For employees who are covered under EPF(Employee Provident Find or EPF), besides their compulsory contribution to PF there is a provision for an additional or Voluntary contribution to EPF popularly called as Voluntary Provident Fund or VPF. The employer will not contribute more. How does taxing of interest on EPF contribution of more than 2.5 lakhs affects VPF? Will it lead to the death of VPF? Let’s find out more about what is VPF? How to contribute? Should one contribute?
From 1 Apr 2021, tax on the interest earned on Employee Provident Fund (EPF) above Rs 2.5 lakh per annum. This was earlier exempt.
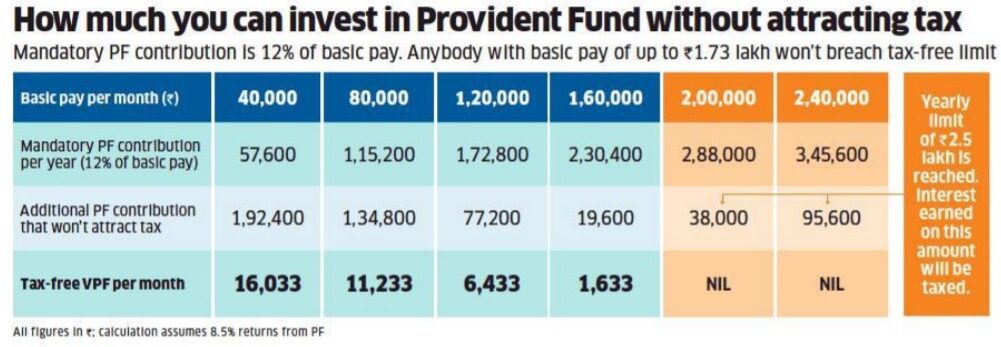
This means that a person contributing only up to Rs 20,833 a month to PF i.e has a basic salary of up to Rs 1.73 lakh a month will not have to pay the tax.
Under the new wage code, effective from 1 Apr 2021, at least 50% of the wage/salary will be a basic salary
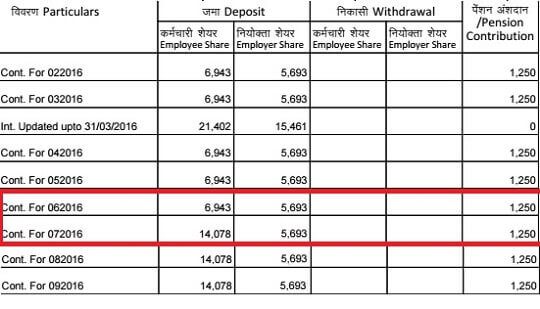
Table of Contents
What is the Voluntary Provident Fund or VPF?
In EPF, an employee has to contribute 12% of his basic pay towards his provident fund account. An equal amount is contributed to by his employer. Apart from contributing the normal 12% of his basic pay, an employee may voluntarily choose to contribute more than 12% he can do so up to 100% of basic and D.A. This is called Voluntary Provident Fund. But the employer will contribute an amount matching only the 12% Here are some of the basic VPF Rules & Guidelines:
- VPF scheme can be availed only by salaried professionals enrolled with the EPF. And its Voluntary.
- An employee may voluntarily choose to contribute more than 12%. But the employer will contribute an amount matching only the 12%
- You can contribute 100% of basic pay plus dearness allowance(DA) as an investment in VPF.
