This article talks about Income Tax Return for AY 2016-17 or FY 2015-16. This article talks about Tax slabs for Financial year 2015-16 or Assessment Year 2016-17, gives Overview of Income Tax,Focuses on Income Tax for a Salaried Employee on HRA,LTA , Medical exemptions and submission of proof to employer.
Table of Contents
ITR For AY 2016-17 or FY 2015-16
The Income Tax Department has released the ITR (Income Tax Return) Forms for Financial Year 2015-2016 (i.e. Assessment Year 2016-2017). Filing for the new forms begins with the onset of the new Financial Year 1 Apr 2016. Taxpayers can file their ITRs till the stipulated deadline of July 31 5 Aug 2016.
The tax rates are applicable on the income earned during 1 April 2015-31 march 2016. The assessment of income tax according to this slab rate will be done in the year 2016-17 by filing Income Tax Return or ITR by 5 Aug 2016. Your total income shall be taxed according to the income tax slabs applicable for this year FY 2015-16
- New ITR Forms can be downloaded from www.incometaxindia.gov.in/Pages/downloads/income-tax-return.aspx
Changes in the ITR
There are no changes in structure of ITRs. The following features introduced in FY 2015-16 have been retained.
- columns seeking declaration of foreign assets and income by entities and individuals
- one needs to provide details like Aadhaar number, personal mobile phone number and email id
- Furnishing of Passport details has not been made mandatory this time too.
- One needs to furnish total number of savings and current bank accounts held by the individual or entity, at any time during the previous year, (excluding dormant accounts)
- E-verification of Income Tax Returns and Generating EVC through Aadhaar, Net Banking
Tax Collected at Source (TCS)
ITRs feature an additional column to mention the Tax Collected at Source (TCS) .
Assets and Liability in ITR for those with income above 50 lakhs
Income Tax Department has introduced a fresh reporting column in the new ITRs called Asset and Liability at the end of the year which is applicable in cases where the total income exceeds Rs 50 lakhs. Individuals and entities coming under this income bracket will also have to mention the total cost of such assets. So, while immovable assets like land and building have to be furnished under the new ITR regime, movable assets like cash in hand, jewellery, bullion, vehicles, yachts, boats and aircraft will also have to be disclosed .
The entity reporting these high-value possessions will also have to describe their “Liability in relation” to these items.
ITR-2A and Pass Through Income (PTI)
The ITR-2A, to be filled by those individuals and HUFs who do not have income from either business, profession or by way of capital gains and do not hold foreign assets, has the new column called Pass Through Income (PTI) and seeks details from business trust or investment fund as per section 115UA and 115UB of the Income Tax Act (investments made in a venture capital company) which pertains to emerging companies or startup firms.
ITR for AY 2016-17 or FY 2015-16
There are 9 types of ITR or income tax return forms. Which income tax return form a taxpayer should file depends on the taxpayer’s income and sometimes on the disclosure requirements applicable to the taxpayer, where he/she may be a resident with foreign income or assets. ITRs for Individual / Hindu Undivided Family are given below
| Form | Category | Details |
| ITR-1 SAHAJ | Individual | 1. Income from salary/pension: or 2. Income from one house property 3. Income from other sources( excluding winnings from lottery and income from races horses) |
ITR 2A |
Individual/HUF | Newly introduced Form applicable from AY 2015-16.1. Income from salary/pension 2. Income from more than 1 house properties 3. Income from other sources( excluding winnings from lottery and income from races horses) |
| ITR-2 | Individual/HUF | 1. Income from salary/pension 2. Income from house property(s) 3. Income from other sources( excluding winnings from lottery and income from races horses) 4.Income from Capital Gains. 5. Income from foreign assets. They should not have Income from Business or Profession. |
| ITR-3 | Individual/HUF | Being partners in firms and not carrying out business or profession under any proprietorship. |
| ITR-4S SUGAM | Individual/HUF | It is applicable for small businessmen and professionals from business or profession and gross receipts upto Rs. 60 lacs a year |
| ITR-4 | Individual/HUF | having income from business or profession (such as insurance agent, doctor, CA, lawyer etc.) with gross receipts of more than RS. 60 lacs a year |
Tax slabs for Financial year 2015-16 or Assessment Year 2016-17
Every individual whose total income before allowing deductions under Chapter VI-A of the Income-tax Act, exceeds the maximum amount which is not chargeable to income tax is obligated to furnish his return of income. The maximum amount not chargeable to income tax in case of different categories of individuals is given below. Other than increase of Surcharge from 10% to 12% for income tax when taxable income is more than 1 crore there is no change in the tax slabs compared to FY 2014 or 2015-16. The tax calculator can be used to find your tax liability.
| TAX | MEN and WOMEN | SENIOR CITIZEN(Between 60 yrs to 80 yrs) | For Very Senior Citizens(Above 80 years) |
| Basic Exemption | 250000 | 300000 | 500000 |
| 10% tax | 250001 to 500000 | 300001 to 500000 | – |
| 20% tax | 500001 to 1000000 | 500001 to 1000000 | 500001 to 1000000 |
| 30% tax | above 1000000 | above 1000000 | above 1000000 |
| Surcharge | 12% of the Income Tax, where total taxable income is more than Rs. 1 crore | ||
| Education Cess | 3% on Income-tax plus Surcharge. | ||
Some changes in deductions in FY 2015-16
- Exemption of transport allowance increased from Rs 800 pm to 1600 pm
- Investment in Sukanya Samriddhi Scheme will be eligible for deduction u/s 80C and any payment from the scheme shall not be liable to tax.
- Limit of deduction u/s 80D of the Incometax Act increased from Rs 15,000 to Rs 25,000 on health insurance premium (in case of senior citizen from Rs 20,000 to Rs 30,000).
