This article provides Income Tax Overview and how to file Income Tax Returns. The filing of income tax return is a legal obligation of every person whose total income and wealth tax during the previous year exceeds the maximum amount which is not chargeable to income tax under the provisions of I.T. Act, 1961. Under the Income tax Act every person has the responsibility to correctly compute and pay his due taxes.The return should be furnished in the prescribed form on or before the due date(s).
Income tax assessment comprises of following stages:
- Computation of total income.
- Deducting valid deductions.
- Determination of the tax payable thereon.
- Paying the tax.
- Filling Income Tax Return Form.
The income tax returns need to filed every year. Each year there are some modifications. The financial year is not the same as calendar year. So let’s start with some definition of Financial Year , Previous Year, Assessment Year
Financial Year, Previous Year, Assessment Year
Calendar year starts on January 1 and ends on December 31 but a Financial year (FY) is from April 1 to March 31. As per the Income Tax Act, income earned in a financial year (FY) is taxed in the next Financial Year. FY to which the income belongs is called the Previous year (PY) and the FY in which the income is taxed is called the Assessment year (AY).
| Income Earned Between | FY | AY | Due Date for filing ITR | Last date for filing ITR | Notes |
| 1 Apr 2019 to 31 Mar 2020 | FY 2019-20 | AY 2020-21 | 31 Jul 2020 | 31 Mar 2021 | Current Financial Year. Advance Tax to be paid |
| 1 Apr 2018 to 31 Mar 2019 | FY 2018-19 | AY 2019-20 | 31 Jul 2019 | 31 Mar 2020 | ITR to be filed |
| 1 Apr 2017 to 31 Mar 2018 | FY 2017-28 | AY 2018-29 | 31 Aug 2018 | 31 Mar 2019 | Cannot file ITR. |
Our article What is Financial Year and Assessment Year, Difference, ITR, Fiscal Year of World covers it in detail
Table of Contents
Important Tax Dates For Individual for Income Tax
| Date | What to do |
| 31st July | Submission of return of income for individuals for PV |
| 15th Jun | 1st installment of advance tax for individuals for current FY |
| 15th Sept | 2nd installment of advance tax for individuals for current FY |
| 15th Dec | 3rd installment of advance tax for individuals for current FY |
| 15th March | 4th installment of advance tax for individuals for current FY |
- If there is no pending tax to be paid, you may file your return without paying any penalty by 31 March of that Assessment Year.
- But if you still have a tax liability, you will have to pay monthly penal interest on the tax due if you file your return by 31 March of Assessment Year.
- You can revise your form to correct any mistake or deletions, by 31 March of Assessment Year.
- If you have incurred losses on shares during the year, you will be able to carry forward the losses for future tax set-off only if you file the return within the deadline.
Income Tax Slabs
For the Financial year 2018-19 or Assessment Year 2019-20
| TAX | MEN and WOMEN | SENIOR CITIZEN(Between 60 yrs to 80 yrs) | For Very Senior Citizens(Above 80 years) |
| Basic Exemption | 250000 | 300000 | 500000 |
| 5% tax | 250001 to 500000 | 300001 to 500000 | – |
| 20% tax | 500001 to 1000000 | 500001 to 1000000 | 500001 to 1000000 |
| 30% tax | above 1000000 | above 1000000 | above 1000000 |
| Surcharge | 10% of tax where total income exceeds Rs. 50 lakh
15% of tax where total income exceeds Rs. 1 crore |
||
| Education Cess | Health & Education cess: 4% of tax plus surcharge | ||
For income tax rates of earlier years checkout our Income Tax rates Since AY 1992-1993
What is Total Income in Income Tax
The gross total income is the sum of all sources of income that an individual has or the total income he earns in a financial year. It can fall into one of the five heads:
1. Income from Salary:
2. Income from House Property: Any residential or commercial property that you own will be taxed. Even if your piece of real estate is not let out, it might be considered earning rental income and you will need to pay tax on it. If you have taken a home loan, then claiming Interest on Loan also comes under this category. Our article Tax and Income from House property discuss it in detail.