- The contribution is to EPF and not to EPS, Pension Scheme
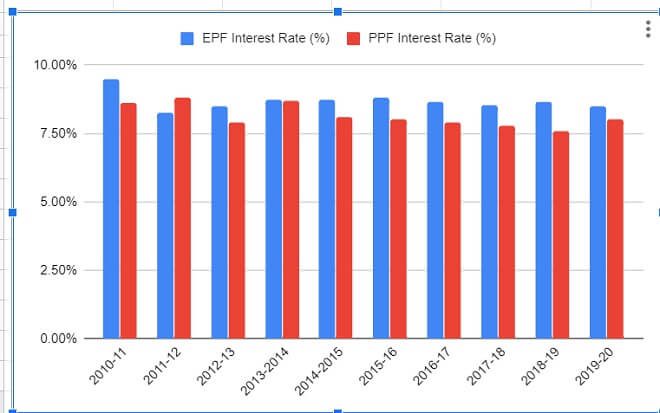
- The contribution will earn the same rate as normal EPF contribution. The interest rate for the Year 2019-20 is 8.5% while for year 2018-19 was 8.65%
- Investments in VPF are considered equivalent to investment in any other investment instruments under section 80C. The tax exemption is till Rs.1.5 lakh.
- VPF is deposited to your existing PF account
- Theoretically one can start contributing to VPF any time and can stop contributions at any time as well. One can also change the amount to contribute to VPF anytime. But usually, the Finance/Payroll department in the company allows the change once or twice a year and usually at the beginning of the financial year.
- Once the contribution is made through VPF, it is treated exactly like contribution through PF, there is no difference. All rules that apply to interest rate/loan/transfer/withdrawal from EPF apply to VPF as well.
- In passbook, VPF contribution does not appear differently.
- When you transfer/withdraw PF, you will automatically transfer/withdraw VPF amount too.
- So If the EPF money is withdrawn within five years, you will have to pay tax on the interest amount earned from your contribution towards the VPF.
While one gets a good risk-free return, one should be prepared to have your money locked in, till the time of retirement/withdrawal on resignation. In case one makes a premature withdrawal, before five years of continuous service and contributions in EPF as discussed one will have to pay tax.
Basic Salary and Dearness Allowance
As the name suggests, Basic Salary forms the very basis of salary. This is the core of salary, and many other components may be calculated based on this amount. It usually depends on one’s grade within the company’s salary structure. It is a fixed part of one’s compensation structure. Many allowances and deductions are described in terms of percentage of the Basic Salary. For example, Your PF is deducted at 12% of your Basic Salary. HRA is also defined as a percentage of this Basic Salary.
Under the new wage code, effective from 1 Apr 2021, at least 50% of the wage/salary will be a basic salary. Details in our article New Wage Code: Will Your Salary fall? How it affects EPF, Gratuity
HRA, LTA are examples of Allowances Allowance is defined as a fixed quantity of money or other substance given regularly in addition to salary for meeting specific requirements of the employees. Some allowances are taxable, some are partially taxable and some are tax-free.
Dearness Allowance is allowance is paid to the employee against the price rise in country economy i.e to reduce the impact of inflation. In India, the Dearness Allowance (DA) is a cost of living adjustment allowance paid to Government employees, Public sector employees (PSU) and pensioners. Private employers typically do not get Dearness Allowance.
Our article, Salary, Net Salary, Gross Salary, Cost to Company: What is the difference, explains it in detail. The formula and payslip showing salary are shown below.
Gross Salary = Basic Salary + Allowances + Perquisites + Fees, Commission and Bonus + Variable Pay+ Retirement Benefits (EPF/NPS)
Net Salary = Gross Salary – Tax (Income Tax, Professional Tax)
CTC = Net Salary + Indirect Benefits( Food coupons, Interest Free Loans)
Sundar Pichai, CEO of Alphabet(Google) was awarded $281 million in compensation? But Pichai’s annual salary in 2019 was $650,000 and the rest was in stock options
Can one change contribution to VPF?
Typically one can start contributing to VPF any time and can stop contributions at any time as well. One can also change the amount to contribute to VPF anytime. But usually, the Finance/Payroll department in the company allows the change at the beginning of the financial year. Please check with your employer.
Typically, the employee must give his option and amount of contribution in writing at the beginning of the financial year, i.e. in April. The amount of contribution can be reduced or increased within the permissible limit once a year, also in the month of April.
VPF and Tax
Both EPF and VPF are exempt from tax implications, under Section 80C. Investments in VPF are considered equivalent to investment in any other investment instruments under section 80C. The tax exemption is Rs.1.5 lakh.