- The limit of deduction increased in case of very senior citizens u/s 80DDB of the Income-tax Act on expenditure on account of specified diseases from Rs 60,000 to Rs 80,000.
- The limit of deduction increased u/s 80DD of the Incometax Act in respect of maintenance, including medical treatment of a dependant who is a person with disability, from Rs 50,000 to Rs 75,000.
- The limit of deduction increased from Rs 1 lakh to Rs 1.25 lakh in case of severe disability
- the limit of deduction increased u/s 80CCC of the Incometax Act on account of contribution to a pension fund of LIC or IRDA approved insurer from Rs 1 lakh to Rs 1.5 lakh.
- the limit of deduction increased u/s 80CCD of the Incometax Act on account of contribution by the employee to National Pension Scheme (NPS) from Rs 1 lakh to Rs 1.50 lakh.
- Also a deduction of upto Rs 50000, under new section 80CCD(1B), over and above the limit of Rs 1.50 lakh in respect of contributions made to NPS is provided for. Therefore for financial year 2015-16, Total Deduction under Section 80C, 80CCC, 80CCD(1) and 80 CCD(1B) is Rs 2,00,000. From assessment year 2012-13, Employer’s contribution under section 80CCD(2) towards NPS is outside the monetary ceiling mentioned above. Our article Should you Invest in NPS the National Pension Scheme for additional 50,000 and save tax talks about it in detail.
Information about the ITRS would be made available in April once the new Forms are released.
Overview of Income Tax
Time period for earning the income is between 1 Apr to 31 Mar of next year. So here we will be focussing on Income earned between 1 Apr 2015 to 31 Mar 2016, which is called FY 2015-16, PY 2015-16 or Assessment Year 2016-17. The return for income earned will be filed by 31 st July 5 Aug 2016.
Who pays the income tax: Income-tax is to be paid by every person. The term ‘person’ as defined under the Income-tax Act covers natural as well as artificial persons. For the purpose of charging Income-tax, the term ‘person’ includes Individual, Hindu Undivided Families [HUFs], Association of Persons [AOPs], Body of individuals [BOIs], Firms, LLPs, Companies, Local authority and any artificial juridical person not covered under any of the above.
As per Income tax laws, there are five kinds of Income:
- Salary by working for someone or Pension having worked for someone, comes under category of Income From Salary. Proof is Form 16 and Form 12BA
- Selling items like gold, house comes under category of Income from capital gain
- Having a house or many houses comes under category of Income from House Property
- Having a business or profession ex shop, doctor, consultant comes under category of Income from Business or Profession
- Having income which does not fit into any of above category,comes under the category of Income From Other Sources. Such as interest on Bank Account, Interest on Fixed Deposits, Dividends from companies, Family pension ,Insurance commission,Income from royalty,gift amount etc.
The Income Tax Act, 1960 allows you to save tax by investing your income. Depending on where you invest , the maximum amount, section of Income tax act which governs it changes For example :
- Under Section 80C,80CCD, 80CCC, 80CCCE etc one can save tax by investing upto 1 lakh in different options, each suited to a different need. One can choose a combination of fixed income, life insurance and market-linked investments depending on one’s financial goals and investment horizon.
- Under Section 80D one can save tax by paying Premium for health insurance of youself, your spouse, children or dependent parents
- Under Section 80E one can save tax if one has taken Education Loan
- Under Section 80G one can save tax if one has donated money to charity.
| Income Tax Section | Gross Annual Salary | How Much Tax Can You Save? |
|---|---|---|
| Sec. 80C | Across all income slabs | Upto Rs 46,350 saved on investment of Rs. 1,50,000 |
| Sec. 80CCC | Across all income slabs | Upto Rs 30,900 saved on Investment of Rs 1,50,000 |
| Sec. 80 D | Across all income slabs | Upto Rs 10,815 saved on investment of Rs 35,000
(Inclusive of Rs. 20,000/- towards health insurance of parents who are senior citizens)
|
Everyone does not have to pay same tax. Income tax depends on the
- Income earned, more the income, more the tax.
- Residence(india/non-resident India) : You’re considered a Resident in a financial year if you satisfy one of the conditions below. You are an NRI or Non Resident Indian, if you do not meet any of these conditions.An exception is made for Indian citizens working abroad and members of a crew of an Indian ship or a PIO visiting India, where 60 days is replaced with 182 days.
- You are in India for 182 days or more during that financial year OR
- You are in India for 60 days or more during that financial year AND you are in India for at least 365 days during the 4 years preceding that financial year.
- It also varies with with age: Based on Age there are three categories, Ordinary(below 60 years),Senior Citizen(age between 60 years to 80 years), Super Senior Citzien(above 80 years). If an Individual attains the age of 60 years or 80 years during the financial year, his age shall be regarded as 60/80 (as the case may be), for that whole Financial Year. For the purpose of ascertainment of the applicable tax slab, For FY 2015-16 or AY 2016-17 an individual can be classified as follows:
- Ordinary: Resident individual below the age of 60 years. i.e. born on or after 1.4.1956
- Senior Citizen: Resident individual of the age of 60 years or above at any time during the year but below the age of 80 years. (i.e. born during 1-4-1936 to 3 1-3-1956)
- Super Senior Citzien(above 80 years) : Resident individual of the age of 80 years or above at any time during the year. i.e. born before 1.4.1936
- Non-resident individual irrespective of the age.
How to compute Income Tax
Steps involved in Computation of Income Tax are as follows. The tax calculator can be used to find your tax liability.
- Computation of total income.
-
- Subtract the exemptions of HRA, Conveyance and Medical expense from the gross salary.
- Add the extra income of interest, commission and bonuses, if any.
- Add the rental income, if any.
- Add the capital gains, if any.
- Add Interest from all Saving bank accounts. Subtract 10,000 from the sum.
- Add Income from other sources: Interest on FD, RD etc.