3. Income from Profits and Gains of Business or Profession: Income earned through your profession or business is charged under the head ‘profits and gains of business or profession.’ The income chargeable to tax is the difference between the credits received on running the business and expenses incurred
4. Income from Capital Gains: Any profit or gain arising from the sale of a capital asset held as investments are chargeable to tax under the head capital gains. The gain can be on account or short- and long-term gains.
- Capital Gain Calculator from FY 2017-18 with CII from 2001-2002
- How to Calculate Capital gain Tax on Sale of House or property?
- Short Term Capital Gains of Debt Mutual Funds, Tax, ITR
- Long term Capital Gains of Debt Mutual Funds, Tax and ITR
- Budget 2018: Long Term Capital Gain on Stocks & Equity Mutual Funds
5. Income from other Sources
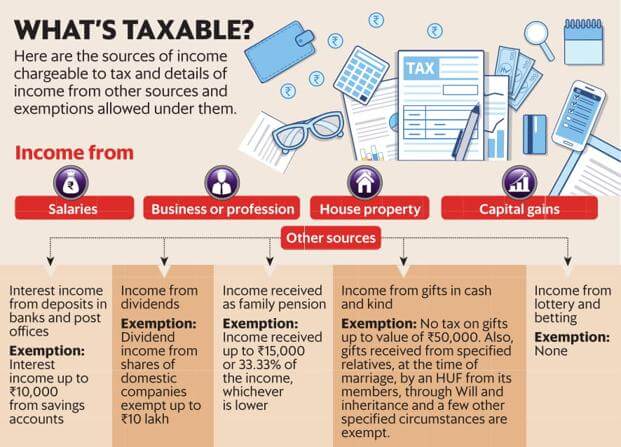
Tax Deductions
Tax Deduction is a legal way to reduce the income hence the tax that one needs to pay. One can claim the reduction under different heads given in table below.
| Code | Maximum Limit | Schemes | |
| 80C | 1.5 lakh |
This section has been introduced by the Finance Act, 2005. |
|
| 80CCC | 1.5 lakh | Payment of premium for annunity plan of LIC or any other insurer.The Finance Act 2006 has enhanced the ceiling of deduction under Section 80CCC from Rs.10,000 to Rs.1,00,000 with effect from 1.4.2007. | |
| 80CCD | 10% of his salary. | Deposit made by an employee in his pension account. | |
| 80CCF | Rs. 20,000. | Subscription to long term infrastructure bonds. Was for the financial year 2010-11 and 2011-12. However, the exemption is no longer present from financial year 2012-13. | |
| 80D | Rs 35,000.00
|
Premium in health insurance of you, your spouse, children or dependent parents | |
| 80DD | Rs. 50000.Rs. 75000 if disability is severe. | Medical treatment (including insurance) of disabled dependent. It includes(a) expenditure incurred on medical treatment, (including nursing), training and rehabilitation of handicapped dependant relative.(b) Payment or deposit to specified scheme for maintenance of dependant handicapped relative.W.e.f. 01.04.2004 the deduction under this section has been enhanced to Rs.50,000/-. Further, if the dependant is a person with severe disability a deduction of Rs.1,00,000/- shall be available under this section. | |
| 80DDB | Rs 40,000 andRs 60,000 for senior citizen. | Expenditure must be actually incurred by resident assessee on himself or dependent relative for medical treatment of specified disease or ailment. The diseases have been specified in Rule 11DD. A certificate in form 10 I is to be furnished by the assessee from a specialist working in a Government hospital. | |
| 80E | No Limit | Interest paid on educational loan taken for higher education of you, your spouse or children. | |
| 80G | 100% of donation amount for special funds50% of donation amount for all other donations. | Donation to certain funds, charitable institutions etc. | |
| 80GG | Rs. 2000 per month or 25% of your gross salary, whichever less. | House rent in excess of 10% of income, if no HRA is received. | |
| 80U | 1 lakh or Rs 1,00,000 | To an individual who suffers from a physical disability (including blindness) or mental retardation | |
| 80RRB | Rs. 3 lakhor the income received,whichever is less. |
Income by way of royalty in respect of a patent registered on or after 01.04.2003. | |
| 80 QQB | Royalty or copyright income received in consideration for authoring any book of literary, artistic or scientific nature other than text book | ||
| 24 | Rs. 1,50,000 | Interest paid on housing loan. |
Ref:Finotax:Deductions Allowable under various sections of Chapter VIA of Income Tax Act,NiftyPredictions:INDIA INCOME TAX ACT- TAX DEDUCTIONS, TAX EXEMPTIONS 80C 80D 80DD 80E 80GG 24 80G
Verify Tax Deducted at Source
Tax deducted at Source or TDS is a certain percentage deducted at the time of payments of various kind such as salary, commission, rent, interest on dividends etc and deducted amount is remitted to the Government account. This withheld amount can be adjusted against tax due. The person/organization deducting the tax is called as Deductor while the person from whom the tax is deducted is called Deductee.
