What are various types of bank accounts in India? Such as Saving and Current Bank Accounts? What are Fixed Deposits and Recurring Deposits? What are accounts for Non-residents? What is the difference between different type of bank accounts?
Table of Contents
Overview of Bank Accounts in India
A bank is a business establishment in which money is kept for saving. To save money in a bank, one needs to open an account with the bank. Then one needs to put money in the bank. Putting money in the bank is called a deposit. Bank would provide a chequebook and an ATM card. Our article What is Bank? explains Banks in detail.
There are various types of banking accounts in India, all of which are listed below:
- Demand Deposits, which are of these types
- Savings Account
- Current Account
- Term Deposits, which have further sub-categories as:
- Fixed Deposits
- Recurring Deposits
- Non-Resident Account
- Other Accounts
DEMAND DEPOSITS
As the name suggests, in demand deposits, money is payable “on demand”. Demand Deposits include two types of accounts, which are easier to remember as CASA (Current Account and Savings Account respectively).
Savings Account
A savings account is an account on which interest is paid (i.e. interest-bearing), held at a bank. There are three types of savings accounts:
- Savings Bank Account
- Basic Savings Bank Deposit Account (BSBDA)
- Basic Savings Bank Deposit Account Small Scheme
Savings Bank Account
Savings Bank Account is the most common account for individuals meant for saving purposes. Any individual either single or jointly can open a savings account. Most of the salaried persons, pensioners and students use Savings Account. We all have at least one savings accounts as savings account offer a safe place to keep our money. Savings accounts offer easy access to the cash you can make withdrawal easily and quickly. A savings bank account helps you park your savings, earn a higher interest rate on it, all the while enabling you to carry out basic transactions
- When you have money in a bank savings account, your money earns interest.
- The interest is calculated on the daily balance in your account.
- Interest is credited to the account at quarterly intervals. Interest will be paid only if works out to Rs. 1 or more
- Cheque book, ATM-Debit card are provided.
- Various facilities such as internet banking, phone banking and mobile banking are available in normal savings bank accounts.
- The minimum balance in normal savings bank account varies from bank to bank. While some banks may have a minimum balance of 1000, other banks may have 5000.
- If you don’t maintain your minimum balance you need to pay penalty.
- Interest earned on Saving Account is considered as Income from other Sources. This needs to be declared in your income tax returns. But you get deduction upto 10,000 Rs under section 80TTA on interest earned on all your saving bank accounts.
Example of limits on the Saving Bank Accounts:
- The first three cash withdrawals in a month from other bank ATMs will be free. Following this, a charge of Rs.20 will be levied.
- The first five cash withdrawals in a month from SBI ATMs will be free. Following this, a charge of Rs.10 will be levied.
- Debit card holders will be charged Rs.15 per quarter for SMS alerts, provided that the account has an average quarterly balance of up to Rs.25,000.
- If the account has a balance of at least Rs.25,000, then the account holder will not be charged for withdrawals from SBI ATMs.
- If the account has a balance of at least Rs. 1 lakh, then the account holder will not be charged for withdrawals from other banks ATMs.
- UPI/USSD transactions of up to Rs.1,000 will not be levied any charges.
- SBI will charge Rs.50 for every cash transaction following the first three cash deposits each month. This limit is relevant to savings accounts only.
- Bank accounts will have to retain a minimum Monthly Average Balance (MAB).
- If the MAB is not maintained, charges up to Rs.100 plus service tax can be levied.
- The MAB and charges vary according to the location of the bank. It is set to a minimum level in rural branches.
- In metros such as Chennai, Delhi, Mumbai, and Bengaluru, a charge of Rs.100 + service tax will be levied if the balance goes below 75% of the minimum balance.
- If the account falls short of 50% of the MAB, the charge will be Rs.50 + service tax.
Our article, Saving Bank Account: Do you know how interest is calculated and more, covers Saving Bank accounts in detail.
Basic Savings Bank Deposit Account (BSBDA)
These accounts are simple bank accounts without any age or income restrictions. The KYC (Know Your Customer) norms are applicable to these accounts. An individual can open only one such account. Features of Basic Savings Bank Deposit Account are as follows
- Basic ATM-cum-Debit card will be issued free of cost and no annual maintenance charge will be applied.
- Receipt/ credit of money through electronic payment channels like NEFT/RTGS will be free
- Deposit/ collection of cheques drawn by the Central/State Government will be free
- No charge on activation of inoperative accounts
- No account closure charges.
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana, No frills account or zero balance account comes under this category.
A no-frills account is a zero-balance bank account, free from unnecessary services or frills, for a limited period of time, introduced by RBI in 2005 to provide banking facilities to the poor section of the society. RBI laid down guidelines in August 2012, which stated that all banks are required to convert their “no- frills” accounts to “Basic Savings Bank Deposit” account.