Budget 2021 and effect of Tax on Interest on EPF
Union Budget 2021 proposal which comes into effect from 1 Apr 2021, that employee contributions made to the Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF) or exempted PF trusts above ₹2.5 lakh would trigger taxability on the interest accrued on the amount above the threshold limit. The tax would eat into returns from VPF.
Will it make sense to continue investing in VPF after this change, especially for those in the higher tax bracket?
How much contribution to VPF is tax-free?
A person contributing up to Rs 20,833 a month to PF i.e has a basic salary of up to Rs 1.73 lakh a month will not have to pay the tax.
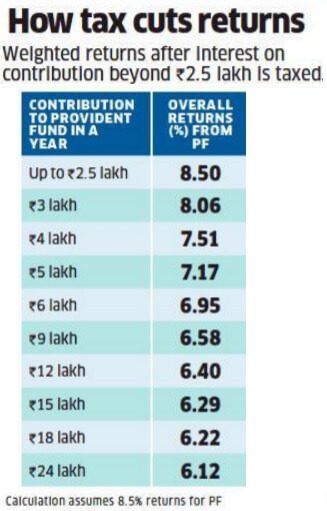
What are EPF returns after the tax?
The tax would eat into returns from VPF as shown in the image below.
Alternatives to VPF?
VPF investors will have to assess their risk appetite and look for alternatives like Small savings schemes(PPF, KVP etc), Fixed Deposit, NPS, Gilt funds
The interest rate on EPF is typically higher (8.5 percent) rather than other small savings schemes such as public provident fund, senior citizen savings scheme, Kisan Vikas Patra, and Sukanya Samriddhi and fixed deposit.
This higher rate prompts employees to put higher corpus in EPF, which in turn makes it difficult for the government to pay interest on the same
Tax-free bonds give a yield of 4.5% which is lower than the post-tax return of VPF
One can invest in PPF(Public Provident Fund) if one has not exhausted the limit of Rs 1.5 lakh.
For conservative investors, gilt funds or constant maturity gilt funds, or target date gilt/index funds would be a good option.
NPS and VPF
NPS has scored in terms of returns over EPF in the past few years, but its returns are not as risk-free as EPF’s, but they are competitive in terms of tax efficiency now.
Returns on NPS are market-linked. Over the past five years, equity schemes in NPS have given returns of 15-16%, corporate bond funds 9-10%, and government bond funds 10-11%. However, these returns fluctuate considerably compared to the 8-9% interest historically paid out on EPF. Details in All About NPS, National Pension Scheme
They both get a tax deduction at the contribution stage (EPF up to ₹1.5 lakh and NPS up to ₹2 lakh);
Interest accumulation is tax-free for both
but there is a minor difference at the withdrawal stage. While the entire EPF corpus is tax-free until FY20 (which will now change once the budget proposal is implemented in FY21), only 60% of the NPS corpus is tax-free. The remaining 40% mandatorily goes into buying an annuity which is taxable.
The image below shows the comparison of NPS and EPF
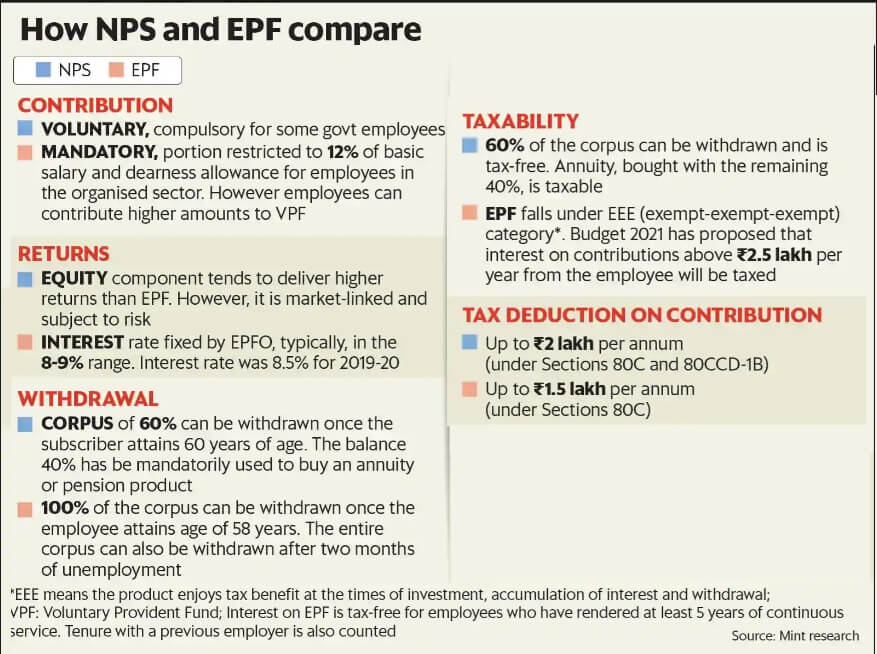
Should One invest in VPF?
