Taxes are an integral part of our life. Tax is used by the government to provide certain basic provisions to citizens. Individuals who earn i.e have income more than a certain amount are expected to pay taxes, as per the existing Income tax slabs. The Government also provides certain provisions wherein one can save tax. Tax deductions can help one reduce the taxable income, lowering their overall tax liability and thereby helping them save on taxes. This article covers all about Income Tax Savings, Steps to Save Tax, Understanding Tax Deductions, Tax Saving options like PPF, NPS, ELSS, Tax Saving FD with the link to our articles.
Table of Contents
All About Income Tax Savings
Steps for Income Tax Savings
Saving Tax consists of steps given below.
- Knowing your income and its tax under various categories. The word Income has a very broad and inclusive meaning. For a salaried employee, all that is received from the employer in cash, kind or as a facility is considered as income. For a businessman, net profits will constitute income. Income may also flow from investments in the form of Interest, Dividend, Commission, etc. Under the Income Tax Act, 1961, all Income earned by persons are classified into 5 different heads, such as:
- Income from Salary
- Income from House Property
- Income from Business or Profession
- Income from Capital Gains
- Income from other sources
- Knowing how much you have saved
- For Salaried employee through EPF, Allowances like HRA, Medical Allowances, LTA.
- On Loans you have taken like Education Loan, Home loan.
- Knowing How much more to save. It means understanding the Income Tax Limits, tax percentage. Income Tax for AY 2018-19 or FY 2017-18
- What Tax Deductions are available?
- Deduction refers to the amount that you can reduce from your taxable income.
- It means understanding alphanumeric combinations like Section 80C and 80DD. Our article Tax saving options : 80C,80CCC,80CCD,80D,80U,80E,24 discusses these Tax Deductions in Detail.
- In Budget Speech of 2015 Finance Minister Arun Jaitely had said that an Individual Taxpayers enjoys tax deductions of up to Rs.4.44 lakh a year. But if If we add all the tax deductions available under section 80C to 80U plus other allowances and tax-free reimbursements, the tax deductions sum up to Rs.10.22 lakhs.
- Maximum Tax Benefit one can get is ₹63,345 on investment of ₹ 2,05,000 at the highest tax slab rate of 30.90% under Income Tax Act, 1961, assuming that the total income is below ₹1 crore and is not subject to the applicable surcharge.
- Understanding the Tax saving options like PPF, Insurance, Health Insurance, Donations Articles like Choosing Tax Saving options : 80C and Others
- Understanding the returns
- Understanding the time period
- Understanding frequency of investment option
- Understanding any tax implications of stopping or on maturity.
- Understanding your risk profile.
- Choosing the option that suits you.
- Understanding TDS deducted
- Check TDS in Form 26AS
- Fill Form 15G/15H
- Submitting the proofs to the employer
- Keeping the document proofs safely
- Claiming tax deductions while filing income tax return (explained in detail in e Filling ITR-1)
An Example of Saving Tax is as follows:
- Let us assume that your taxable income is Rs. 5.5 lakhs that means that your total tax liability is Rs. 35,000.
- If you submit medical bills worth Rs. 12,000 as a part of your medical allowance. Your taxable income becomes Rs. 5.38 lakhs and Tax liability Rs. 32,600.
- If you claim House rent allowance deductions of Rs. 83,000 then taxable income comes down to down to Rs. 4. 55 lakhs which means that the new tax you have to pay is just Rs. 18,500
- Now if you invest Rs. 30,000 in tax saving option (PPF, Life Insurance ) etc your taxable income comes down to Rs. 4.25 lakhs (4,50,000 – 30,000). This means that now the tax you have to pay is Rs. 15,500 which is less than half of 35,500.
Following image shows the Income Tax Flow.
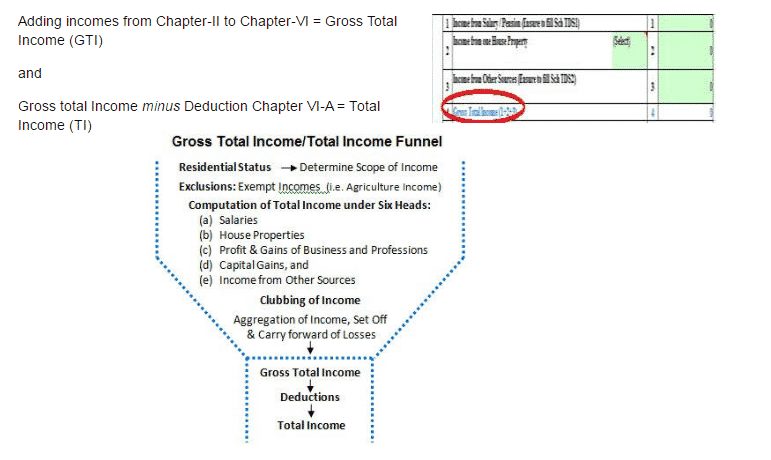
Income Tax
Assessment Year is a twelve months period starting from April 1 of the previous year to March 31 immediately following the previous year. In the Assessment Year, the return is filed for the income earned in the previous year, for e.g. for Financial Year 2016-17, the Assessment Year is 2016-17.