Basic Savings Bank Deposit Account Small Scheme
This account can be opened by any individual above 18 years old, who do not have Officially Valid KYC documents. There are many restrictions in operation of the account due to the relaxed KYC. The account can be converted to Regular Savings Account upon submission of KYC documents. Primarily meant for poorer sections of society to encourage them to start saving without any burden of charges or fees. But it comes with some restrictions, which are:
- The person cannot deposit more than 50,000 Rupees in a year.
- The total of all withdrawals and transfers in a month should not exceed Rs 10,000.
- The total of all credits in a Financial Year should not exceed Rs 1 lakh.
- Maximum 4 withdrawals in a month, including ATM withdrawals at own and other Bank’s ATMs and transactions through other modes including RTGS/NEFT/Clearing/Branch cash withdrawal/transfer/internet debits/standing instructions/EMI, etc. No further customer debits would be allowed during the month.
- The accounts are valid for a period of 12 months but can be extended for another 12 months with the use of proof of official valid documents. If KYC documents are not submitted to the Bank within 24 months of the opening of the account, no further transaction other than for closure of account will be permitted.
CURRENT ACCOUNT
Unlike Savings Account, a Current Account is an account in which the bank does not pay any interest when one keeps money in the bank account. Typically Business Persons open a current account. The various features of Current Accounts are:
- There are no restrictions on the number of transactions that are allowed in a day.
- Overdraft facility: A person with this account can withdraw an amount of money more than that in his account, with a condition of returning the extra money withdrawn within a given amount of time. This time span will be decided by the bank. The bank will take charge from the customer.
Difference between Savings and Current Accounts
The table below shows the difference between Savings and Current Account.
| Description | Saving Bank Account | Current Bank Account |
| Purpose | To Save | For Business |
| No. of Transactions | A limited number of transactions which varies from bank to bank | Unlimited transactions. However, most private banks charge a fee for transactions over a certain limit for some accounts. |
| Interest | They give interest on money deposited. The interest rates vary with different banks. |
They don’t give any interest. |
| Required Balance | Low minimum required balance | High minimum required Balance |
| Overdraft Facility | It is not available. | It is available. The maximum limit depends on the bank. |
TERM DEPOSITS
Time deposits mean the money is deposited for a specific time period or term. Compared to Savings Accounts, the interest rates are more in these accounts. The rates are slightly more for Senior Citizens i.e citizens with age more than 60 years. Term deposits are popular with investors who prefer capital security and a set return as opposed to the fluctuations of, say, the share market.
These Deposits have two further sub-categories, as follows:
- Fixed Deposits
- Recurring Deposits
FIXED DEPOSITS
- Money is deposited in these accounts for a time span ranging from seven days to ten years, with an interest rate which is fixed on the day of the investment.
- Money is a deposited in a lump sum or one time.
- A person can withdraw the money deposited in the fixed deposits by paying a small fine, which is again set by the bank. This is called breaking the FD.
A sample FD receipt from our article Overview of Fixed Deposits is shown below
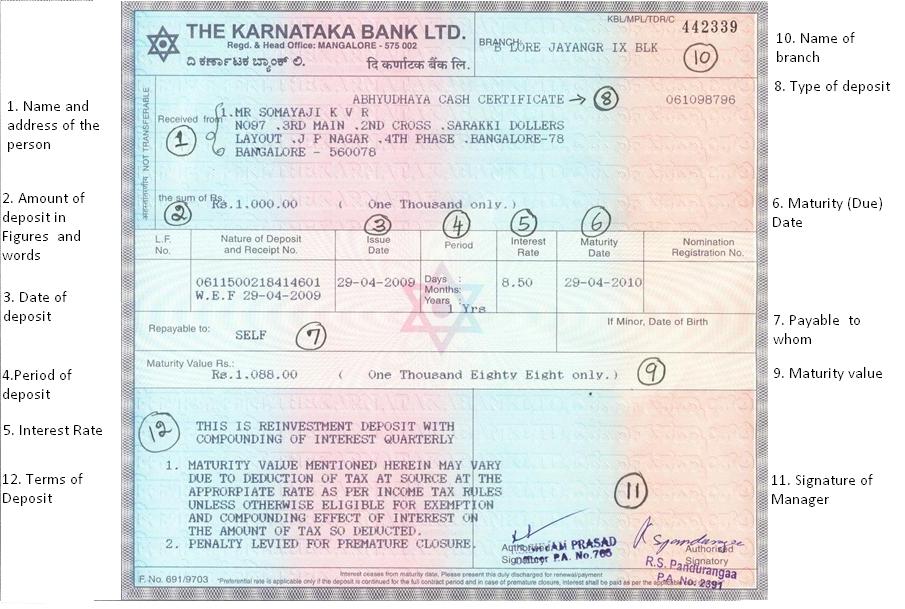
Fixed Deposit or FD certificate
RECURRING DEPOSITS
“Boond boond se sagar banata hai” (little drops of water make an ocean) As per this saying, small but periodic investments can grow to a large sum at maturity. This is the basic investment logic behind recurring deposit schemes.
