This article focuses on Senior Citizen and Income Tax, their sources of income, tax deductions exemptions, their tax slabs. TDS and Form 15H, filing of the income tax return. Does Senior Citizen have to pay advance tax? Scrutiny and Senior Citizen.
As per Budget 2021, applicable from FY 2021-22(i.e from 1 Apr 2021), the senior citizens will be exempted from filing income tax returns if pension income and interest income are their only annual income source. Section 194P has been newly inserted to enforce the banks to deduct tax on senior citizens more than 75 years of age who have a pension and interest income from the bank.
Table of Contents
Who is Senior Citizen?
Who is a senior citizen?
From Income tax perspective there are two categories of Senior Citizens given below.
- Senior Citizen: For age of 60-80 years
- Very Senior Citizen: Above 80 years
This has come into effect from FY 2012-13 was suggested in Budget 2011-12. Before FY 2012-13 age limit to be considered a senior citizen was 65 Years.
Under the Income Tax Act, a senior citizen is a person who at any time during the previous year has attained the age of 60 years or more i.e for a person who is of age 60 but less than 80 years on end date of financial year (for 2016-17 is 31-Mar-2017) will be considered as senior citizen for that Financial Year. So
- A person who is of age between 60-80 years on 31st Mar 2017(including 31st Mar) will be considered as Senior Citizen for FY 2016-17 or Assessment Year 2017-18.
- A person who is above 80 years on 31st Mar 2017(including 31st Mar) will be considered as Senior Citizen for FY 2016-17 or Assessment Year 2017-18.
According to Income Tax Act, 1961, those who on last day of financial year (for 2016-17 is 31-Mar-2017) , have attained 60 years of age belong to the Senior citizen category and those aged 80 or more belong to the Very senior citizen category. These definitions apply ONLY to Resident individuals and not to those who qualify as non-resident in any tax year.
How is the age calculated for senior citizen?
On the last day of the financial year if the person is 60 years of age then he/she will be treated as Senior Citizen. So for FY 2016-17(Assessment Year 2016-17) if person is 60 years old on 31.03.2017, i.e date of birth is 31-Mar-57 or before he/she will be treated as a senior citizen. Similarly for very senior citizen age should be 80 years on last day of the financial year.
Income Tax and Senior Citizens
What are the tax slabs for senior citizens?
The age for Senior Citizen(and Very Senior Citizen) and the various tax slabs are announced in Budget every year. Income Tax for AY 2017-18 or FY 2016-17 isare as follows.( Our article Understanding Income Tax Slabs,Tax Slabs History discusses Tax slabs etc in detail) Income Tax for AY 2017-18 or FY 2016-17
| AX | MEN and WOMEN below 60 years | SENIOR CITIZEN(Between 60 yrs to 80 yrs) | For Very Senior Citizens(Above 80 years) |
| Basic Exemption | 250000 | 300000 | 500000 |
| 10% tax | 250001 to 500000 | 300001 to 500000 | – |
| 20% tax | 500001 to 1000000 | 500001 to 1000000 | 500001 to 1000000 |
| 30% tax | above 1000000 | above 1000000 | above 1000000 |
| Surcharge | 15% of the Income Tax, where total taxable income is more than Rs. 1 crore | ||
| Education Cess | 3% on Income-tax plus Surcharge. | ||
What are deductions available to Senior Citizen?
Deductions under 80C up to limit of 1.5 lakh are available to Senior Citizen just like any other resident individual. This includes Life insurance premium, contribution to Public Provident Fund or Provident Fund, Investment in Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS) of mutual funds, Home loan principal repayment, National Savings Certificates, Fixed deposit with any scheduled bank or post office for 5 years, Senior citizens savings scheme etc.
What are the exemptions provided to senior citizen?
In terms of healthcare, the Income Act provides for higher tax relief for senior citizens on their medical expenditure. The relief is available against actual expenditure on health insurance premiums up to Rs 30,000 under Sections 80D and on expenditure up to Rs 60,000 on medical treatment for specific diseases under Sections 80DDB of the Income Tac Act.
TDS and Senior Citizen
What is Form 15H?
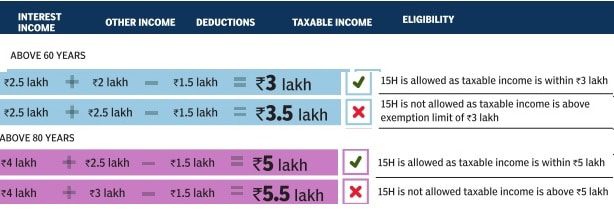
Senior citizens can file Form 15H to prevent banks, post office etc from deducting tax at source on the interests payable on their money if their estimated taxable income for the financial year is less than the basic exemption limit. Our article Avoid TDS : Form 15G or Form 15H discusses it in detail.