- Understanding Income Tax Slabs,Tax Slabs History
- Income Tax for AY 2018-19 or FY 2017-18
- How to Calculate Income Tax
- Examples of Income Tax Calculation
Salaried Employee and Income Tax Savings
Your Take-home salary will include
- Gross Salary received each month
- minus allowable exemptions such as HRA, LTA, conveyance allowance etc.
- minus income taxes payable (calculated after considering Section 80 deductions)
Articles to help a Salaried Employee understand parts releated to Tax Savings.
Typically 12% of the Basic, DA, and cash value of food allowances has to be contributed to the EPF account of employee. Employee’s contribution is matched by Employer’s contribution(till 12%). The employer contribution is exempt from tax and employee’s contribution is taxable but eligible for deduction under section 80C of Income-tax Act. The EPF amount earns interest as declared by Government.
- Basics of Employee Provident Fund: EPF, EPS, EDLIS
- HRA
- LTA:
- What is Leave Travel Allowance or LTA
- How to claim LTA
- Tax Exempt Allowances in Salary Schedule S in ITR2
- Medical Allowance
Income Tax Proof Submission to the Employer
During December or January, employers start asking employees to submit documentary proofs of investments and expenses that qualify for tax deduction and exemption under various sections of Income tax Act, 1961. This is in respect of the investment declaration made by the employee at the beginning of the financial year, to the employer. Income Tax Proof Submission to the Employer discusses it in detail.
Income Tax Deductions
- Deduction refers to the amount that you can deduct from your taxable income.
- It means understanding alphanumeric combinations like Section 80C and 80DD. Our article Tax saving options : 80C,80CCC,80CCD,80D,80U,80E,24 discusses these Tax Deductions in detail.
- The table below gives an overview of the various Tax Saving Deduction Sections such as 80C, 80D.
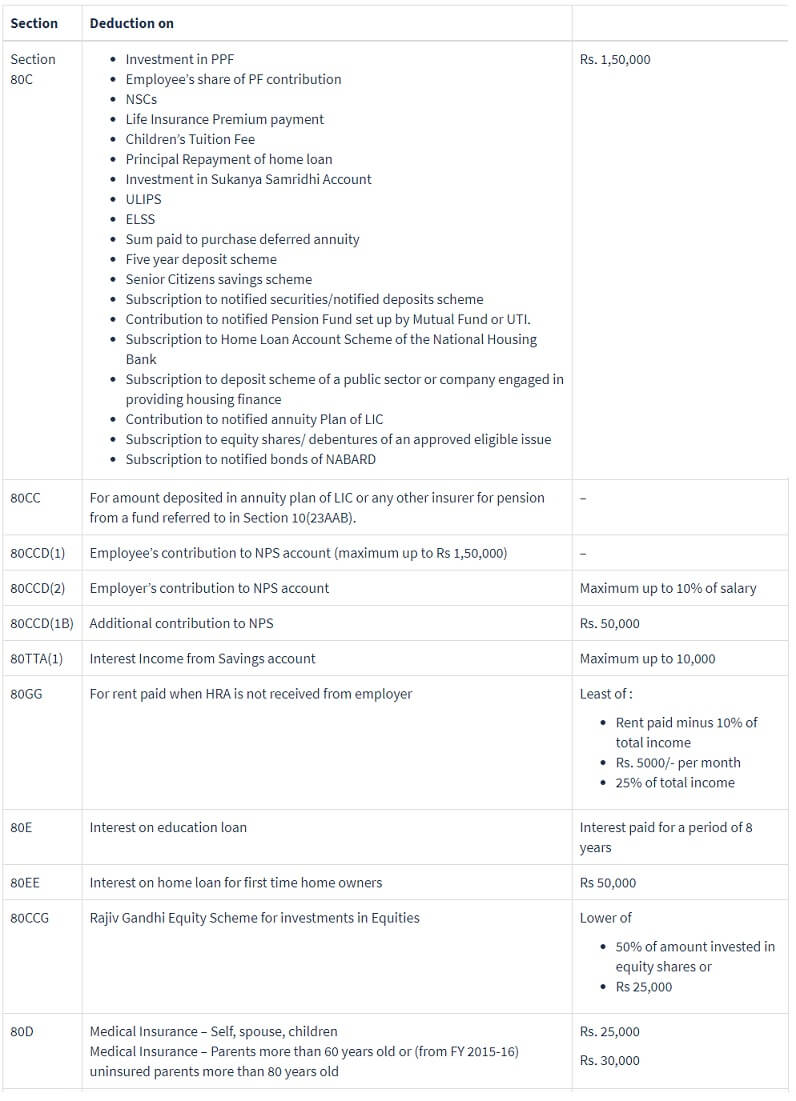
Tax Saving Options
ELSS
Equity Linked Saving Scheme or ELSS Mutual funds offer a choice to investors of providing equity exposure along with tax deduction benefit under Section 80C but come with a three year lock-in. These funds are an alternative to other tax saving instruments like NSC, PPF and fixed deposits.