Deductee can know his TDS details through online Form 26AS. Those who wish to view their TDS details can register their names with PAN no in Income Tax website or view it directly if they have bank account with selected banks. This helps to eliminate the mismatch and the above changes also help to avoid the mismatch in form 26AS and in Form 16A.The Tax Credit Statement or Form 26AS is generated when valid PAN has been reported in the TDS statements.
Basics of Tax Deducted at Source or TDS explains about TDS.
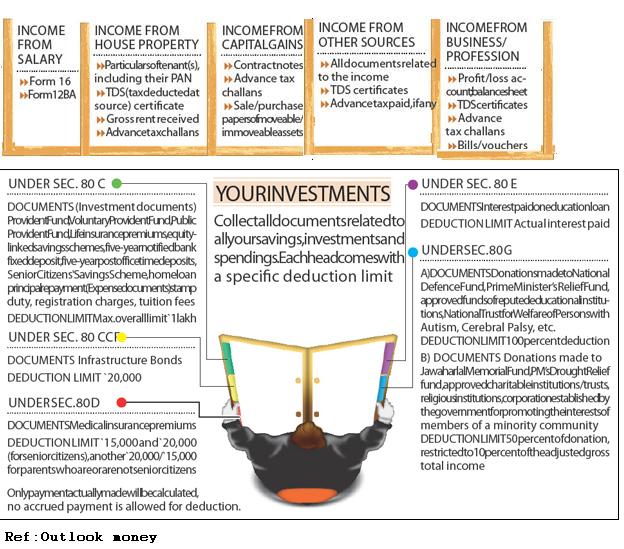
Documents needed for filing Income Tax
The various documents that one need for income tax calculation other than the bank account statements are as follows. Earlier the documents were attached with the income tax return form. The new return form are annexure less. Hence no documents need to be attached. But the financial records need to be kept for atleast 7 years. Paper Work A Necessary Headache (Dec 2011) is about the financial papers that need to be kept.
Calculation of Income Tax
The image below recaps the process of calculating income tax.
