“Everything about filling income tax return is taxing“, replied my colleague, “I just don’t know what information is required and why. I just hand over to my tax consultant, sign where he says and done with and at 200 Rs it is cheap also“. This was in response to the mail of our company arranging the tax consultant who will file income tax returns with just Form 16 and PAN card copy. When others also nodded and agreed with him , I was thinking “WHY is that a person with post graduate engineering background, who can solve complex algorithms with ease was finding filling of income tax return difficult?” I had faced the questions few years ago when I was forced to deal with income tax returns and the answer I realized was because
We do not allow people to drive without a license test but allow them to enter complex financial world without much financial education.
So this post is dedicated to all such people. Picture below shows example of two different incomes and their calculation (Ref EconomicTimes 1 Mar 2013)
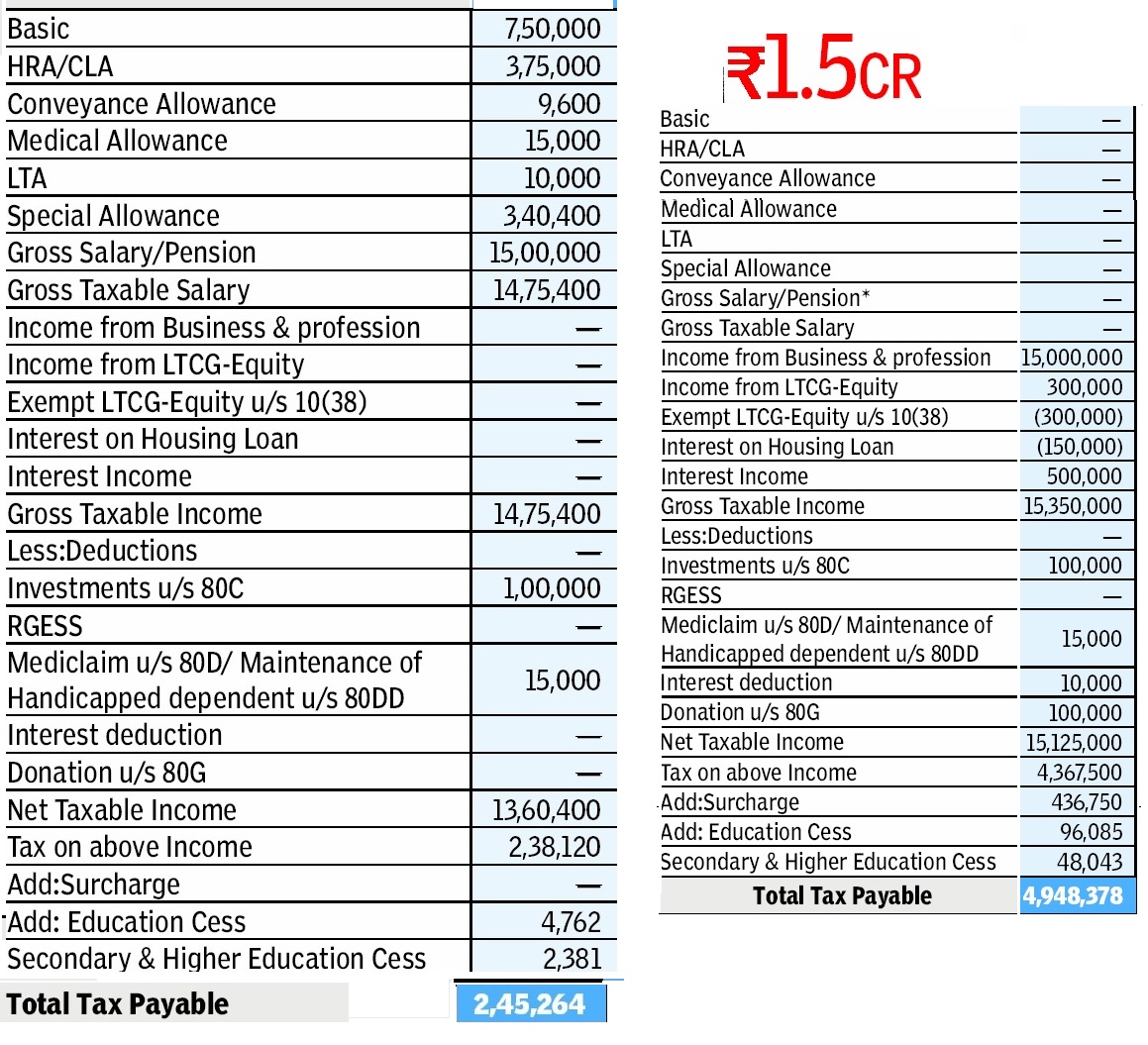
Table of Contents
Find out types of income earned
As the name income tax suggests it is tax on income.
