The tax an Indian pays every year is calculated on the basis of his/her gross total income. The tax is calculated according to the income tax slabs announced by the government every year in the Budget usually in February. This article discusses the Income tax slab rates for the financial year 2016-17 or Assessment year AY 2017-18, Changes for AY 2017-18, Comparison of tax deductions across different Financial Years.
Table of Contents
Income Tax Forms for FY 2016-17 or AY AY 2017-18
On 31 Mar 2017, The Income Tax Department released the ITR (Income Tax Return) Forms for Financial Year 2016-2017 (i.e. Assessment Year 2017-2018). These ITR forms will be applicable for your income tax return for income earned from 1st April 2016 to 31st March 2017 which comes under FY 2016-17 or AY 2017-18.
The due date of submission of ITR for FY 2016-17/AY 2017-18 has been extended till 5 Aug 2017. will be 31st July 2017. Major changes in the form are as below.
- Mentioning Aadhaar number or Aadhaar enrollment id is mandatory. Article Income Tax: How to Link Aadhaar with PAN for filing ITR talks about in detail.
- Single page ITR Form for those with income upto Rs 50L. For the forms and how to fill you can go here.
- ITR -1 can only be filed by those with ONE house property
- Schedule AL has been taken off from ITR-1
- New section added in ITR-1 for mentioning exempt long term capital gains. Mandatory to e-file tax returns for those with LTCG of Rs 2.5L or more, even though their total taxable income may be below Rs 2.5L.
- Old ITR-2, ITR-2A and ITR-3 have been done away with and merged to NEW ITR-2
- Old ITR-4 is now NEW ITR-3 and Old ITR-4S(Sugam) is now NEW ITR-4(Sugam)
- Paper returns can only be filed by those who are above 80 years of age O8R by an individual or HUF whose income does not exceed five lakh rupees and who has not claimed any refund in the return of income.
Tax slabs for AY 2017-18 or Financial year 2016-17
Every individual whose total income before allowing deductions under Chapter VI-A of the Income-tax Act, exceeds the maximum amount which is not chargeable to income tax is obligated to furnish his return of income. The maximum amount not chargeable to Income tax in case of different categories of individuals is given below. The tax calculator can be used to find your tax liability.
| TAX | MEN and WOMEN below 60 years | SENIOR CITIZEN(Between 60 yrs to 80 yrs) | For Very Senior Citizens(Above 80 years) |
| Basic Exemption | 250000 | 300000 | 500000 |
| 10% tax | 250001 to 500000 | 300001 to 500000 | – |
| 20% tax | 500001 to 1000000 | 500001 to 1000000 | 500001 to 1000000 |
| 30% tax | above 1000000 | above 1000000 | above 1000000 |
| Surcharge | 15% of the Income Tax, where total taxable income is more than Rs. 1 crore | ||
| Education Cess | 3% on Income-tax plus Surcharge. | ||
The income tax slab for individuals, females, senior citizen remains same in the FY 2016-17. There is no change. The basic exemption remains same at 2.5 lakhs. There is no extra concession for females.
- Income Tax Rebate: The income tax rebate is increased to Rs 5000. In the FY 2015-16, it was Rs 2000, now the tax rebate is increased by Rs 3000 to Rs 5000. This rebate is available to those whose taxable income is below 5 lakhs. It means, that the tax liability of such people would come down by Rs 5000. For details, you may read our article Income Tax Rebate under Section 87A
- Rent Deduction: The tax deduction for the rent payment under section 80GG is increased from 24,000 to 60,000. This deduction is available to those who lives in rented house and do not get House Rent Allowance from the employer. For details, you may read our article HRA increased from 24,000 to 60,000 under section 80GG
- Deduction On Home Loan Interest: For the first time home buyers, an additional deduction of Rs. 50,000 annually will be allowed under section 80EE for interest payments towards loans taken up to Rs. 35 lakhs. The value of the house should not exceed Rs. 50 lakhs. In FY 2014-15, The government has given similar tax benefit on the home loan interest.
- Surcharge Rate For Individuals: The income tax surcharge is levied on the taxpayers who earns more than Rs one crore in a year. For individuals, this surcharge was 12%. But For AY 2017-18 Surcharge has been increased to 15%. The surcharge for all other categories of the taxpayers would remain same.
- TDS on EPF Withdrawal: EPF withdrawal before completing 5 years is subject to TDS. Till now EPF withdrawal up to 30,000 was not subject to TDS. Now this limit has been increased up to 50,000.
- Sovereign Gold Bond: There would be NO capital gains tax on redemption of the Sovereign Gold Bond. The long-term capital gains arising from the transfer of Gold Bond would be eligible for Indexation benefit.
- Gold Monetization Scheme: The Government would not charge any capital gains tax on the interest income of gold monetization scheme.
