A share is a unit of ownership of a company. One can buy or sell shares on the Stock Exchange or the Stock Market. A market is a place where we buy things. Stock Market is a place where we buy stocks or shares. The company makes the share available to the stock exchange during Initial Public Offering or IPO. Once listed, the stocks issued can be bought, sold by people in the stock market. The prices of stocks changes depending on the demand and supply. What is Stock or Share? What is IPO? What is the stock exchange? Who is Broker? What is Demat and Trading account? How does buying and selling of shares happen? Why do the stock prices change?
Table of Contents
What is Share? What is IPO?
Buying a share or stock of a company simply means you are buying a unit of the company. But why would a company allow people to invest in it, these people would be sharing its profits!, The simple answer is because companies need money! There are two ways for companies to raise money for long-term business investment – they can borrow it and/or they can issue shares – otherwise known as stocks. In the world of corporate finance, stocks are called equity capital. If the company borrows money it needs to pay interest but by issuing shares it gets money and it also gets people to share with it the risk too. and is offered for sale in the market when a company needs to raise money for further growth.
First, a company has to get listed in the stock exchange, it does through the Initial Public Offering (IPO). To be listed company must meet strict financial requInitials. The price of IPO of a company is decided based on how much the company is estimated to be worth, and how many shares are being issued. In its offer document, called Red Herring Prospectus, it gives details about the company, the stocks being issued, and so on. During the listing, the stocks issued are allotted to investors who have bid for the same. This is called the Primary market.
In Mar 2017, in IPO D-Mart parent company Avenue Supermarts, which had started in 2002, launched its IPO for Rs 1,870 crore for issue size of 4.43 crore shares which was 10% of company shares. The rest of the company is owned by the promoters or owners of the company, Mutual Funds, foreign institutions etc. The D Mart was listed on BSE and NSE on 21 Mar 2017.
In Mar 1997, When Amazon first went public in May 1997 in US, its stock was priced at just $18 per share. JefBezoszs now holds 78.89 million shares which is around 17% of the company.
Jeff Bezoz, Amazon, Richest Man covers Jeff Bezoz in Detail.
Once listed, the stocks issued can be bought/sold by the investors in the stock market. This is called the secondary market. This is where most of the trading happens. In this market, buyers and sellers gather to conduct transactions to make profits or cut losses. A company gets only the amount collected through Initial Public Offer (IPO). The money from buying or selling of the stock of the company on the exchanges is not received by the company. Investors gain or lose money in the market depending on the rise and fall in share value of the company.
The image below shows the process of the company getting listed on stock exchanges
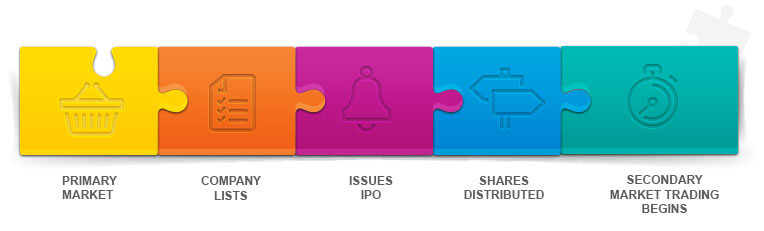
How companies get listed on the stock exchange
Video on What is IPO?
This 7: 06-minute Video in Hindiexplains what is IPO with the example of DMART.
What is the Stock Exchange?
A stock exchange, securities exchange or bourse, is a facility where people can buy and sell securities, such as shares of stock and bonds and other financial instruments. India has two major stock exchanges – National Stock Exchange of India (NSE) and Bombay Stock Exchange of India (BSE). Most of the share trading in the Indian equity market takes place on these two stock exchanges.
We can compare the stock exchange to a supermarket that sells a variety of things in one place offering convenience to customers. It’s more convenient buying from the supermarket that going to different shops or buying from the farmer and the baker. The stock exchange is a supermarket for stocks. It can be thought of as a big room where stocks are sold and bought. If a particular company is traded on an exchange, it is referred to as “listed”.