Time period for earning the income is between 1 Apr to 31 Mar of next year. For example for the Income earned between 1 Apr 2012 to 31 Mar 2013 will be considered for filing returns this year called as Financial Year(FY) 2012-13 or Assessment Year (AY) 2013-14.
Income can be earned in many ways :
- Salary by working for someone or Pension having worked for someone, comes under category of Income From Salary. Proof is Form 16 and Form 12BA
- Selling items like gold, house comes under category of Income from capital gain
- Having a house or many houses comes under category of Income from House Property
- Having a business or profession ex shop, doctor, consultant comes under category of Income from Business or Profession
- Having income which does not fit into any of above category,comes under the category of Income From Other Sources. Such as interest on Bank Account, Interest on Fixed Deposits, Dividends from companies, Family pension ,Insurance commission,Income from royalty,gift amount etc.
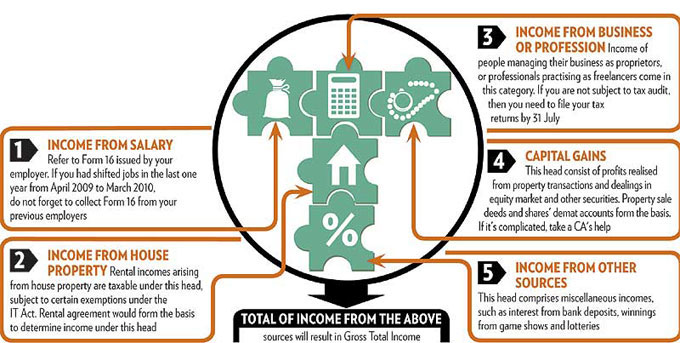
Picture below shows various kinds of income.
Different income tax return forms are made available by Income Tax Dept every year based on kind of income. You should choose a return form according to your status(resident etc) and nature of income. For example ITR-1 or SAHAJ needs to be filed with Individual having following income Income from salary/pension, or Income from one house property or Income from other sources( excluding winnings from lottery and income from races horses). Our article Which ITR Form to Fill? explains it in detail
Find the tax rules of each kind of income
Understand each kind of income. For each kind of income some part is taxable some is not.
- For Income from Salary, Medical allowance and Conveyance Allowance are not taxable.
- For Income from Capital Gains, rules differ based on type of item sold for example Gold, Mutual funds, time it was held (long term or short term which again differ based on type of asset sold), some income is exempt such as long term capital gains from sale of shares or Equity mutual funds. Some gains/loss can be adjusted. Our article Basics of Capital Gain talks about in detail.
- For Income from House property, tax rules are different if you have one or many houses if you have taken house on loan interest for a self occupied property can be claimed upto Rs 1,50,000. Our articles Joint Home Loan and Tax, Tax : Income From House Property, Tax and Income from Let out House Property cover it in detail
- For Income from Business or Profession some expenditures can be claimed as expenses and deducted.
- For Income from Other Sources : Of the incomes mentioned as Income from other sources, some income is exempt that is one need not pay any tax on it but some income is taxable .
- Example of income which is not taxed is Income from Dividends from Mutual funds or Companies, gift amount received from a relative or under will or inheritance is not taxable but gift amount exceeding Rs. 50,000 not from any relative or on the occasion of marriage of the individual or under a will or inheritance. Income from saving back account upto 10,000 Rs.