- NPS Withdrawal: The 40% withdrawal of NPS (National Pension System) would be exempted from the tax. Along with this the NPS, wealth give to the nominee after the death of the subscriber would be 100% exempt from the tax.
- Pension Fund: If an employer invests into the pension fund of an employee, the invested amount is exempt from tax. This year’s budget (2016) has increased the exemption limit from Rs. 1 lakh to Rs. 1.5 lakh.
- Presumptive Tax Scheme under section 44AD:
- The turnover limit to avail the Presumptive Tax Scheme under section 44AD has been increased from Rs 1 crore to Rs 2 crore. The taxpayers carrying a business will be allowed to avail this scheme for which they will have to declared profits at minimum 8% of the total turnover and they will be exempted from the requirement of maintaining any books of accounts.
- Earlier the Presumptive Tax Scheme under section 44AD was available only to individuals carrying a business. With effect from 1st April 2016, the benefits of this scheme are extended to the Professionals whose annual turnover does not exceed Rs. 50,00,000, provided the declared profits from such profession are not less than 50%. The professional availing this scheme will be exempted from maintaining any books of accounts.
- Trading of securities of unlisted firms: Any gains resulting from trading of securities of unlisted firms would be long-term capital gains if the period of holding of such securities is 24 months or more. Earlier the holding period requirement was 36 months.
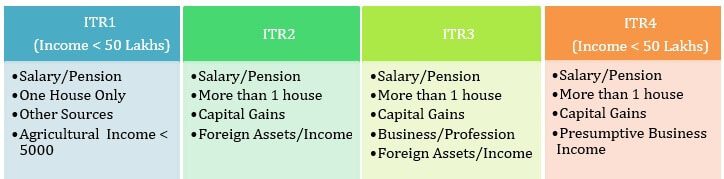
Which ITR to Fill
There are various ITR forms such as : ITR-1 (Sahaj), ITR2 , ITR3, and ITR-4S( Sugam) ITR-5 ITR-6 which differ in the information required and hence the number of pages. Type of Form to fill depends on who has to fill (individual, Hindu Undivided Family(HUF), Business etc) and type of Incomes.
The table below gives a summary of which ITR Form to use for FY 2016-17 or AY 2017-18 for Individuals or Hindu Undivided Family (HUF)
| ITR Forms | ITR 1 (Sahaj) | ITR 2 | ITR 3 | ITR 4 (Sugam) |
| Total Income | Income Less than Rs 50 Lakhs | No Limit | No Limit | Income Less than Rs 50 Lakhs |
| Income from Salary | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Income from House Property | Only One | More than One | More than One | More than One |
| Income from Business and Profession | No | No | Yes | Only Presumptive Business Income |
| Capital Gains | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Income from Other Sources | All except Income from Lottery/Race Horse | Yes | Yes | All except Income from Lottery/Race Horse |
| Exempt Income | Yes if Agriculture Income less than Rs 5,000 | Yes | Yes | Yes if Agriculture Income less than Rs 5,000 |
| Foreign Assets/Foreign Income | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Carry Forward Loss | No | Yes | Yes | No |
The Image below shows the overview of various ITR Forms for Individuals
Comparison of Tax Deductions in different Financial Years
| Description | AY 2015-16
OR FY 2014-15
|
AY 2016-17or
FY 2015-16 |
AY 2017-18or
FY 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exempted amount of transport allowance | Rs. 800 per month | Rs. 1,600 per month | Rs. 1,600 per month |
| Section 80D – Deduction for Health Insurance premium | Rs. 15,000 | Rs. 25,000 | Rs. 25,000 |
| Section 80D – Deduction for Health Insurance premium for Senior Citizens | Rs. 20,000 | Rs. 30,000 | Rs. 30,000 |
| Investment in Sukanya Samriddhi Scheme | – | Eligible for deduction u/s 80C and any payment from the scheme shall not be liable to tax. | Eligible for deduction u/s 80C and any payment from the scheme shall not be liable to tax. |
| Section 80DDB – Deduction in case of very senior citizens (>80 years) on expenditure on account of specified diseases | Rs. 60,000 | Rs. 80,000 | Rs. 80,000 |
| Section 80DDB – Deduction in case of expenditure on account of specified diseases | Rs. 40,000(<60 years)Rs. 60,000(>60 years) | Rs. 40,000 (<60 years)Rs. 60,000 (>60 years) | Rs. 40,000 (<60 years)Rs. 60,000 (>60 years) |
| Section 80DD – Maintenance, including medical treatment of a dependent who is a person with disability | Rs. 50,000 | Rs. 75,000 | Rs. 75,000 |