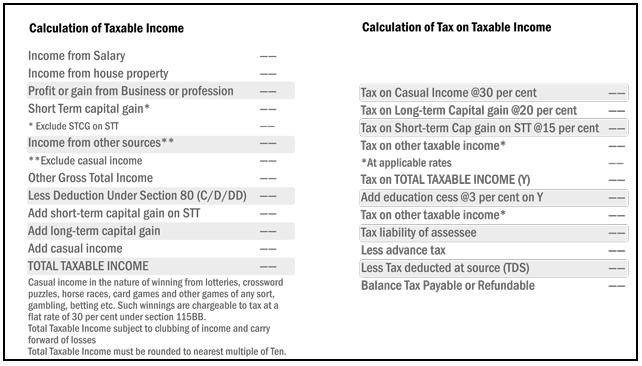
Some calculators that might help you are incometaxindia.gov.in Calculator to calculate tax liability based on Total income
Income Tax return (ITR) Forms
To file Income tax returns one needs to fill different Income Tax returns form which are : ITR-1 (Sahaj) ,ITR-2 ,ITR-3, ITR-4 and ITR-4S( Sugam). ITR-5 and ITR-6 can only be filed through e filing mode. These forms are released every year by Income Tax Department. Details of forms for individuals and Hindu Undivided Family (HUF) are as follows:
| Form | Category | Details |
| ITR-1 SAHAJ | Individual | 1. Income from salary/pension: or 2. Income from one house property(excluding where loss brought forward from previous year): or 3. Income from other sources( excluding winnings from lottery and income from races horses) |
| ITR-2 | Individual/HUF | Those who can not file Sahaj above as the total income also includes Income from Capital Gains. So sources of income become:1. Income from salary/pension: or 2. Income from one house property(excluding where loss brought forward from previous year): or 3. Income from other sources( excluding winnings from lottery and income from races horses) 4.Income from Capital Gains. They should not have Income from Business or Profession. |
| ITR-3 | Individual/HUF | Being partners in firms and not carrying out business or profession under any proprietorship. |
| ITR-4 | Individual/HUF | It is applicable for small businessmen and professionals covered under presumptive taxation. They derive business income which is computed in accordance with special provisions referred to in section 44AD and section 44AE of the Act. |
| ITR-4 | Individual/HUF | Carry out any business or professional activity in addition to having sources of income applicable to ITR-3 i.e Not covered in ITR 1 to 4S mentioned above and deriving income from a proprietory business or profession |
Forms for the year 2012-13 can be downloaded from Income tax website:NEW RETURN FORMS FOR ASSESSMENT YEAR 2012-13
Note: In a case where income of another person like spouse,minor child,etc.is to be clubbed with the assessee this return form can be used only if the income being clubbed falls in to above income categories
Where to pay Income Tax
If you have some tax to pay you can pay through
• Online deposit
• Nationalised banks
Challan No. ITNS 280 is used for payment of Income tax. It’s pdf from tin.nsdl website..
How to fill Income Tax Return
Computing and filing your I-T return could be done both offline and online.
Offline
- You could either hire a Chartered accountant(CA) who will do the entire groundwork as well as compute your tax liability, or
- you can do it yourself.
With CA you will provide the information required above. He will do the calculation, ask you to pay any extra tax amount due and sign on the relevant ITR form. The CA would also take care of the task of submitting the from to the income tax office concerned and provide you the acknowledgement. The CA may typically charge you anywhere between Rs. 200 and Rs. 3,000, depending on how varied your sources of income are and other factors such as complexity in calculating tax returns for ex: capital gains.
If you do it yourself then you would need to download the relevant ITR Form from www.incometaxindia.gov.in . Fill up the required details in the form, submit it at the ward concerned at the income-tax office and collect the acknowledgement.
Online
You can use Indian Govt tax e filing website which is free or non-govt e-filing websites such as taxspanner.com, taxshax.com, taxsmile.com and taxsum.com.
The non-government websites differ from each other on two counts, the number of income sources they cover and the process involved. They also have different packages, offers and discounts. Remember that when you file your returns online, you are sharing important personal financial details, such as your income, savings and investments, bank account details, and so on. So how should you choose a tax-filing portal?
- Check whether the portal provides the form that you want. While most offer ITR 1 and ITR 2, only few have the others.
- If the portal accounts for all the sections ex: Carrying forward losses from the previous years.
- Most important step is to go through the site’s security and privacy policy. You must check that the portal encrypts the saved and transmitted data and is protected from hackers.
To check the authenticity of the portal, you can access the list of E-Return intermediaries (ERI) Know your ERI on incometaxindiaefiling .gov.in Most portals usually charge a fee only when you have to submit the returns, so you can go through these and choose the one in which the user interface is the smoothest. A good portal will prompt you to fill up a slot you have missed or ask you to rectify a mistake . This reduces the chances of making errors. Image below compares some of the e-filing websites( Ref:OutlookMoney:Many Happy returns(Jul 2011))
Submission of ITR V form
In AY 2015-16 Income Tax Department introduced E-Verification of Income Tax Returns through which one could electronically verify the submitted ITR . If one electronically verifies ITR then one . Our article E-verification of Income Tax Returns and Generating EVC through Aadhaar, Net Banking explains the process in detail.