-
- Deducting valid deductions.
- Determination of the tax payable thereon.
- Deducting TDS. Verifying Tax already paid such as TDS deducted from Salary income, From FD.
- Paying the tax.
- Filling Income Tax Return Form
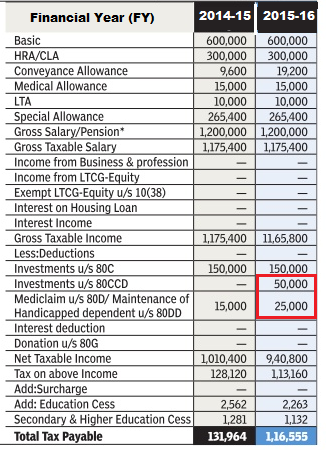
Image below shows the tax calculation for an employee with salary of 12 lakh for FY 2014-15 and FY 2015-16. By paying Medical Insurance of Rs 25,000 and Investing in NPS under 80CCD he is able to save around 15,000 Rs tax more.
Income Tax for Salaried Employee
An overview for income tax Salaried employee is given here. Money earned by working for someone or by receiving Pension after having worked for someone, comes under category of Income From Salary.
- Money that is received under Employer-Employee relationship is called as Salary. If one is freelancer or is hired by an organization on contract basis, their income would not be treated as salary income. In such case the income is treated as income from business and profession.
- The salary consists of Basic Salary, Allowances and Perquisite.
- Employer deducts TDS on the income every month.
- There are various Kinds of Allowances that one can get under the Head Salary some of which are exempt partially or fully. Some popular Allowances are House Rent Allowance or HRA, Conveyance allowance,Leave Travel Allowance.
- One can also claim benefit of Interest on Home Loan , Income Tax Deductions from Sec 80C to 80U. One needs to submit proof to the employer to claim these deductions.
- Proof of Income from Salary,TDS, Allowances and Deductions claimed is Form 16 and Form 12BA which is given by the employer sometime in May 2016 . You must verify Form 26AS.
Exemptions a salaried employee can claim
- HRA Exemption for Salaried Employees : House Rent Allowance or HRA is given by the employer to the employee to meet the expenses of rent of the accommodation which the employee has taken for his residential purpose. A portion of the House Rent Allowance is exempted from the levy of the Income Tax. To claim HRA exemption, If you are paying rent of more than Rs 8,333 per month you need to provide landlord’s PAN Landlords without a PAN must be willing to give you a declaration. If you pay house rent to your spouse, this does not qualify for exemption. But you can claim exemption on rent paid to others including parents, brother, sister in-laws etc. Our article HRA Exemption for Salaried Employees discusses it in detail.
- Leave Travel Allowance :Many employers also give allowance, called as Leave Travel Allowance, to their employees to go on a vacation in India with their family which is exempted from tax. Only the travel costs are covered so expenses on hotel rooms, sightseeing, food, etc, cannot be included. You can claim exemption for up to two journeys in a block of four calendar years. The new block started on January 1, 2014 and will end on December 31, 2017. This amount can only be claimed through the employer, if the employee actually goes on a vacation in India and bills for the same has to be furnished. Our article What is Leave Travel Allowance or LTA discusses it in detail.
- Medical Bills: You can claim income tax relief for your medical expense depending on whether the employer pays medical allowance or reimburses the bills. For the purpose of medical expenses a family is defined as the spouse and children of the employee. The employee’s parents and siblings of the employee can also be considered for such benefits but the condition is that they need to be completely dependent on the employee. Please claim these by submitting bills to your employer.
- Medical reimbursements are the actual amount that the employer’s gives to an employee when they submit bills for medical treatment availed. Medical reimbursements are exempt from taxes till the limit defined by the IT Act, which is Rs. 15,000.
- Medical Allowance: Many employers don’t provide reimbursements. They pay their employees a fixed amount, in their monthly salary, as medical allowance. This payment can be of Rs. 1,250 a month or Rs.15,000 a year. If the employee incurs medical expenses then the amount up to Rs 15,000 is exempt from taxes. . For example: An employee,whose company pays Medical allowance, suffers from Typhoid and is ill for a few weeks. His treatment and the medicines cost him Rs. 5,000. He retains all the bills relevant to his treatment and when he gets back to work he submits them to his company. In this case, since the medical allowance is already paid to him as a part of the salary, he will not have to claim the amount. He will instead get tax benefits for the Rs. 5,000 spent on the treatment. If he submits no other bills then the remaining Rs. 10,000 of the medical allowance will be liable for tax.
Investment Proof Submission to Employer
Please plan you tax liability at the beginning of financial year. Calculate how much tax you need to save under 80C and other sections like 80D for medical insurance premium. Don’t rush at last minute and buy Insurance policy just to save tax. Before Buying Insurance Policy to Save Income Tax Our article Income Tax Proof Submission to the Employer discusses it in detail.
- The employers asks employees for declaration of the their proposed investments for tax exemptions/deductions from employees in the beginning of the financial year (April itself) . Based on your declaration and the investments that qualify for deductions and exemptions, your employer deducts tax on your salary every month.
- E-filing : Excel File of Income Tax Return,
- By December or January employer asks for submission of the proofs for all proposed tax saving investments. If you submit proof to your employer for amount less that declared , employer will recompute your tax liability and deduct more tax in remaining months. If you submit proof to your employer for amount more than declared , employer will recompute your tax liability and deduct less tax in remaining months. If Your tax liability is not recomputed or somehow you still have extra tax paid you can claim it while filing income tax return.
- You can share your saving bank interest, FD/RD interest earned during year, any capital gains from shares or mutual fund, rental income and other kind of incomes with your employer, so that they get a complete picture of your taxable salary/Then your employer would recalculate your tax liability and also pay tax on your other investments like FD on your behalf. But if you don’t then you need to pay the tax due yourself through Challan 280 either as Advance Tax or Self Assessment Tax.