| Section 80DD – Maintenance, including medical treatment of a dependent who is a person with severe disability | Rs. 1,00,000 | Rs. 1,25,000 | Rs. 1,25,000 |
| Section 80U – Person with disability | Rs. 50,000 | Rs. 75,000 | Rs. 75,000 |
| Section 80U – Person with severe disability | Rs. 1,00,000 | Rs. 1,25,000 | Rs. 1,25,000 |
| Section 80CCC – Contribution to provident fund of LIC or IRDA approved insurer | Rs. 1,00,000 | Rs. 1,50,000 | Rs. 1,50,000 |
| Section 80CCD – Contribution by the employee to National Pension Scheme (NPS) | Rs. 1,00,000 | Rs. 2,00,000
Tax deduction up to 10% of Salary (Basic + DA) under Section 80 CCD(1) within the overall ceiling of 1.5 Lakh under Sec 80 CCE Additional deduction of 50,000 under section 80CCD (1B)
|
Rs. 2,00,000
Tax deduction up to 10% of Salary (Basic + DA) under Section 80 CCD(1) within the overall ceiling of 1.5 Lakh under Sec 80 CCE Additional deduction of 50,000 under section 80CCD (1B)
|
| Section 80EE for additional benefit on Home loan interest for first-time buyer | The deduction was limited to maximum Rs 1lakh in total and was available for only 2 financial years , FY 2013-years,FY 2014-15 only | The deduction allowed under this section is for interest paid on home loan up to maximum Rs 50,000 per financial year |
To calculate how much to save under 80C
80C has overall limit of 1.5 lakh. While calculating amount you need to save please consider your EPF contribution. If you have bought some life insurance policy, then you claim it too.
Amount you need to save : 1,50,000 – Employee EPF contribution – Tuition fees for two children – Principal of Home Loan – Life Insurance Premium -Stamp Duty , Registration charges of new House
Filing of Income Tax Return
Income Tax Return is a prescribed form through which the particulars of income earned by a person through various sources(like salary, business, professional fees, interest, capital gains, etc.) in a financial year and taxes paid on such income is communicated to the Income tax department after the end of the Financial year, called as income tax return or ITR. It is like your report card in school but instead of marks you have income and taxes. It is the constitutional obligation of every person earning income to compute his income and pay taxes correctly. Different forms are prescribed for filing of returns for different Status and Nature of income. Last date for filing ITR is usually 31 Jul , which is extended in some cases. Last date for filing ITR for AY 2017-18 is 31 Jul 2017.
The process of electronically filing Income tax returns through the internet is known as e-filing. One can file directly(incometax website) or through an e-Return Intermediary.
E-Filing Returns is compulsory for:
- Individuals earning over Rs 5 lakh a year. They are required to file their tax returns in the electronic format from AY 2013-14 (FY 2012-13) and subsequent assessment years.
- Individual/HUF, having total Income of Rupees 10 lakhs. It was made mandatory from AY 2012-2013((FY 2011-12) and subsequent assessment years.
- Individual/HUF /Firm auditable under section 44B of the IT Act, 1961. It was made mandatory for AY 2012-2013 and subsequent assessment years.
- All Companies
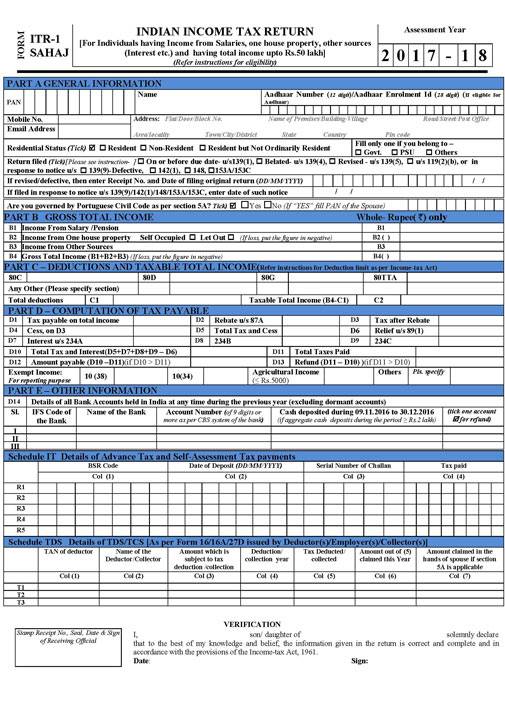
Single 1 Page ITR1 fro FY 2016-17 or AY 2017-18 is shown below. All forms can be downloaded from Income Tax Download Webpage
Related Posts:
- Mistakes while Filing ITR and CheckList before submitting ITR
- E-verification of Income Tax Returns and Generating EVC through Aadhaar, Net Banking
- Articles to Understand Income Tax, How to Fill ITR,Income Tax Notice
- Filing ITR : Video on Steps to File ITR, Ways to File,Documents required
- Advance Tax:Details-What, How, Why
- Paying Income Tax Online, epayment: Challan 280

24 responses to “Income Tax for AY 2017-18 or FY 2016-17”
Thanks for the info! As am not working can I choose Not Applicable from the Employer Category ( General information tab)? Please let me know
Yes as you are not salaried you would choose Not applicable for Employer category
Thank you!! for answering all my questions.
