India
- Maternity Leave :Duration, Wages, Maternity Benefit Act
- What are Employee Stock Options (ESOP)
Allowances
HRA or House Rent Allowance
- HRA Exemption,Calculation,Tax and Income Tax Return
- How to show HRA not accounted by the employer in ITR
- Claim HRA while living with parents
- How to show HRA not accounted by the employer in ITR
Leave Travel Allowance
Income Tax Proof Submission to Employer
- Income Tax Proof Submission to the Employer
- Submitting Home Loan Interest Proof to the Employer with PAN of Lender
- Form 12BB for claiming Income Tax Deductions by Employees
- How to Claim Deductions Not Accounted by the Employer
- Form 16, Form 12BA
Employee Provident Fund
- Basics of Employee Provident Fund: EPF, EPS, EDLIS
- Understanding Employee Pension Scheme or EPS
- Voluntary Provident Fund, Difference between EPF and PPF
- Withdrawal or Transfer of Employee Provident Fund
- EPF Private Trust, the Exempted EPF Fund
- EPF Refund and Bank Account Problems
- Tax on EPF withdrawal
- EPF Calculator-Method I:3.67%
- EPF Calculator – Method II
- Transfer EPF account online : OTCP
- How much EPS Pension will you get with EPS Pension Calculator
- What are EPF,Pension and Insurance Changes from1 Sep 2014
- How EPFO Manages Money, EPFO invesment in Stock Market
UAN
- UAN or Universal Account Number and Registration of UAN
- FAQ on UAN number and Change of Job
- UAN Problems, Password,Mobile Number,Incorrect Details and Help Desk
- EPF Form 11 on Joining a New Job
Income Tax For Employee
- Understanding Form 16: Part I,
- Understanding Form 16: Chapter VI-A Deductions,
- Understanding Form 16: Tax on income
- Understanding Form 16 – Part 3
- HRA Exemption,Calculation,Tax and Income Tax Return
- Understanding Perquisites
- Basics of Income Tax Return
- Understand Income Tax, How to Fill ITR,Income Tax Notice
On Changing Jobs
- Changing Jobs:Take Care Of Bank Account,Tax Liability
- Changing Jobs and Tax, Form 12B
- EPF Form 11 on Joining a New Job
- Encashing Earned Leaves : Exemption and Tax
- What is Gratuity? :
- After 5 years of working in the company an employee becomes eligible for Gratuity. Gratuity is a lump sum payment made by employer to the employee based on the duration of his total service when the employee leaves the job . The reason for leaving the job can be either by resignation, death, retirement or termination, etc. The amount you get as gratuity depends on the number of years you have served and the last drawn monthly salary. Roughly, you get half a month’s Basic and Dearness Allowance(DA) for every completed year of service. The gratuity received by an employee is NOT taxable if it is received on his retirement, his becoming incapacitated prior to retirement or if such gratuity is received by his widow, children or dependants on his death. So if one doesn’t retire and is below the retirement age then Gratuity is not tax free. Gratuity is taxed under the head Income from Salaries.
ESOP, RSU, ESPP, MNC
Companies often reward their employees with their stock, either in the form of employee stock option plans (ESOP) or Restricted Stock Units(RSU) or employee stock purchase plans (ESPP).
If you work for MultiNational company then you might get stocks listed on stock exchanges listed outside India like the USA. Then these become your foreign assets.
- Declare ESPP,ESOP,RSU of MNC in ITR as Foreign Assets
- RSU of MNC, perquisite, tax , Capital gains, ITR, eTrade
- What are Employee Stock Options (ESOP)
- Employee Stock Purchase Plan or ESPP
Misc
- MBA :CAT, IIM, Global MBA,Job
- Job Squeeze : Hiring is slow
- Case Study: Single, New in Job and Loans
- An Interview: 20s and Money