To calculate how much to save under 80C
80C has overall limit of 1.5 lakh. While calculating amount you need to save please consider your EPF contribution. If you have bought some life insurance policy, then you claim it too.
Amount you need to save : 1,50,000 – Employee EPF contribution – Tuition fees for two children – Principal of Home Loan – Life Insurance Premium -Stamp Duty , Registration charges of new House.
Income Tax on Leaving a Job
When a person switches the job in between the financial year i.e between 1 Apr 2015 to 31 Mar 2016, he would get two Form 16, one from previous employer and one from new employer. He might also get leaves encashed and Gratuity.
- Exemption on Encashment of Leaves for Salaried Employees : Most employers give all their employees a certain no. of days which can be claimed as leaves. However, in case a person does not claim these leaves, many employers also give their employees the option for en-cashing these leaves i.e. the employers pays extra to the employees for the leaves which were allowed to be taken but were not taken.This amount received as Leave Encashment is also allowed to be claimed as an exemption up to a certain extent. Our article Encashing Earned Leaves : Exemption and Tax covers it in detail.
- Income Tax Exemption on Gratuity for Salaried Employees : Gratuity is a gift made by the employer to his employee in appreciation of the past services rendered by the employee. Gratuity can either be received by The employee himself at the time of his retirement or leaving job a)after 5 years of working with the same employer or b) The legal heir at the time of the death of the employee. Our article What is Gratuity? covers it in great detail.
- Multiple Form 16: When you change job in a financial year you need to make sure that the deductions and exemptions regarding tax liability are made only once. Our article Changing Jobs and Tax, Form 12B talks about how basic exemption is accounted by two employers, correct way to calculate tax when one switches jobs, how Form 26AS will have multiple entries. It is better to give a copy of your full and final settlement from previous employer to new employer so that new employer can take care of tax liability and you have to refer to just one Form 16 while filing ITR. Else you will have to take care of it while filing ITR. Our article How to Fill ITR when you have multiple Form 16 talks about filling ITR with multiple Form 16.
- EPF: It is best if you submit your UAN number to your new Employer so that new Member ID is linked with it. And transfer your EPF account. If you withdraw before 5 years of contribution to EPF the withdrawal is taxed and you have reverse earlier 80C deductions.
A video (14 min) by bemoneyaware on Understanding what is income and Income slabs
Related Articles:
Income Tax for AY 2015-16: Tax slabs, ITR Forms
E-verification of Income Tax Returns and Generating EVC through Aadhaar, Net Banking

67 responses to “Income Tax for AY 2016-17 or FY 2015-16”
Dear Sir/Mam, My Mother is a pensioner [was a govt employee]. She gets a medical reimbursement of RS 10500/- per year, only if she provides the medical bills to her office, if the bills are not provided than she does not get a single penny. For AY 2015 – 2016, she provided bills of Rs. 9000/- and she got a reimbursement of that amount in her pension account along with her pension. My query is, if she is supposed to fill ITR 1 form [please advice on this too whether itr 1 or any other form], than as per my knowledge this Rs 9000/- are non taxable .. than where to disclose this amount in the form ??
Secondly, there is a mismatch of pension amount.. as per bank pass book records it shows Rs. 250000/- credited in the financial year 2014-2015 but form 16 given by her employer shows 200000/- as salary/pension paid.. when spoked to the employers accounts officer.. he says the form 16 given by him is right and maximum medical reimbursement amount i.e. is Rs 15000/- should be deducted from 200000/- and disclosed in the form under head salary..
Please guide what to do in such situation. Waiting for your valuable reply. Regards
Form 16 has to be used as a proof of the income from salary.
An employer may pay other benefits like medical, travel costs which are credited to the employee’s account.
Which ITR form she has to sign depends on her income from various sources. Our article Which ITR Form to Fill explains it and suggests a form based on your inputs.
Our article How to fill ITR1 for Income from Salary,House Property,TDS explains the process in detail.
My pension income is 2,50,000 and my interest income is Rs.100000. I have invested an amount of Rs.1,50,000/-in Post Office 5 years Term Deposit Scheme u/s 80C for income tax benefit. I took Voluntary Retirement from Central Govt Service in April, 2016. My age is 54 years.
Kindly tell me – Am I eligible to file Form 15G in bank so as to avoid TDS on interest income.
I always read your blog and this is very nice to explain the income tax Accounting
and this give me sufficient detail related my topic, So I want give lot of thanks for this.
Medical allowances are not tax-exempt afaik but medical reimbursements are.
Hello Sir,
May I know the meaning of ‘disclosed income’. I have filed my IT returns for this year. It is the first time I am doing it. Is it ….
Gross total income – deductions = Total income
Does it mean the ‘total income’ is the disclosed income (after taking care of all deductions including tax). Pl correct me if I am wrong.
Hi,
I am a senior citizen of 68 yrs and have been submitting 15 H form to the bank for non deduction of tax. For FY 2015 – 2016 I.e A.Y 2016-2017, my total income is as follow.
Income from family pension – Rs 110000
Income from FD’s. – Rs 2,85,000 ( Form 15 H submitted no TDS has been cut)
Income from SB interest – 20000
LIC pension – 10000
Total income – 1,10,000+2,85,000+20000+10000=4,25,000/-
Investment
5 year senior citizen saving scheme in 2015 Oct – 4,00,000
Deductions under 80C (for 5 yr senior citizen scheme) – 1,50,000
80TTA deduction – 10000
Total deductions – 1,60,000
Net taxable income = 4,25,000 – 1,60,000 = 2,65,000
Senior citizEn exemption limit = 3,00,000
So, the net taxable income is less the exemption limit.
So tax to paid for A.Y 2016-2017 = zero
I have filed zero tax returns. But, the family pension , I showed in Income from salary or pension and the remaining under Income from other sources. Hope it is not a problem.