- Examples of Income mentioned as Income from other sources which is taxed is Income tax on Fixed Deposit, Gift amount above Rs 50,000 received from a friend or not a legal relative.
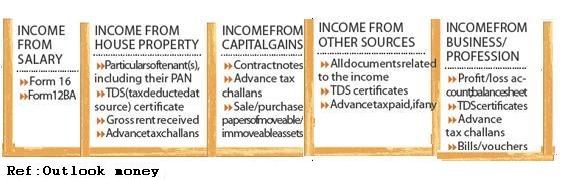
Picture below shows the documents required for each type of Income
Have you saved Tax ?
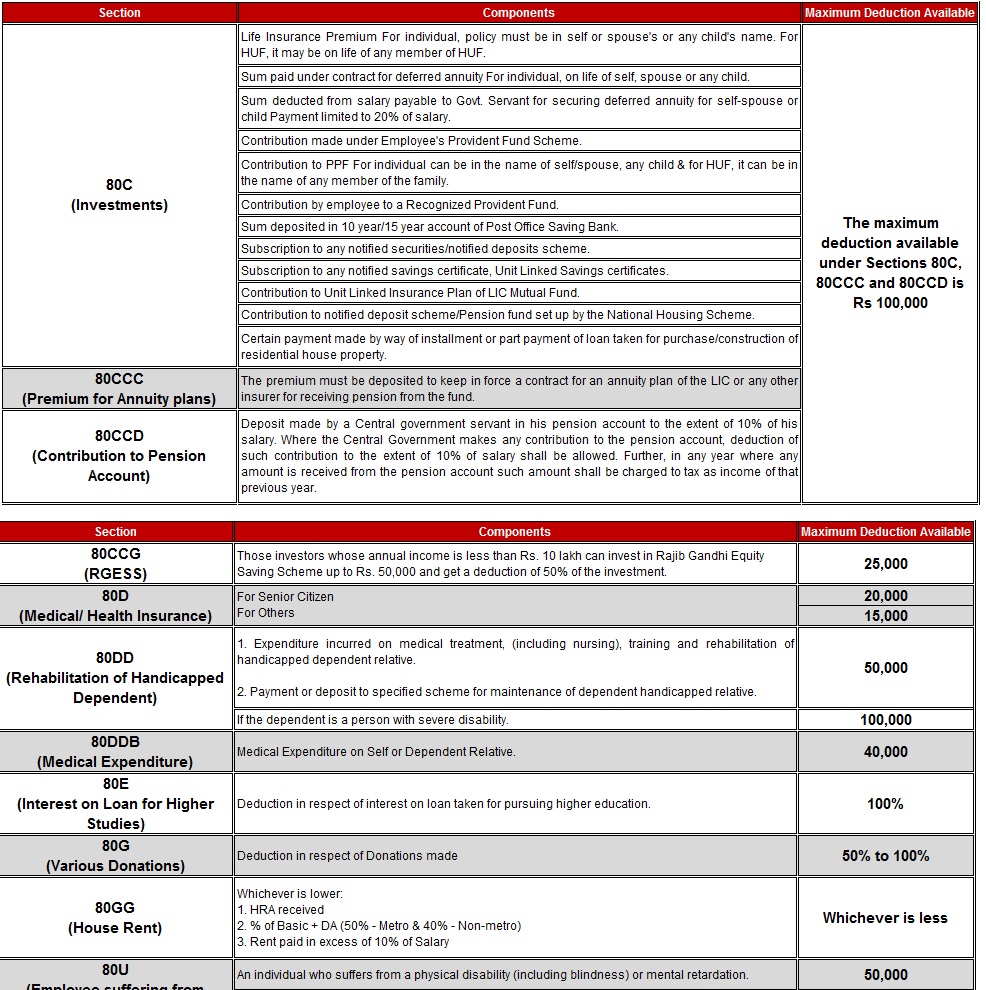
The Income Tax Act, 1960 allows you to save tax by investing your income. Depending on where you invest , the maximum amount, section of Income tax act which governs it changes For example :
- Under Section 80C,80CCD, 80CCC, 80CCCE etc one can save tax by investing upto 1 lakh in different options, each suited to a different need. One can choose a combination of fixed income, life insurance and market-linked investments depending on one’s financial goals and investment horizon.