Stock exchanges are key companies that allow the stock market to work as efficiently as it does. They list shares prices for thousands of companies, they list the bid/ask prices of shares and enable quick electronic transfers of shares between people. As and when trades are conducted, share prices change. This is because the prices of shares, like any other goods, are dependent on the perceived value. This is reflected in the rise or fall in demand for the stock. As demand for the stock increases, there are more buy orders. This leads to an increase in the price of the stock.
Each country has at least one stock exchange. Famous stock exchanges are the New York Stock Exchange(USA), NASDAQ(USA),Japan Exchange Group, London Stock Exchange Group.
Biggest Stock Exchange is New York Stock Exchange in the United States of America which is on Wall Street.
The first stock exchange was Amsterdam Stock Exchange established in 1602 in the Netherlands and it traded shares of the Dutch East India Company.
Listed companies have to comply with the rules and regulations of concerned stock exchange and work under the vigilance (i.e supervision) of stock exchange authorities. The stock market in each country now is governed/controlled by the corresponding governing bodies in that country. Ex: SEC (Securities Exchange Commission) for the USA, SEBI (Securities & Exchanges Board of India) for India.

Stock exchanges of the world
Video explaining how the Stock Exchange Works
Kurzgesagt – In a Nutshell, explains in 3.33 mins in English, how the Stock exchange works.
Who is Broker? Demat and Trading account
Individuals can’t directly go the stock exchange and buy or sell stocks/shares. The people who are authorized to buy and sell in the markets are called brokers. A broker can be an individual or company or even an online agency, registered and licensed by the Securities and Exchanges Board of India (SEBI), who regulates the share markets. To be able to invest in the share market, you need to find a broker first. Examples are ICICI Securities, HDFC Securities and Kotak Securities, Zerodha, ShareKhan etc.
A Demat account will hold the stocks or shares in your name and the same will reflect in your stock portfolio as you can’t hold or store shares in physical form. For buying and selling shares in the stock market you will require a Trading account. It’s like an intermediary who facilitates the buying and selling.
How does buying and selling of shares happen?
As and when trades are conducted, share prices change. This is because the prices of shares, like any other goods, are dependent on the law of supply and demand. This is reflected in the rise or fall in demand for the stock. As demand for the stock increases, there are more buy orders. This leads to an increase in the price of the stock. More is explained in the Video here.
There are multiple parties involved in the process behind the scenes.
- Once you place an order to buy a particular share at a said price, it is processed through your broker at the exchange.
- The exchange ensures the seller has the required stock to sell or not. The exchange confirms the details of the buyers and the sellers to ensure the parties don’t default.
- The stock exchange then facilitates the actual transfer of ownership of shares and payment of money. This process is called a settlement. Earlier, it used to take weeks to settle trades. Now, this has been brought down to T+2 days. For example, if you conducted a trade today, you will get your shares deposited in your demat account by the day after tomorrow ( i.e. two working day).
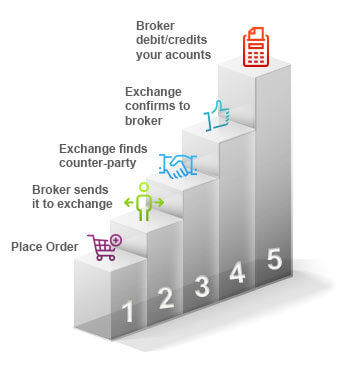
How stock exchange works
Why do the stock prices change?
The price of a stock represents the “value” of the corporation. Stock prices change often (sometimes many times a minute) as the result of market forces. By this we mean that share prices change because of fluctuations in their supply and demand. If more people want to buy a stock at a given moment (demand) than sell it (supply), then the price moves up. if more people are motivated to sell a stock than buy it, there would be greater supply than demand, and the price would fall. Of course, for any trade to actually happen there needs to be exactly one buyer and one seller – so the number of buyers and sellers is technically the same.