Also I didn’t claim the family pension deduction of 15000 which is allowed.
Can you please confirm that the above calculations and process is correct. Hope there won’t be any issues.
Also I have already submitted 15 H for 2016-17 also and the interest is getting credited monthly and quarterly and I don’t know exactly how much will be my total income in FY 2016-2017 ( as there could be increase or decrease in pension with the 7 the pay commission which is not yet finalized), can I calculate the total income for FY2016-2017 at the time of filing the return in June- July 2017 and pay the tax accordingly, as it is difficult to plan investment due to changing pension due to 7 the pay commission.
Request tax experts to please help and confirm on the above scenarios.
Thanks
Dear Sir,
I don’t have any jobs, I have earned only on my self and my wife FD, it may come around 350000 / per year, I have house, from that rent per year is 144000, and another FD by private finance to get 25000 per per year total is , 519000. Should I pay tax and how much. Please note. I’m 47 years abroad return on June 2015, Not a salaried person.
Hello Sir/Madam,
Sir from may 2015 to dec 2015 interest paid is Rs.85423 and principal is Rs.7239 and after possession i.e from Jan 2016 to march 2016 interest is Rs.44272 and principal is Rs.3422.Soplease tell me which amount should i show while filing itr and under which section whether i have to show the interest amount in negative
Please tell me with amount of interest ane principal that i should show while filing itr1.One more query my stampduty is Rs.52431 as you said i can claim it under section 80c so should i have to show it twice i.e first for registration of flat and second for claiming it or only one time that means for both registring and claiming
As well as please tell me which interest amount can i claim and where i think interest amount will reflect twice one under income from house property and second amount for claiming and will the interest amount under both section will be same or different and should the interest amount under both the section should be negative or only i have to show negative under income from houseproperty and positive for claiming under section?
I took the Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima of Rs.330/- can i show it while filing itr1 if yes then under which section
Last query i took the flat but i am not residing there i stay with my parents in october i will shift there but the flat is vacant so do i have to submit any document and while filing under the head income of houseproperty should i select the type selfoccupied
Sir i am finding difficulty in filing itr 1 in may 2015 i purchased a flat which was underconstruction and in dec 2015 i got the possession but from may to dec 2015 i paid pre emi so the total amount from may2015 to march 2016 is Rs.140356/-principal amount is Rs.10661/- and interest is Rs.129695/- stamp duty and registration Rs.52351/-total cost of flat is Rs.25lakhs including stamp duty and registration so my question is where should i take interest amount while filing itr 1 as well as proncipal and stamp duty amount also.Secondly can i claim for it if yes then what amount should i take principal,interest or stampduty and registration please help me with the amount detail.Waiting for your reply
I have eFiled my tax return for AY 16-17 on 28.07.2016. I am due for a refund. The same day I got a text message that due to merger of the 2 adjacent breaches of the bank with which I have my account, the IFSC/MICR codes of my branch have changed. Unfortunately, I have given the original IFSC code of my branch. I have not yet sent my acknowledgement. Given this background, I would like to know if I am required to file a revised return so that I get my refund without any difficulty.
Regards
N Ramesh
Please revise your return and update the new bank details. So that you don’t have any problem in getting refund
Thank you..
Regards
N Ramesh
I have spend on MRI,THYROID & HORMONES TEST about 10000.00. this amount can I claim the amount for Tax Deduction under Section 80 D if not received medical allowance in gross salary. and rebate under section 80DDB I spend 3 lacs on my treatment this year in private hospital of pituitary macroadenoma (tomur). so it covered under 80DDB. If yes do i need to get this certified from Govt cancer hospital only.
In which column of deductions in ITR1 should I place deduction u/s 57ii of rs.15000.00 (Family pension)
Family pension comes under income other sources. in ITR1 there is just one field for Income from other sources. So you have to add it to all your income from other sources like :Saving Bank Account Interest, Interest from FD etc.
in case of family pension, a standard deduction to the extent of 1/3rd of the family pension or Rs 15,000, whichever of the two is lower is allowable.
The deduction is allowable under Section 57(iia) of the Income-tax Act, 1961 (The Act).
a) Family pension is to be shown under the head “income from other sources” in the Income-tax Return.
b) No attachments are allowed along with the return as per the new rules.
I have a FD opening in 2009 with amount Rs30000 for 3years, in the year 2012 I refixed it for another 3years. In 2012 I have received any interest or any principal, now in 2015 (July) I have received 48606 (Principal+Interest), I am salaried person from 2014, my income is over 400000,
my question is how much amount should I have to pay tax for it for AY2016-17?? is it 48606-30000=18606?? since this interest earned during 6yrs. Bank didn’t deduct any TDS.
It seems you missed the interest on FD in earlier years.
TDS on FD is deducted if interest in a year is more than 10,000 Rs.
So yes the interest earned is 48,606-30,000=18606.
I had submitted 15G in 2009, so bank didn’t deduct any TDS,
so should I have to pay tax of whole (6yrs) interest in AY2016-17???
Interest on FD is taxed as per the income tax slab.
As you have submitted form 15G It is in Govt records, it shows on Form 26AS.
Hello,
I have income from Gratutity. Which ITR should i file for AY 2016-17
If you are working in a private company then Gratuity upto 10 lakhs, over all your job changes,is tax exempt.
Above 10 lakhs is taxable.
So which ITR you fill depends on your other income. Even a basic ITR1 will do .
our article on What is Gratuity discusses it in detail.
Thanks for the prompt reply
Hi.. I need a clarification on the following. I was employed with ICICI bank from june’10 – aug’13 and now in Mar’16 I have withdrawn the EPF. For the same the tax too had been deducted. Now would i have to show the same in ITR filing? In my ITR login page under the “Tax details section”, i can find the EPF amount mentioned and along with the TDS deducted against it, apart from my current employers Income/ tds. Plz guide..
sir what is tax free gratuity amount after increasing new limit of gratuity from 10 lakhs to 20 lakhs please share detailes.