Advance Tax and Senior Citizens
Do Senior Citizens have to pay Advance Tax?
According to a provision inserted by the Finance Act, 2012, a resident senior citizen, who does not have any income from a business, would be exempted from the payment of advance tax. Advance tax is normally payable if the tax on one’s income is more than Rs 10,000 on what is deductible at source. In that case, the advance tax has to be paid in three installments during a year, failing which, one suffers interest on the defaulted amount. However, senior citizens are relieved of this burden by virtue of the above provision. They can compute their tax liability after the close of a tax year and deposit the same before filing their tax returns. They can pay the exact tax as is liable, instead of paying first and then claiming tax refund later.
Income and Senior Citizens
What are Sources of Income for Senior Citizen?
Senior citizens largely depend on passive sources of income, such as pensions, fixed deposits,Rental incomes of house properties, Senior Citizen Saving Scheme,Post office scheme, interest on savings, Reverse Mortgage etc.
Senior Citizen Tax and Pension
As per Section 17 (1) (ii) of the Income Tax Act, 1961 pension is a payment made by the employer as a reward for past service to employee. If it is paid to wife/children of the employee after the death of employee it is called Family Pension. The Pension is normally paid a periodical payment on a monthly basis which is fully taxable, under the head Income from Salary, in the hand of the employee, whether Government employee or non-government employee. The pension may be fully or partly commuted. i.e. in lieu of pension a lump sum payment is made to the employee.
The pension may be fully or partly commuted. i.e. in lieu of pension a lump sum payment is made to the employee. Example At the time of retirement, you may choose to receive a certain % of your pension in advance. Such pension received in advance is called commuted pension. For e.g. – At the age of 60, you decide to receive in advance 10% of your monthly pension of the next 10 years of Rs 10,000. This will be paid to you as a lump sum. Therefore, Rs 10% of 10000x12x10 = 1,20,000 is your commuted pension. You will continue to receive Rs 9,000 (your uncommuted pension) for the next 10 years until you are 70 and post 70 years of age, you will be paid your full pension of Rs 10,000.
The treatment of the two kind of pensions is as follows:
- Uncommutted Pension : Periodical pension fully taxable in the hand of the employee, whether Government employee or non government employee.
- Commuted Pension : Exemption under section 10 (10 A)
Tax and Senior Citizen Savings Scheme (SCSS)
It’s a government backed scheme which provides an assured 9%(around) return paid every quarter to senior citizens. Our article Senior Citizen Savings Scheme, SCSS discusses Senior Citizen Scheme in detail. Tax on Investing in Senior Citizen Scheme are as follows:
- The sum invested in the SCSS on or after April 1, 2008 is eligible for tax deduction under section 80C of the Income Tax Act. It is one-time deduction that one can claim in the year in which one invested in Senior Citizen Scheme
- However, the interest earned on the deposit is fully taxable and tax is deducted at source (TDS) only if the total interest in a year is above Rs 5,000.However, if the income is not taxable, one has to provide form 15H so that no tax is deducted at source.
Senior Citizens, Fixed Deposits, and Tax
Banks offer a higher rate of interest on fixed deposits to senior citizens. The offering is 0.25-0.75% more than the prevalent interest rates. Other than that Fixed Deposit is similar for Senior and other citizens. Our article Senior Citizen,Fixed Deposits and Tax discusses it in detail.
- Tax or TDS is deducted by the bank, if the aggregate interest income from fixed deposits that you are likely to earn for all your deposits held in a branch is greater than Rs 10,000 in a financial year. If Bank deducts TDS then bank would give you FORM 16A and it would also come up in FORM 26AS.
- Whether TDS is deducted or not interest in Fixed Deposit is taxable ,
- Form 15H is a declaration made by senior citizen for Bank to not deduct tax.
- Tax on FD is calculated by adding interest income from FD as income from other sources to your salary etc and then tax is calculated as per your income slab.
Tax and Rental Income from House Properties?
It is treated in the same way as for a non-senior citizen. The first property that one buys is exempt from income tax, but only if it is not let out on rent. A notional rent value based on the market rental value will be adopted as taxable income from second property onwards, even if it’s kept under lock and key. So even if you earn no income whatsoever from the second property, it will be taxable as if you have put it out on rent. There are two types of tax deductions available on income from property apart from the actual municipal taxes paid given below. Our article Tax : Income From House Property, Tax and Income from Let out House Property discusses it with examples.
- The first is standard deduction of 30%. This means 30% of the rental income can be reduced as a standard deduction for repairs, maintenance etc. irrespective of the actual amount spent, if at all, during the financial year.
- The second deduction is to do with interest on mortgage finance if the property is purchased on mortgage or loan. For rented properties, the entire amount of interest payable can be adjusted against the rent and any amount that is left over may be carried forward in the tax return as loss from property to the next year.