But what does a company’s value represent? A company has stuff and it sells stuff. The stuff it has – buildings, machinery, patents, money in the bank, etc. – constitute its book value, or the amount of money a company would get if they sold all that stuff at once. But companies are primarily in business of trying to make a profit, and in doing so they earn cash by selling products or services, so the total value of a company has to do with the stuff it owns now and the cash flows it will receive in the future.
Because the future is unknown today, various peoples’ estimates will be different from one another, giving some a higher expected stock price and some a lower stock price. If the current price is lower than their expected price, people will buy it. If it is higher, people will sell it.
Investors often have differing opinions about particular stocks or about the direction of the economy as a whole. Each trading day is analogous to a struggle between optimists and pessimists who buy and sell at various prices given different expectations. The stock market is said to incorporate all of the information that exists about the companies it represents, and that manifests itself as price. When optimists dominate, prices trend upwards for a period of time, and we say that we are in a bull market. When the opposite is true, and prices trend lower, we are in a bear market.
A bull market is when everything in the economy is running objectively well and stock prices of the company and indices are increasing every day. Bull markets are defined by the market going up aggressively over a period of time.
The bear market definition is exactly the opposite of a bull market. A bear market is informally defined as a 20% drop in broad indices. Bear markets happen when the economy appears to be in or near recession, unemployment rises, corporate profits fall, and GDP contracts.
Stock Market Index: The Basics explains what are stock market indices like BSE and NSE in detail.
Video explaining why the stock prices change?
Why do the stock price keeps on changing? This 4:18 sec video explains.
Stock Exchanges in India
The BSE, Asia’s first stock exchange, was established in 1875. BSE is one of the world’s fastest stock exchanges, with a median trade speed of 6 microseconds. is the world’s 11th largest stock exchange with an overall market capitalization of $1.83 Trillion as of March, 2017. More than 5500 companies are publicly listed on the BSE.
The NSE, on the other hand, was founded in 1992 and started trading in 1994, as the first demutualized electronic exchange in the country. It was the first exchange in the country to provide a modern, fully automated screen-based electronic trading system which offered easy trading facility to the investors spread across the length and breadth of the country. The NSE has a total market capitalization of more than US$1.41 trillion, making it the world’s 12th-largest stock exchange as of March 2016.
Both exchanges – BSE and NSE – follow the same trading mechanism, trading hours, settlement process, etc.
Stock Market Regulator or SEBI
The stock market in each country now is governed/controlled by the corresponding governing bodies in that country. Ex: SEC (Securities Exchange Commission) for the USA, SEBI (Securities & Exchanges Board of India) for India.
The Securities & Exchange Board of India (SEBI) manages the overall responsibility of development, regulation and supervision of the stock market in India. Sebi was formed in 1992 as an independent authority to lay down market rules in line with the best market practices. In case of any breach, Sebi reserves the right to impose penalties on market participants.
Books About Stock Market
- One up on wall street–How To Use What You Already Know To Make Money In the Market by Peter Lynch 1980’s best seller. One Up on Wall Street explains the investment principles that Lynch used during his market-beating tenure as the manager of Fidelity’s Magellan Fund.
- Beating the street by Peter Lynch, published in 1993. Beating the Street fleshes out these principles by providing case studies of the stocks that Lynch recommended in the 1992 Barron’s roundtable.
- Common Stocks & Uncommon Profits by Phili Fisher: Warren Buffett said that this book “enables one to make intelligent investment commitments.”
- The Intelligent Investor by Benjamin Graham
- “A little book that still beats the market” (by Joel Greenblatt)
- “Stocks to Riches” by Parag Parikh
- “The Little Book of Valuation” (by Aswath Damodaran)




Very informative article. Thank you.