Achyut Shukla
Rajkot
The Seventh Pay Commission had recommended increase in the gratuity ceiling to Rs 20 lakh from the earlier level of Rs 10 lakh.
For government employees, Rs 20 lakh is the maximum amount that can be paid as gratuity.
For non Govt employee Maximum amount specified by the government is still Rs 10 lakh
Thanks for the prompt response sir
You are welcome Sir. Glad to know we could be of help.
Thanks!
Money was transferred online by son as gift to my account for the purpose of booking a property/flat.
No Gift deed was executed, only in the bank online, the purpose was chosen from drop-down menu as ‘Gift to relatives/friend.
Is it at all necessary to execute a gift deed?
Can a gift deed be executed after year?
If a salaried person having ppf interest more than 5000.than which income tax he has to fill ,form-1 or form-2.please help.
PPF interest is tax free and is exempt. You can fill ITR1.
Rule has been changed , agricultural income which is exempt should not be more than 5000 for ITR1
Sir,
Myself transferred around ₹ 100000 to my would be wife ( as a gift) in the year 2014. She made FD of that amount. We got married in march 2015. Now my question is whatever she earns through her 2014 FD in the FY 2015-2016, is clubbed with my total income? But She has not made any FD of those amount which I transferred to her in the FY 2015-2016 .
Is there any tax liability for me in the FY-2015-2016.
please note that she is housewife and she doesnot have any source of income.
grateful if you Kindly advice me for the same.
Assumption your wife has no income or her income is less than 2.5 lakh, the exemption limit.
What you gave before marriage is hers as she is not in relative definition.
After marriage if you opened a FD using your money and her name as first holder then clubbing of income will come into play. Please be careful here if TDS is deducted then it would be against the PAN of first holder i.e your wife.
Theoretically Interest from FD earned should be added to your income as Income from other sources and tax paid by you.
Sir,
Myself transferred 3 lakh Rps to my would be wife in the year 2014 when we were not married. We got married in march 2015. Now my question is whatever she earns through her FD in the year FY 2015-2016, is clubbed with my total income.In the year she has not made any FD.
If yes, how can I show that clubbing amount and deducted TDS in my ITR.
Kindly advice.
Thanks
I have query regarding the subject of compliance to Non-filers Monitoring System (NMS). My wife got a mail from income tax department seeking reasons of compliance of non filler for the financial year 2013-2014 . My Wife has submitted the response online that No taxable income.
Now my question is whether hard copy of COMPLIANCE RESPONSE SHEET needs to send to income tax department, if yes where i can find out the address.
Kindly advice.
Thanks
How to reply to the Non Compliance Income Tax notice? from our article
Do Not Panic. By sending the notice the department has asked you to furnish the information requested. Please respond to notice within time limit.
Income Tax sends various notices. Our article Income Tax Notice :Sections,What to check,How to reply talks about various notices that Income Tax Department sends. First you need to understand why have you received notice and for which year .
Please login to https://incometaxindiaefiling.gov.in with your user-ID and password. The Income Tax Department has created a new tab in its DashBoard called Compliances. If you are not registered at efiling website, it is easy to get registered. The taxpayer will be provided the information about the third party information received by the ITD
Taxpayers are required to submit the response on the e-filing website following the steps below:
Step 1: Login to e-filing portal Login to e-filing portal at https://incometaxindiaefilling.gov.in and click on “Compliance Tab”.
Step 2: View Non-filers information Non-filers Information and Information summary can be viewed under Compliance tab.
Step 3: Submit online response Submit online response (Follow Step by Step Guide to submit response of non-filing of IT return).
Dear Sir/Madam,
I am a retired PSU employee. I am getting a sum of Rs. 2115/ p.m.under Family pension scheme. Whether this is taxable ?
I am regularly filing retuns for this amount along with other income. Now I came to know that, 1/3rd of family pension or 15000, which ever is lower, is exempt from Income tax as per “under section 57(iia) of the Income tax Act 1961”. Whether this is correct ? Please advise.
Regards.
Yes, in case of family pension, a standard deduction to the extent of 1/3rd of the family pension or Rs 15,000, whichever of the two is lower is allowable.
The deduction is allowable under Section 57(iia) of the Income-tax Act, 1961 (The Act).
a) Family pension is to be shown under the head “income from other sources” in the Income-tax Return.
I need to fill and submit ITR5 for my Discretionary Trust Fund which has only FD interest income.
I entered the interest (including TDS) amount in Tab OS and TDS details in Tab TDS. When I click on Calculate Tax in Tab PARTB – TI – TTI, it calculates tax at 30% and fills in the subsequent fields on this tab.
What am I doing wrong
Dear Sir,
I am a salaried person transferred around 5 Lakhs Rps to My wife’s account on a regular interval( around 10-12 times) throughout the year for the purpose of withdraw the same amount by using her ATM as my ATM is not working. Should i pay tax for those amount which i have transferred to my wife’s account.
Please advice
No..you transferred from your salaried income.
If she has invested in FD then clubbing of income would come into picture
What should income range to declare under Declaration Scheme 2016?
Is it meant for those whose taxable income is beyond a certain limit?
what should be the limit of total taxable income to make declaration?
I am getting LIC maturity amount this year which goes to Bank SB account ! Whether this should be shown in IT returns ? If so in which columns ! Could kindly guided, please !
A property ( here, a flat)is bought on home loan/ bank loan.
Is to be declared as asset in ITR?