Senior Citizen, Tax and Reverse Mortgage
Reverse mortgage enables a person to generate monthly income streams by mortgaging his or her house, subject to certain conditions. According to the scheme, senior citizens have to approach a scheduled bank or a housing finance company registered with the National Housing Bank or any class of institution notified by the Government of India. The amount of loan given by a bank against the mortgaged property will depend on factors such as market valuation and life of the property. The cash flow facility is available for a maximum period of 20 years. After the end of the loan tenure, senior citizens can either continue living in the house for their lifetime, or take back the possession of the property by paying off the loan.
From the tax perspective, the monthly cash stream of senior citizens opting for a reverse mortgage is exempted from tax under sub-section (43) of Section 10 from the Assessment year 2008-09. Also, the transaction at the time of mortgaging the house under reverse mortgage scheme is not regarded as transfer under the Act. Therefore, the transaction does not attract any capital gains tax under clause (xvi) in Section 47 from the Assessment year 2008-09.
Senior Citizen and tax on investment options like Mutual Funds, Shares
It is treated in the same way as for a non-senior citizen.
Filing ITR
From the assessment year 2015-16 onwards any taxpayer filing return of income in Form ITR 1/2/2A and having a refund claim in the return or having total income of more than Rs. 5,00,000 is required to furnish the return of income electronically with or without digital signature or by using electronic verification code. However, Income-tax Law grants relaxation from e-filing in above case to very senior citizen.
In other words, a very senior citizen filing his return of income in Form ITR 1/2/2A and having total income of more than Rs. 5,00,000 or having a refund claim can file his return of income in paper mode, i.e., for him e-filing of ITR 1/2/2A (as the case may be) is not mandatory. However, he may go for e-filing if he wishes.
Is Filing of Income Tax Return different for Senior Citizen?
The process for filing of income tax return is same as citizen less than 60 years of age. Other than exemption limit there is no change in Income under various heads, type of ITR form to fil. l So if your income in year is above 5 lakhs you need to e-File your return. If TDS has been deducted (at times even after submitted Form 15H), only way to reclaim is to ask for refund while filing the income tax return. Our article Fill Excel ITR1 Form : Income, TDS, Advance Tax discusses it in detail.
Can there be Scrutiny of Income Tax Return For Senior Citizen?
The Central Board of Direct Taxes has instructed the field officers that cases of senior citizens should not be selected for scrutiny unless there is credible information that warrants such assessment.
Example of Income Tax Calculation for Senior Citizen
Shyam, who is 63 years old, had the following details in respect of her income during the financial year 2016-17. Calculate his tax liability?
- Rental income from house property Rs. 1,00,000
- Income from Pension Rs 3,50,000
- Interest from fixed deposits Rs. 1,00,000
- Interest from PPF account Rs 30,000
- Amount deposited in PPF account Rs. 1,50,000
- Medical insurance premium paid Rs. 22,000
- House tax paid Rs. 10,000
- TDS deducted on Fixed Deposit Rs.10,000
COMPUTATION OF TAXABLE INCOME for Senior Citizen
Income from Salary: 3,50,000
Income from House property
- Rental Income from house property Rs.100000
- Less: House Tax Rs.10000
- Annual value Rs 90,000
- Less: Standard deduction u/s 24 @ 30% Rs. 27,000
- Net income from rent Rs 63,000
Income from other sources
- Interest from fixed deposits Rs.100000
Gross total income Rs 5,13,000
Deduction under chapter VI-A
- Under Section 80C Deposits with PPF Rs.1,50,000
- Under Section 80D Medical Insurance Premium paid Rs.22,000
- Total Deductions from Taxable Income Rs 172000
Total taxable income 3,41,000
- Tax payable on income 4100
- Less: Tax Credit 2000
- (Available only to Individual Resident assessees having total taxable income upto Rs. 5 lacs)
- Total Tax Rs 2100
- Add: Education Cess @3% 63
- Total Tax Liability Rs 2163.