- Unlike fixed deposits, in Recurring deposits, banks accept deposits from customers in instalments, at regular intervals. So, suppose if a person has decided upon depositing the money in ten instalments, then the bank will not accept it in eleven or nine.
- In Recurring Deposits, the time span varies from six months to ten years.
- The amount of deposits varies and can start from as low as Rs. 50.
- The interest rate will be approved by the bank, and it will be compounded every quarter (i.e. every three months).
Our article Overview of Recurring Deposits or RD explains it in detail.
Deposits for Non-Residents Indians
These accounts are held by NRI’s (Non-Resident Indians). It has three further sub-categories:
- Foreign currency Non-Resident (Banks): FCNR(B)
- Non-Resident External Rupee Account: (NRE)
- Non-Resident Ordinary Rupee Account: (NRO)
FOREIGN CURRENCY NON-RESIDENT (BANKS): FCNR (B)
- As the name suggests, the accounts are opened and maintained in the foreign currency, which can be US Dollars, Pound Sterling, Euro, Japanese Yen, Canadian Dollar, Australian Dollar.
- Only term deposit/fixed deposit is allowed,
- the money that has been acquired in the foreign countries can be transferred out of India (i.e. the principal amount is repatriable).
- These accounts are non-taxable in India,
- Prior approval of RBI is necessary for opening this account
- Interest rates are determined by the banks.
NON-RESIDENT EXTERNAL RUPEE ACCOUNT or NRE
- The accounts here are maintained in Indian Rupee, instead of foreign currency.
- These accounts are also non-taxable in India,
- Unlike FCNR, Savings, Current, Fixed and Recurring deposits are allowed
- The principal amount and interest are repatriable.
- In opening this account too, prior approval of RBI is necessary, and the banks have the authority of determining the interest rates.
NON-RESIDENT ORDINARY RUPEE ACCOUNT: (NRO)
- It is maintained in Indian Rupee.
- the only term deposit is allowed,
- These accounts are taxable in India, and but not the principal, but the interest amount is repatriable.
- As an NRI is applicable for an NRO account, hence no prior permission from RBI is required for opening the account.
OTHER ACCOUNTS
Apart from the above three, there are other accounts, such as:
- DEMAT Account or DEMaterialized Accounts. Such an account is used to conduct electronic transactions of the shares.
- Escrow Account: When any transaction is occurring between any two parties, an Escrow account acts as a temporary pass to an account held by the third party/parties. Money is released from the account when the contractual agreement is met by both the parties. For example,
- In real estate, developers of under-construction properties operate by opening escrow accounts to assure home buyers that their use the funds accumulated for a particular project for that project only. This YouTube video Escrow Account – Explained in Hindi explains Escrow Account in detail.
- Fiverr has an Escrow system where a seller gets paid if the buyer accepts the work as being done. When the buyer purchase a gig the money is charged right away however the seller doesn’t get the money until work is submitted and the buyer accepts the finished product.
- GILT Account: In these accounts, Government Securities and Treasury bills are held in DEMAT form, maintained by investors with the primary dealers.
Nowadays, bank operations are not restricted to a national border. Banks can open branches in foreign countries but it is not possible for a bank to open a branch in every country? So banks open an account in the foreign countries’ bank
- Nostro Account: The Indian bank opens accounts in foreign banks in the respective foreign currency. For example, Punjab National Bank has an account of Bank of America in US Dollars. Italian word Nostro means ours. Hence, Nostro account means Our account with you.
- Vostro Account: In Vostro Accounts, foreign banks contain accounts of Indian Banks within them, in Indian Rupees. For example, Bank of America has an account of Punjab National Bank within it in Indian Rupees. Italian word Vostro means yours. Hence, Vostro account means Your account with us
- Loro Accounts: Loro accounts are generally held by a 3rd party bank, other than the account maintaining bank or with whom the account is maintained. For example, Bank of India wants to transact with HSBC in UK, but doesn’t have an account, while SBI maintains an account with HSBC in U.K. Then BOI could use SBI account. The Italian word loro means theirs, so Loro accounts are “Their account with them”
In case of PNB Scam of Nirav Modi, the overseas branches of banks like Canara Bank, Bank of India, State Bank of India, Allahabad Bank and Axis Bank banks in Antwerp, Frankfurt, Mauritius, Hong Kong and Bahrain had credited over Rs 11,400 crore into the Nostro account of Punjab National Bank on the basis of the guarantees (LoUs) given by Nirav Modi and Mehul Choksi.
Related Articles:
- What is Bank?
- Kinds of Cheques
- Saving Bank Account:Do you know how interest is calculated and more
- Interest on Saving Bank Account : Tax, 80TTA
- Best Interest Rates on Saving Account
- Dormant Bank Account