Income Tax Department has introduced a fresh reporting column in the new ITRs called Asset and Liability at the end of the year which is applicable in cases where the total income exceeds Rs 50 lakhs. Individuals and entities coming under this income bracket will also have to mention the total cost of such assets. So, while immovable assets like land and building have to be furnished under the new ITR regime, movable assets like cash in hand, jewellery, bullion, vehicles, yachts, boats and aircraft will also have to be disclosed .
I wish to be more clear about it.
Whereas income is in the tax bracket of Rs.5 Lakhs to Rs.10 Lakhs, Is it necessary to declare the property – flat- bought
jointly on bank loan?
The bank that sanctioned home loan, took the original registration deed in its custody and the practical owner
is bank until the loan with interest is not completely repaid.
Under such condition, is it necessary to declare the asset
while income is far far below Rs.50 Lakhs.
Please make it clear.
When you buy a house with or without home loan your income from that house depends on whether you are living in it,technically called self-occupied or rent that you are earning from it(let out ) property. For self occupied property income from house property = – (home loan interest) upto 2 lakh.
So House is your asset and its cost does not add to your income.
From AY 2016-17 or FY 2015-16, Any individual or Hindu undivided family (HUF) with total income of more than Rs.50 lakh in a year has to adhere to the new disclosure clause. As your income (without cost of house) is much less than 50 lakh you need not declare it.
Whereas income is far below Rs.50 Lakhs, is it necessary to declare the property, i.e., flat bought during Fy 2015-16
on bank loan?
Money accumulated in Employees Co-operative Society (in this case,
School Society) from monthly subscription over the years. The Society
as usually registered for helping its members by short term and long term
loan for house building, purchasing etc. and the interest is eligible for
deduction. After retirement of employee, he/she no longer remain a member
and the fund which accumulated over the years (inclusive of interest) is
paid to the member in full, in a single or multiple payment.
May the accumulation be treated as long term investment like GPF or General provident fund accumulation which is exempted from tax?
Please throw light whether the accumulated amount is treated as “Income from other source” or whether receipt of such accumulation is taxable or not.
what form should Indian earning in aboard for e.g: for NRE a/c – should fill for income tax
An NRI’s income taxes in India will depend upon his residential status for the year.
If your status is ‘resident’, your global income is taxable in India. If your status is ‘NRI’, your income which is earned or accrued in India is taxable in India.
Salary received in India or salary for service provided in India, income from a house property situated in India, capital gains on transfer of asset situated in India, income from Fixed Deposits or interest on savings bank account are all examples of income earned or accrued in India.
These incomes are taxable for an NRI. Income which is earned outside India is not taxable in India. Interest earned on a NRE account and FCNR account is tax free. Interest on NRO account is taxable for an NRI.
NRI or not, any individual whose income exceeds Rs.2,50,000 (for FY ending 31st March 2015 or Rs.2,00,000 for FY ending 31st March 2014) is required to file an income tax return in India.
NRIs must file their returns when they:
want to claim a refund
have a loss that they want to carry forward
Dear Sir,
I own two houses. Out of which I sold one and purchased another house during FY 2015-16.
House A- Sold in August 2015 for 63 Lakhs with LTCG of 40 Lakhs approx. Before selling it was self occupied.
House B- In joint ownership with my wife. Given on rent.
House C- Purchased in November 2015 for 55 Lakhs after selling House A. This house is self occupied from Nov 2015.
My questions are
Question 1. While filing ITR-2, in House Property schedule, Whether to show House A also? Asking this as it was sold in August 2015 and now I am no longer its owner. Effectively my ITR-2 HP schedule will contain 3 Houses. Do you agree? If yes which House to be shown as self occupied House A or House C?
Question 2. As House C purchase amount (55Lakhs) is less than that of House A sell amount (63 Lakhs), Can I claim deduction of whole amount of LTCG of 40 Lakhs under section 54?
Kindly review and reply at the earliest.
Please let us know which Income tax Form should be filled up for an individual who has income from sources like taking tution, saving bank interest.
Further, will the IT form get different if that individual also have income from FD interest and long term capital gain.
Yes Sir. Income Tax Return Form is based on the types of income earned. Income Tax Department classifies income into different types such as Income from Salary, Income from Capital Gains. Our article Which ITR Form to Fill? explains it. We have also covered it in a video.
Income from tution comes under Income from Business or Profession . It can also be covered under Income from Other Sources if you have salary as main income.
Saving Bank Interest upto 10,000 is exempted from tax under section 80TTA
FD Interest is Income from Other sources
Long term capital gain is exempt for stocks, equity mutual funds but is taxed for property.
Please let us know which Income tax Form should be filled up for an individual who has income from sources like taking tution, saving bank interest.
Further, will the IT form get different if that individual also have income from FD interest and long term capital gain.
Yes Sir. Income Tax Return Form is based on the types of income earned. Income Tax Department classifies income into different types such as Income from Salary, Income from Capital Gains. Our article Which ITR Form to Fill? explains it. We have also covered it in a video.
Income from tution comes under Income from Business or Profession . It can also be covered under Income from Other Sources if you have salary as main income.
Saving Bank Interest upto 10,000 is exempted from tax under section 80TTA
FD Interest is Income from Other sources
Long term capital gain is exempt for stocks, equity mutual funds but is taxed for property.
I have own house constructed first floor and part of the house is given rent w.e.f. Apr’16 I have receiving a rent of Rs.7000/- PM. I am a central govt. employee and drawing Basic of Rs.26540/- please provide me HRA calculation for the above.
I have own house constructed first floor and part of the house is given rent w.e.f. Apr’16 I have receiving a rent of Rs.7000/- PM. I am a central govt. employee and drawing Basic of Rs.26540/- please provide me HRA calculation for the above.
Well written. I enjoyed this blog post. It was inspiring and informative.
Well written. I enjoyed this blog post. It was inspiring and informative.
Sir,Salaried individuals who live in a rented house can claim House Rent Allowance or HRA to lower taxes.