- Less : TDS 10,000 (for interest from FD)
- Net Refund due Rs 7837
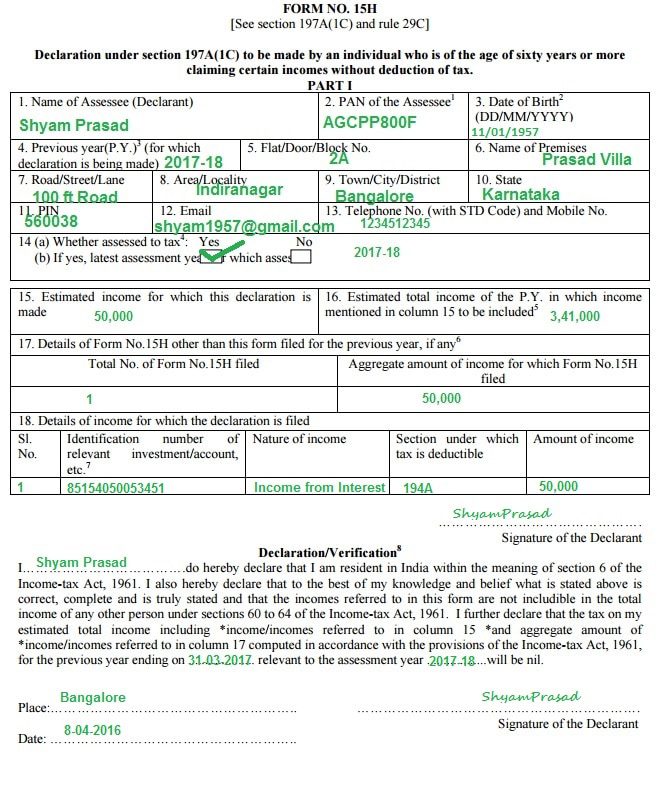
To avoid refund, Shyam should submit for 15H to the bank to not deduct TDS. If Shyam has 2 FD earning 50,000 as interest from bank then he has to submit Form 15H to each bank so that no TDS is deducted. Sample Form 15H is shown below.
Related Articles:
- Senior Citizen,Fixed Deposits and Tax
- Tax : Income From House Property
- Avoid TDS : Form 15G or Form 15H
- Fill Excel ITR form : Personal Information,Filing Status

17 responses to “Senior Citizen : Income and Tax”
Is the amount received of Rs.5000/ p.m.,by parents (senior citizens) from children for maintenance as awarded under Sr. Citizens Act. 2007, taxable in the hands of parents?
Amount received from children is not taxable in hands of parents
Sir my father retired on march 2014.He is receiving pension 18440*12=221280 /annum.
He has 3 fixed deposits in bank yielding interest=167176 on which TDS is continuously deducted since 2014.No form 15H has been filed.Even Pan card is not updated on his account.
Now i want to know that can he file form 16 for ITR.
He has not filed ITR or paid any tax(except TDS) in last two years. Is there any process to get return of tax paid for 2 years.
How do I obtain TDS amount deducted for SCSS scheme of Post Office as the TDS amount is not reflected in the Post Office Savings account Pass Book. Thank you.
Sir,
I am 65 year old retired govt. employee and pensioner. I have annual income of more than 4.5 lacs from pension and other sources. I have invested in Sr.Citizen Saving Scheme for getting benefit of income tax rebate under section 80C. Is it right option? How I will show the invested amount for rebate under section 80C in online return ITR-1(Sahaj).
my pension is 490000 plus intrest of rs 1310000/- how much i have to pay income tax
Sir your income is
Income from Pension : 4.9 lakh
Interest (which I assume is from FD): 13.1 lakh
Total income : 18 lakh
Questions:
Are you between 60-80 or above 80. – this decides the basic exemption limit
Is your entire interest taxable or some is tax free
Is TDS deducted or not.
Useful information contained in the article. Well written in simple and lucid language.
Useful information contained in the article. Well written in simple and lucid language.
This is great info for senior citizens many of whom don’t know the intricacies of Income Tax. Thanks for sharing.
This is great info for senior citizens many of whom don’t know the intricacies of Income Tax. Thanks for sharing.
Nice and Informative not only helpful to senior citizens but also to others
Nice and Informative not only helpful to senior citizens but also to others
extremely helpful post !
extremely helpful post !
Sir my father retired on march 2014.He is receiving pension 18440*12=221280 /annum.
He has 3 fixed deposits in bank yielding interest=167176 on which TDS is continuously deducted since 2014.No form 15H has been filed.Even Pan card is not updated on his account.
Now i want to know that can he file form 16 for ITR.
He has not filed ITR or paid any tax(except TDS) in last two years. Is there any process to get return of tax paid for 2 years.
You need to update PAN details with bank first.
If excess TDS has been deducted by the bank, here are the steps you need to take to correct the situation:
First note that only the I-T Department can give you a refund on excess TDS, not the bank. This is because the bank has already deposited your TDS with the government.
So reach out to the bank and request them to update their records with your PAN details.
Inform the bank about the discrepancy in TDS deduction and request them to revise the TDS return they submitted. Anyone who deducts TDS has to submit a TDS Return of all the TDS deducted by them and that is how this information reaches your Form 26AS. When they revise their TDS return and include your PAN details, this TDS will then get reflected in your Form 26AS correctly.
Once this TDS is reflected in your return, you can adjust it from your final tax liability if any. You may also end up with a refund due from the government if you did not have any tax payable.