Understanding ELSS Funds or Equity Linked Saving Schemes
NPS
The New Pension System has generated a lot of interest ever since Budget 2015 announced additional tax benefits for investments in the scheme. For someone in the 30 per cent tax bracket, this is a clear benefit of Rs 15,000 on investment of Rs 50,000 over and above the Rs 1.5 lakh allowed under Section 80 C.
- Understanding National Pension Scheme – NPS
- eNPS : Open NPS account online, contribute to NPS online
- NPS Tax Benefits and sections 80CCD(1), 80CCD(2) and 80CCD(1B)
- Should you Invest in NPS the National Pension Scheme for additional 50,000 and save tax
Public Provident Fund PPF
- Understanding Public Provident Fund, PPF
- Voluntary Provident Fund, Difference between EPF and PPF
- On Maturity of PPF account
- PPF Account for Minor and Self
- How to Deposit in PPF amount
- How to Close PPF account Before Maturity
- How to activate Dormant PPF account?
- Transferring PPF account
- PPF Partial Withdrawals
- Filling ITR-1 : Bank Details, Exempt Income, TDS Details
- Premature closure of PPF
- How to take Loan from PPF
- How to nominate: Demat Account and PPF
- On Death of PPF account holder: How to Claim using Form G
Tax Saving Fixed Deposits
Life Insurance and Tax Savings
Premiums paid towards these insurance plans buys you protection . What’s more – you can also get tax benefits on the maturity amount/returns from insurance plans. For employees Jan-Feb is season of submitting income tax proof. Many people buy insurance policy, in a hurry, to save tax and submit the proof to employer. Buying an insurance policy is a long time commitment, similar to marriage. So It is advisable to understand all aspects of claiming tax benefit in buying insurance policy
- Before Buying Insurance Policy to Save Income Tax
- Insurance : Surrender or Make policy paid up or Continue
- Mis-Selling or Mis-Buying: It’s My Money, My Responsibility
- Personal Finance and Scott Adams,Dilbert
- Mixing Insurance with Investment
Choosing Tax Saving Options
- Choosing Tax Saving options : 80C and Others
- How to Save Tax
- Five Best Tax Saving Options In Financial Year 2016-17
TDS Deducted
It requires that the person, upon whom responsibility has been cast, is to deduct tax at the appropriate rates, from payments of specific nature which are being made by him to a specified recipient. The deducted sum is required to be deposited to the credit of the Central Government. The recipient from whose income tax has been deducted at source, gets the credit of the amount deducted in his personal assessment on the basis of the certificate issued by the deductor.
- Basics of Tax Deducted at Source or TDS
- Avoid TDS : Form 15G or Form 15H
- How to Fill Form 15G? How to Fill Form 15H?
- Viewing Form 26AS on TRACES
- What to Verify in Form 26AS?
- Filling ITR-1 : Bank Details, Exempt Income, TDS Details
Tax-planning exercise should not be a random, out of blue kind of activity. Last minute tax planning should be avoided as much as possible (how many of us have regretted the life insurance policy we tool just to submit the tax proof).

16 responses to “All About Income Tax Savings: sections 80C,80D, claim in ITR”
The Stamp duty & registration charges and other expenses which are directly related to the transfer are allowed as a deduction under Section 80C.
Daily Capital Market DoseThe maximum deduction amount allowed under this section is Rs.1,50,000. 80C includes EPF,Life insurance premium etc.
It is great article. Keep posting these type of article. This is very informative and helpful information post. thank you for sharing wonderful article it helps a lot.