But what if you don’t get HRA but still pay rent? This could be the case with self-employed professionals, businessmen or even the salaried folk whose emoluments do not include the HRA component. The Income-Tax Act provides relief to this category of rent-payers, too. Discussed in detail later
Deduction for tuition fees u/s. 80C of the Income Tax Act 1961 is available to Individual Assessee
Deduction for tuition Fees is available up to Rs. 1,50,000 (Rs. 1.50 Lakh from A.Y. 2015-16). Please Note that aggregate amount of deduction under section 80C , 80CCC and 80CCD shall not exceed Rs. 1,50,000/- (Rs. 1.50 Lakh from A.Y. 2015-16).
Deduction available on payment basis: – Deduction under this section is available on payment basis. Fees may be related to any period. For example feed paid for April 2009 if Paid in March 2009 will be eligible for deduction u/s. 80C in A.Y. 2009-10.
In essence, the maximum deduction you can claim on rent paid if you do not receive house rent allowance from your employer is Rs. 2,000 a month (Rs 24,000 annually), irrespective of how much you shell out as rent.
Conditions
To claim the tax benefit under Section 80GG, you must pay rent for the house you live in, and not get HRA for even a part of the year.
You cannot claim deduction on rent paid for a house in which not you but someone else (your parents, for instance) resides. Of course, you won’t be denied the benefit if anyone else lives with you in the house.
Next, to claim the tax benefit, you must not own a house in the place in which you live, or work, or carry on business. Your spouse or minor child or Hindu Undivided Family (if you are part of one) should also not own a house in that place.
So, if you or a person mentioned above owns a house in the city you live or work in, but you choose to stay in a rented place, then sorry — no tax relief for you.
There is one more condition. Say, you own a house at another place, which you declare as self-occupied. If you use it for your own residence, you don’t get the deduction. For example, say you rent a house in Mumbai where you work. But you also own a house in Thane (a neighbouring city) which you occupy as your residence. In such a case, you are not eligible for the deduction.
What these conditions mean is that you can claim the deduction only if you do not own and occupy a house anywhere, and if your spouse or minor child or Hindu undivided family does not own a house in your place of stay.
Finally, to claim the deduction you must file a declaration in Form No. 10BA.
Limits
Satisfy all the above conditions and you can claim tax deduction of an amount restricted to the least of the following: Rs. 2,000 a month, rent paid in excess of 10 per cent of your total income or 25 per cent of your total income.
Here, total income means your taxable income from all sources (salary, capital gains, house property, business or profession, and other income) and considering all deductions except that under Section 80GG. See the accompanying table for an example.
Sir,Salaried individuals who live in a rented house can claim House Rent Allowance or HRA to lower taxes.
But what if you don’t get HRA but still pay rent? This could be the case with self-employed professionals, businessmen or even the salaried folk whose emoluments do not include the HRA component. The Income-Tax Act provides relief to this category of rent-payers, too. Discussed in detail later
Deduction for tuition fees u/s. 80C of the Income Tax Act 1961 is available to Individual Assessee
Deduction for tuition Fees is available up to Rs. 1,50,000 (Rs. 1.50 Lakh from A.Y. 2015-16). Please Note that aggregate amount of deduction under section 80C , 80CCC and 80CCD shall not exceed Rs. 1,50,000/- (Rs. 1.50 Lakh from A.Y. 2015-16).
Deduction available on payment basis: – Deduction under this section is available on payment basis. Fees may be related to any period. For example feed paid for April 2009 if Paid in March 2009 will be eligible for deduction u/s. 80C in A.Y. 2009-10.
In essence, the maximum deduction you can claim on rent paid if you do not receive house rent allowance from your employer is Rs. 2,000 a month (Rs 24,000 annually), irrespective of how much you shell out as rent.
Conditions
To claim the tax benefit under Section 80GG, you must pay rent for the house you live in, and not get HRA for even a part of the year.
You cannot claim deduction on rent paid for a house in which not you but someone else (your parents, for instance) resides. Of course, you won’t be denied the benefit if anyone else lives with you in the house.
Next, to claim the tax benefit, you must not own a house in the place in which you live, or work, or carry on business. Your spouse or minor child or Hindu Undivided Family (if you are part of one) should also not own a house in that place.
So, if you or a person mentioned above owns a house in the city you live or work in, but you choose to stay in a rented place, then sorry — no tax relief for you.
There is one more condition. Say, you own a house at another place, which you declare as self-occupied. If you use it for your own residence, you don’t get the deduction. For example, say you rent a house in Mumbai where you work. But you also own a house in Thane (a neighbouring city) which you occupy as your residence. In such a case, you are not eligible for the deduction.
What these conditions mean is that you can claim the deduction only if you do not own and occupy a house anywhere, and if your spouse or minor child or Hindu undivided family does not own a house in your place of stay.
Finally, to claim the deduction you must file a declaration in Form No. 10BA.
Limits
Satisfy all the above conditions and you can claim tax deduction of an amount restricted to the least of the following: Rs. 2,000 a month, rent paid in excess of 10 per cent of your total income or 25 per cent of your total income.
Here, total income means your taxable income from all sources (salary, capital gains, house property, business or profession, and other income) and considering all deductions except that under Section 80GG. See the accompanying table for an example.
I am s retired SR. Citizen. I am in a rented house @ ₹ 10,000 pm and a son Aged 13 years studying in 9th std. I request you to please advise if I can get exemptions of house rent and rebate on son’s school fees.
Hi sir , I can help you in filing your return and getting all deductions with minimum tax liability..
I am s retired SR. Citizen. I am in a rented house @ ₹ 10,000 pm and a son Aged 13 years studying in 9th std. I request you to please advise if I can get exemptions of house rent and rebate on son’s school fees.
Hi sir , I can help you in filing your return and getting all deductions with minimum tax liability..