It’s our pleasure. Thanks for leaving the comment.
Hello Sir!
I am not working from Aug 07 2015. Could you please let me know if I can use ITR 1 to file nil returns?
The ITR you file depends on type of income you have.
What income did you have between 1 Apr 2016 to 31 Mar 2017?
You can read our article Which ITR Form to Fill? for more details
Sir!
I am not earning any money, I opted out of job to take care of my new born son
Thanks,
Deepthi.
Then it is not necessary for you to file your ITR as your taxable income is less than 2.5 lakh.
Do you still want to file ITR?
Yes Sir! Just for continuity sake, thought of filing nil returns. Please let me know if that’s OK.
Yes Sir! Just for continuity sake, thought of filing nil returns. Please let me know if it’s OK to do so
That’s a good idea.
Legally, you are not required to file the return of income as your income doesn’t exceed the basic exemption limit.
As you intend to start working again, you will have to file your income tax return. Besides, filing of income tax returns has several benefits. Income tax returns of earlier years are asked at various places like Visa applications, loan applications etc
Filing a nil return is no different from filing a regular income tax return.
Enter your income details and deductions. Income tax is computed and you will be shown that you have no tax due.
Submit your return to the Income Tax Department. And send your ITR-V to CPC Bangalore to complete the e-filing process.
You can check this video on YouTube How to file nil return?
hi plz help me out
i am working in itbp.i am try to fill itr1 self and unable to full info in 80g i dont know donee name place pan card number amout etc so plz tall me what should be fill in this section
thanks
I am filling ITR-2 after downloading excel utility from income tax website and converted into xml file but when I tried to upload xml it gives error of “uploading xml in latest utility”.Can you please help.
Warm Regards
Please check if you have used the Utility for correct year for AY 2017-18.
dear sir I am filling ITR-2 after downloading excel utility from income tax website and converted into xml file but when I tried to upload xml it gives error of “uploading xml in latest utility”.Can you please help.
Warm Regards
Sir,
I am a salaried person and have filed the ITR 1 for AY 2017-2018 and e verified it, successfully .
I had deposited rs 15500 (fifteen thousand five hundred only) in my bank acct in old cash during demonitisation period, as required by govt.
I had shown this deposited cash of 15500/ in the return (even though it says one has to enter the amt if they have made cash deposits >= 2 lakhs)
Request, if it is ok to declare cash deposits less than 2 lakhs in ITR 1 even though column in ITR1 is asking for only cash deposits above 2 lakhs during demonitisation?
schedule AL is mandatory to be filled in for income 50lahks and above.that is what the itr2 efile says. when i want to proceed without AL as my income is much less error is shown and i am asked to fill in the columns.
is there any software problem?
how does anyone whose income is below the mandatory limit but who has to use ITR2 for other
requirements proceed further?
what is the general experiance?
could you please help me?
Hello,
How should one look at the taxability of the buy back option for IDFC infrastructure bonds Tranche1 issued in Dec. 2011?
I had invested Rs. 20,000/- and opted for cumulative buy back option. It got exercised after 5 years lock in in Dec. 2016 and I received a sum of Rs. 30,780/-
Que: Should I include Rs. 10,780 (interest income?) as income from other sources to be taxed as per my slab? OR it has to be considered as long term capital gains and taxed as per debt LTCG (20% with indexation)?
Dear Sir,
Just wanted to know i have filled ITR-4 instead of ITR-1 unknowingly. Now I want to check whether I can change it to ITR-1 from ITR -4. I am a salaried person and has received form -16 from my company. All my previous returns are ITR-1. Pls let me know what is the process for changing the same or is it ok if i continue the same for this year as i do not have any refund or any liability.
I have not yet forwarded the file to Bangalore for processing .
Thank you.
A correctly filed ITR in a form which is not applicable to you would be treated as defective
As you have filed before time you can revise the return using ITR1.
ITR 3 Procedure to file return – really awesome
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a9YU6ZcB1mE
Try this link – really informative
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hEEAm0cpQkg
This statement in the article:
“Mandatory to e-file tax returns for those with LTCG of Rs 2.5L or more, even though their total taxable income may be below Rs 2.5L”
I’ve a query:
Is it mandatory to e-file tax returns for those
with LTCG from sale of house property of Rs. 2.5L or more
but income less than Rs. 5L and no refunds claimed?
Very useful guidance. Thanks. Pratap