This is very attention-grabbing, You’re an excessively professional blogger.
I’ve joined your feed and sit up for searching for more of your great post.
Additionally, I have shared your web site in my social networks
I found your article very informative and I totally love how the concepts are explained in this blog post. Thanks for sharing your insights. It helps a lot.
Dear Sir,
Property registry/stamp duty charges is exempted or not? Please confirm.if exempted then in which section we can get benifit and how much limit for it.
Stamp duty & registration charges and other expenses which are directly related to the transfer are allowed as a deduction under Section 80C. The maximum deduction amount allowed under this section is Rs.1,50,000.
80C includes EPF,Life insurance premium etc.
Hi, I am working in IT with 30% tax bracket. Also, doing software consultation in India and US. Getting paid from the US in Dollars and India in Rupees. Q1. How should I pay my taxes?
For my consultation work one of my client deducting the tax at 10%.
Q2. Can I have two tax deductions from two companies?
Thank you for the help.
Yes you can have more than 1 deduction from different companies.
Income received from consultancy is termed as income from profits and gains of business or profession whereas income from employment is termed as salary income.
So your income is taxable.
Every person who is a resident of India must pay taxes in India on his or her global income. A resident of India is defined as a person who has been in India for a period of 182 days or more in the financial year or who has been in India for 60 days or more in a financial year and 365 days or more in the 4 years before that financial year (section 6).
Broadly, taxability in India depends on the following factors:
►* Source of income
►* Residential status
Typically, the source of income lies where the services are performed, or where the asset from which the income arises is located.
Any income, the source of which is located in India, is taxable in India (irrespective of residential status).
Residential status is dynamic and is required to be determined for each financial year (FY) (1 April to 31 March). Residential status is determined on the basis of physical presence of an individual in India during the relevant financial year and last 10 financial years.
How to show income from consultancy
A salaried employee is not required to maintain books of account or get his or her accounts audited by a chartered accountant (CA). In fact, employers maintain the income records for their salaried employees in the form of Form 16 which contains details like salary received, exemptions, deductions, tax paid and payable etc. Specified professionals – such as lawyers, doctors, engineers, architects and other professionals – whose income or the gross receipts exceed the specified amount, maintenance of regular books of accounts along with a record of the work-related expenses is mandatory. These records and the books of account need to be maintained for 4-6 years after filing the return. Moreover, consultants, whose gross receipts from consultancy income exceeds Rs. 25 lakh, are required to get their accounts audited by a chartered accountant.
Benefits under new Section 44ADA of Income Tax Act
The Finance Bill, 2016 has provided for a special provision for computing profits and gains of the profession on the presumptive basis with effect from April 1, 2017. A consultant can opt for this scheme if his or her total receipts in one financial year are Rs. 50 lakh or less. By opting for this scheme, their taxable income will reduce to half, which is not possible in case of salaried individuals. This scheme will reduce their compliance burden, and they will not be required to keep detailed accounting records. Consultants can file income tax return form ITR-4 (old ITR-4S) – which is a much simpler form – instead of ITR-3 (old ITR-4) – which is a relatively bulky form.
A consultant, however, needs to pay advance taxes.
If i deposit amount Rs 400000 for FD at interest 7% for only 3 month only and interest will be Rs 7000 for 3 month at maturity. Then tds will be deducted. Please inform me. It is very important for me.
If i deposit amount Rs 400000 for FD at interest 7% for only 3 month only and interest will be Rs 7000 for 3 month at maturity. Tds will be deducted. Please inform me. It is very important for me.
Sir,
If i deposit amount Rs 400000 for FD at interest 7% for only 3 month only and interest will be Rs 7000 for 3 month at maturity. Then tds will be deductd. Please inform me. It is very important for me.
Sir,
If i deposit amount Rs 400000 for FD at interest 7% for only 3 month only and interest will be Rs 7000 for 3 month at maturity. it will be taxable. Please inform me. It is very important for me.
Hi. I would like to ask a few questions related to tax on fixed deposits, cash gifts, mutual funds. How n where do i post my questions? Your blog is informative and good.
Thanks Archana for kind words.
You can post it here
or email us at bemoneyaware@gmail.com
Hi ,
My pf withdrawal uan forms returned from epo vashi office with update that “With ref. to the griev. it is informed that your UAN based claim received in this but same return to your address due to UAN more than one member ID”.how to remove member id that are not active and transfer done.
I actually added your blog to my favorites and will look forward for more updates. Great Job, Keep it up. First of all let me tell you, you have got a great blog .I am interested in looking for more of such topics and would like to have further information. Hope to see the next blog soon.