- Under Section 80D one can save tax by paying Premium for health insurance of youself, your spouse, children or dependent parents
- Under Section 80E one can save tax if one has taken Education Loan
- Under Section 80G one can save tax if one has donated money to charity.
Picture given below captures the various sections (Click on image to enlarge)
How to compute Tax?
Add all the income, make the deductions(80C etc) and find the taxable income. Income tax depends on the income earned, more the income, more the tax. It also varies with with age(less than 60,between 60 – 80 years, more than 80), residence(india/non-resident India), gender(male/female) and financial year. For quite some time tax on income has beed divided into four groups or income slabs
- Amount of income not taxed at all,
- Amount of income taxed at 10%,
- Amount of income taxed at 20% and
- Amount of income taxed at 30%.
Income tax calculation For indian man/woman less than 60 years of age for For Financial year 2012-13 or Assessment Year 2013-14 is as follows. You can also use Income Tax Department Calculator for same purpose. Our article Examples of Income Tax Calculation also explain in detail (for FY 2011-12 or AY 2012-13)
| Level of income | Tax |
| 1. Where the total income does not exceed Rs. 2,00,000 | Nil |
| 2. Where the total income exceeds Rs. 2,00,000 but does not exceed Rs. 5,00,000 | 10% of the amount by which the total income exceeds Rs. 2,00,000 |
| 3. Where the total income exceeds Rs. 5,00,000 but does not exceed Rs. 10,00,000. | 10% on 3 lakh i.e Rs. 30,000 + 20 % of the amount by which the total income exceeds Rs. 5,00,000 |
| 4. Where the total income exceeds Rs. 10,00,000 | 10% on 3 lakh i.e Rs. 30,000 + 20% on 5,00,000 i.e 1,00,000 = Rs. 1,30,000 +30% of the amount by which the total income exceeds Rs. 10,00,000. |
Education Cess at 2% of Tax and Secondary and Higher Education Cess at 1% of tax is added to tax calculated or 3% of tax
For example tax on income for Indian male earning 6,00,000, is calculated as follows:
- 10% on 3,00,000(5,00,000-2,00,000) + 20% on 1,00,000(6,00,000-5,00,000) = i.e 30,000 + 20,000 =50,000
- OR 30,000 + 20% of 1,00,000(6,00,000-5,00,000)
Total tax = Tax + Education cess (2% of tax) + Secondary and Higher Education Cess (1% of tax)n= 50,000 + 1000 + 500 = 51,500
Was tax deducted for you or TDS?
Paying a tax at end of year in one shot is difficult. So at the time of payments of various kind such as salary, commission, interest on dividends , interest on fixed deposits etc, tax is deducted as per the Income tax laws. called as Tax deducted at Source (TDS) . This withheld amount or TDS can be adjusted against tax during tax computation. you can verify that TDS is actually paid to government by checking Form 26AS. Our article Viewing Form 26AS on TRACES explains it in detail.
Did you pay any tax your self?
Other than Taxes deducted at source (TDS) on your salary income at times you may have to pay/paid Advance Tax and Self Assessment Tax which you need to show while filing income tax returns.
Advance tax is the income tax that is payable if your tax due after deducting TDS exceeds Rs 10,000 and should be paid in the same year in which income is received. Our article Advance Tax:Details-What, How, Why covers it in detail.
Self Assessment Tax: If at the time of filing of return you find that you have some balance tax to be paid after taking into account your advance tax, TDS & TCS, the short fall of tax is to be deposited by you(before filling income tax return ) as Self Assessment Tax . Our article Paying Income Tax : Challan 280 explains how to pay Advance Tax, Self Assessment tax in detail.