If you don’t want to verify E returns then you have to print the ITR V form and send it by post to the Central Processing Centre (CPC) Bangalore within 120 days of e-filing your return. The ITR V form should be printed in black ink only and signed personally in blue ink. It should not be folded and the bar code should be clearly visible. Dos and Dont’s for printing and submitting of ITR-Vs to ITD-CPC Bangalore Address of CPC Bangalore is:
Post Bag No.1, Electronic City Post Office, Bengaluru, Karnataka-560100
You can buy and use a Digital signature also. A digital signature authenticates electronic documents in a similar manner a handwritten signature authenticates printed documents. If you file electronically using digital signature you do not have to submit a physical copy of the return.incometaxindiaefiling.gov.in FAQ on Digital signature.
- incometaxindia.gov.in:FAQ
- IncomeTaxIndiagov.in
- Incometaxindiaefiling.gov.in
- OutlookMoney:Many Happy returns(Jul 2011)
Did the overview help? If we missed out anything please let us know.

20 responses to “Income Tax Overview”
Sir, I Am Getting Around 25K monthly from Internet Income in my Bank’s Saving Account.
Am i Eligible to pay IT ?
if yes , What procedure should i follow ?
Admin , Please tell me about this !
know the details about Income Tax Rebate u/s 87a, rebate u/s 87a, Rebate u/s 87a for FY 2017-18
get more details here
Rebate u/s 87a,
get the details about the Slab rates for FY 2016-17 the Income Tax surcharges/ Cess
For complete information click here
Tax slab rates
In the previous year,The income tax level is less compare currently year so
if the income is increase so the tax is also increase definitely.
Slr,
I am 84 years old pensioner from Central Govt, living in Bangalore. I have received an email from IT department recently. It says that they have information about my investing in Mutual Funds during 2013-14 onwards and also having Fixed deposits in Banks such as IDBI, Axis, SBI etc. They have asked me to take necessary action and submit my reply.
I am in consultation with a Chartered Accountant and given him details of Mutual Funds, Bank Accounts and Fixed Deposit details,now awaiting for a call from him.
I request you to let me know if I am proceeding in the proper direction as required by IT dept. You may please guide me as to how best I could complete this action to the satisfaction of IT department.
Thank you for the excellent write-ups.
Kindly explain the tax implications of CAPITAL GAINS/LOSSES on sale of these:
1) Reliance NCDs &
2) TAX FREE BONDS &
3) Debt/Liquid Funds.
Which is better & more tax friendly?
Please clarify/elaborate & oblige.
Very helpful Article for all income tax assessee and also for consultant like me
Nice posting please Try this also.
[…] Income Tax Overview […]
[…] Income Tax Overview […]
[…] Income Tax Overview […]
In the year 2006 I had deposited RS 10000/- in Pension scheme section 80ccc and had taken IT benefit.
Now The total amount is Rs 160000/-. I have not taken any IT benefit after the first installment.
If I withdraw how much tax i have to pay
a. On Rs 10000
b. Or on Rs 160000/-
I do npt want any pension.
Amit, What we understood was:
1) you have made regular investments in Pension scheme
2) you have only take IT benefit only once in 2006.
3) Now you don’t want pension.
What we haven’t understood was that have you completed all the payments required in pension scheme? If you could tell us the name of pension scheme it would help us a lot
[…] Income Tax Overview […]
[…] Income Tax Overview Share Posted in Bank, Investing, Tax , Bank, Investing, Recurring Deposit, tax | No Comments » […]
[…] the Income Tax Act, as discussed in Income Tax Overview, there are five heads of […]
[…] Income Tax Overview […]
[…] the depositors can claim the credit for such TDS in their income tax returns. Our article Overview of Income Tax gives details about how to Calculate Income […]
[…] has a well-developed tax structure. We directly(ex:income tax ) or indirectly(ex:service tax) pay taxes. Indian tax laws have various rules and regulations, and […]
[…] post Income tax overview deals in detail on calculation of Income […]