The following images show income tax calculation in other scenarios for individuals less than 60 years of Age and for FY 2012-13, AY 2013-14 tax . Now are you able to compute tax? You can use calculators that might help you are incometaxindia.gov.in Calculator for finding tax(Please use correct assessment Year)
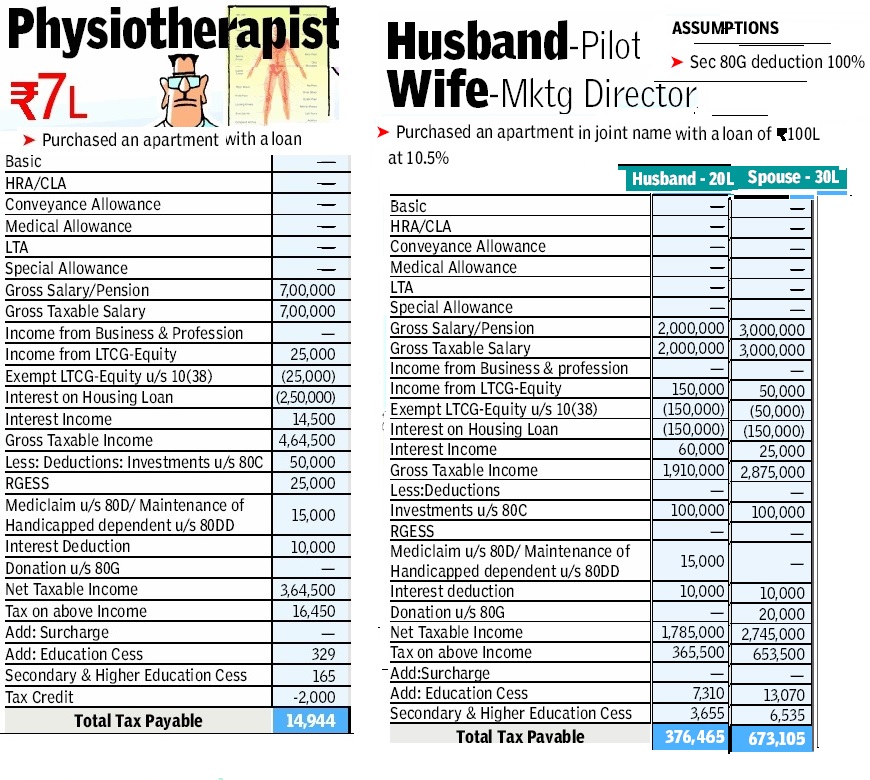
Related Articles:
- Income Tax overview
- E-Filing of Income Tax Return
- Filling ITR-1 : Bank Details, Exempt Income, TDS Details
- E-filing : Excel File of Income Tax Return
- Understanding Form 16: Tax on income, Understanding Perquisites, Understanding Form 12BA
Understanding Income tax is not rocket science. Even if you get it filled by the Tax consultant please go through it yourself, ask him if you have doubts. If you spend time to learn about it then slowly the jigsaw pieces will start fitting. If you have any doubts or questions please don’t hesitate to ask. For questions are not stupid answers might be 🙂

27 responses to “How to Calculate Income Tax”
Some people find it hard to computer their income tax so using income tax calculator is a very good choice. This is very helpful to compute our tax. Thanks for sharing this valuable information on tax computation.
An informative article provided. If you are earning it is very important that you perform tax planning the right way. One of the most important parts of this particular process is to understand how income tax gets calculated. In India taxes are levied on the basis of how much an individual earns. The national government levies these taxes. It has devised a system whereby the process can be done in a fair way. Normally, the more you earn, the more taxes you have to pay. In the 2019-20 union budget, it was decided that people with a taxable income of up to INR 5 lakh a year would not have to pay any tax on their income. Appreciate the effort.
You’re the best to share this. I truly had to know how to ascertain Tax…
Good post on Income tax calculation. Income tax depends on the income earned, more the income means more the tax. But, if you want to calculate your income tax then you can do that through Big Decisions. At Big Decisions different Income tax Calculators available and you can make smart decisions by using these calculators.
I want to understand how I can calculate my taxes. So, Can you please explain more about Income tax calculator.
Your site is indeed very informative. I feel that most people have a basic doubt as to which form to file in case you have a home loan. Do we fill the ITR 1 and show the interest as a negative figure in to income from house property section or do we go through the complicated ITR 2 (It seems intimidating coz of so mny different section in the excel sheet). Also if it could be shown as a negative figure, the one can e-file ITR 1 and get over with it. There’s no option for e-filing ITR 2 other than the excel sheet method.
kudos to the site Administrator and team for running a good show here.
Thanks Jijo for encouraging comments.
There is confusion on which form to fill ITR1 or ITR2 this year.
For ITR1 an individual can fill if he/she has
1. Income from salary/pension: or
2. Income from one house property
3. Income from other sources( excluding winnings from lottery and income from races horses)
Scope of ITR-1 (Sahaj) form has been reduced in AY 2013-14 significantly . You cannot use ITR1 if
One who have negative income under head Income from other sources can not use this form
If one’s exempted income is more than 5,000 then that assessee can not use Sahaj (ITR-1)
Salaried person getting transport allowance which is exempted 800 per month (more than 5000) can not use ITR-1. (Not confirmed)
Salaried person getting HRA exemption (more than 5000) are also not eligible. (Not confirmed)
Other allowances which are exempted also not eligible.
If one has received maturity amount of insurance ,exempted at the time of receipt, more than Rs 5,000 also not eligible
So if you have interest income fromonly one house property then you can show it in ITR1.
It’s not complex only a little different because we are not used to it.
Our articles in filling ITR1 form may be of help.
Fill Excel ITR form : Personal Information,Filing Status
Fill Excel ITR1 Form : Income, TDS, Advance Tax
Fill Excel ITR1: 80G, Exempt Income,Calculation of Tax
Your site is indeed very informative. I feel that most people have a basic doubt as to which form to file in case you have a home loan. Do we fill the ITR 1 and show the interest as a negative figure in to income from house property section or do we go through the complicated ITR 2 (It seems intimidating coz of so mny different section in the excel sheet). Also if it could be shown as a negative figure, the one can e-file ITR 1 and get over with it. There’s no option for e-filing ITR 2 other than the excel sheet method.
kudos to the site Administrator and team for running a good show here.
Thanks Jijo for encouraging comments.
There is confusion on which form to fill ITR1 or ITR2 this year.
For ITR1 an individual can fill if he/she has
1. Income from salary/pension: or
2. Income from one house property
3. Income from other sources( excluding winnings from lottery and income from races horses)
Scope of ITR-1 (Sahaj) form has been reduced in AY 2013-14 significantly . You cannot use ITR1 if
One who have negative income under head Income from other sources can not use this form
If one’s exempted income is more than 5,000 then that assessee can not use Sahaj (ITR-1)
Salaried person getting transport allowance which is exempted 800 per month (more than 5000) can not use ITR-1. (Not confirmed)
Salaried person getting HRA exemption (more than 5000) are also not eligible. (Not confirmed)
Other allowances which are exempted also not eligible.
If one has received maturity amount of insurance ,exempted at the time of receipt, more than Rs 5,000 also not eligible
So if you have interest income fromonly one house property then you can show it in ITR1.
It’s not complex only a little different because we are not used to it.
Our articles in filling ITR1 form may be of help.
Fill Excel ITR form : Personal Information,Filing Status
Fill Excel ITR1 Form : Income, TDS, Advance Tax
Fill Excel ITR1: 80G, Exempt Income,Calculation of Tax
Calculating Income tax was Greek and Latin to me once. But I learned it after helluva efforts. Thanks for the info.
I can empathise with you. I have struggled with Income tax in past but it is becoming easier
Calculating Income tax was Greek and Latin to me once. But I learned it after helluva efforts. Thanks for the info.
I can empathise with you. I have struggled with Income tax in past but it is becoming easier
Thanks a Lot for sharing this…I really needed to know how to calculate Tax..
Thanks a Lot for sharing this…I really needed to know how to calculate Tax..
Very good articles regarding IT. Could you give examples how to fill ITR-I ,when two Form-16 are there.
It will be most useful in the cases where tax payable is compared in two sheets ( tax to be paid or refund to be got ).
A very good idea and we would be taking it in future.
It is a very common situation wherein employee switches employment during the year. If you have worked with different employers during the financial year (from 1 Apr to 31 Mar ) then each of them is required to deduct tax and issue Form 16 and Form 12BA.
Making a job switch in the middle of the year involves making sure that the deductions and exemptions regarding tax liability are made only once. When a new employee joins the company, he is required to give the particulars of income from his earlier employment by filling Form 12B. It is different from Form 12BA issued by employer for showing perquisites. Did you fill the Form 12B?
If you didn’t then both employers would be computing employees’ tax liability after taking into consideration the basic exemption limit ( in financial year 2012-2013 or assessment year 2013-2014 it is Rs 2 lakh) and also the exemption availed under Section 80C. So there is a possibility that your previous employer and present employer may give you these exemptions for the same financial year?
We have touched it in our article Changing Jobs:Take Care Of Bank Account,Tax Liability
Very good articles regarding IT. Could you give examples how to fill ITR-I ,when two Form-16 are there.
It will be most useful in the cases where tax payable is compared in two sheets ( tax to be paid or refund to be got ).
A very good idea and we would be taking it in future.
It is a very common situation wherein employee switches employment during the year. If you have worked with different employers during the financial year (from 1 Apr to 31 Mar ) then each of them is required to deduct tax and issue Form 16 and Form 12BA.
Making a job switch in the middle of the year involves making sure that the deductions and exemptions regarding tax liability are made only once. When a new employee joins the company, he is required to give the particulars of income from his earlier employment by filling Form 12B. It is different from Form 12BA issued by employer for showing perquisites. Did you fill the Form 12B?
If you didn’t then both employers would be computing employees’ tax liability after taking into consideration the basic exemption limit ( in financial year 2012-2013 or assessment year 2013-2014 it is Rs 2 lakh) and also the exemption availed under Section 80C. So there is a possibility that your previous employer and present employer may give you these exemptions for the same financial year?
We have touched it in our article Changing Jobs:Take Care Of Bank Account,Tax Liability
Great information to know but I am more at ease having my accountant do my taxes for me. With all that I have going on sometimes its just best and easier to pay someone to take care of certain things. I know this much went into calculated your income tax.I agree that you should know whats going on since you never know who could be trying to take advantage of your or just missing things on your behalf.
Thomas it’s okay to get it done with an accountant if that makes one comfortable. But you should be able to cross-check whether all the information is reflected correctly. In past for my friends I have seen the accountant entering home loan interest as positive (my friends got a notice from Income tax department) missing out information (interest on FD, exempt income), not taking care of deductions not accounted by employers. So delegate but supervise.
Great information to know but I am more at ease having my accountant do my taxes for me. With all that I have going on sometimes its just best and easier to pay someone to take care of certain things. I know this much went into calculated your income tax.I agree that you should know whats going on since you never know who could be trying to take advantage of your or just missing things on your behalf.
Thomas it’s okay to get it done with an accountant if that makes one comfortable. But you should be able to cross-check whether all the information is reflected correctly. In past for my friends I have seen the accountant entering home loan interest as positive (my friends got a notice from Income tax department) missing out information (interest on FD, exempt income), not taking care of deductions not accounted by employers. So delegate but supervise.
Nice informative article, BM kindly shed light on the Rs.2000.00 tax rebate announced by the FM in budget speech
Upto 2000 Rs rebate is for next year not this year.
For FY 2013-14 or AY 2013-14 10% of amount by which the total income exceeds Rs. 2,00,000
.Less: Tax Credit – 10% of taxable income upto a maximum of Rs. 2000/-.
Nice informative article, BM kindly shed light on the Rs.2000.00 tax rebate announced by the FM in budget speech
Upto 2000 Rs rebate is for next year not this year.
For FY 2013-14 or AY 2013-14 10% of amount by which the total income exceeds Rs. 2,00,000
.Less: Tax Credit – 10% of taxable income upto a maximum of Rs. 2000/-.