With the EPF and VPF scheme, you will receive a fixed rate of interest for the entire tenure of the account
EPF also falls under the EEE tax regime wherein the interest received (on retirement from service or after 5 years of continuous service) is tax-free.
While one gets a good risk-free return, one should be prepared to have your money locked in, till the time of retirement/withdrawal on resignation
Though the Provident Fund scheme is extremely safe, upon retirement, the amount saved up will be sizable but may not be enough to cover the rising costs of living and inflation of the economy. Taking this into consideration, investing in EPF and VPF alongside other investments is advisable. For example, investing in mutual funds and SIPs in diversified equity funds will result in much higher returns. By investing in both, you can reap the benefits of a fixed-income product as well as a long-term growth product.
How much more can I save using VPF?
An employee starts with a basic salary of Rs. 20,000 at 25 years and works till 60 years. Every year, on average, he gets a 5% increment. He contributes 12% of his basic salary towards PF which is matched equally by one’s company, (EPF contribution is 3.67%, EPS 8.67%). Over the course of 35 years of his working life, his total contribution is Rs. 26.01 Lakhs. Of course, his company makes a contribution of Rs. 7.955 Lakhs, a total contribution of Rs 33.967 lakh. And this amount grows into – Rs. 1.38 Crores at the time of his retirement in 35 years!
More the EPF contribution more the compounding, you would save more.
What is the difference between VPF and EPF?
EPF is a compulsory contribution while VPF is voluntary.
Once the contribution is made through VPF, it is treated exactly like contribution through PF – there is no difference.
VPF is deposited to your existing PF account. Therefore, all rules that apply to interest rate/loan/transfer/withdrawal from EPF apply to VPF as well. When you transfer/withdraw PF, you will automatically transfer/withdraw VPF amount too – as VPF is part of your PF account, it can be transferred or withdrawn along with PF amount.
How can one start contributing to VPF?
You can start VPF by contacting the Finance/Payroll department of the company. Submit a joint declaration form given below.

VPF and Passbook
VPF amount is available in the passbook which can be downloaded from EPF site. There is no distinction between mandatory EPF and optional VPF amount. The image below shows the EPF passbook where in Jul 2016 the employee started contributing to VPF. So the contribution on EPF jumped from 6,943 to 14,078. Note employer contribution to EPF or EPS did not increase.

Why is VPF not popular?
With more options available like PPF /MFs the VPF has no major attraction in employee community. This was in practice in early years as many employees’ savings are only through ‘Forced’ deductions. As per Investment Consultant, Sandeep Shanbhag in says “Companies usually do not encourage their employees because it would mean a higher interest cost for the trust”.
While one gets a good risk-free return, one should be prepared to have your money locked in, till the time of retirement/withdrawal. In case one makes a premature withdrawal, before five years of continuous service and contributions in EPF as discussed in , one will have to pay tax.
What is the difference between EPF, VPF and PPF?
EPF is also referred to as PF stands for Employees’ Provident fund and PPF stands for Public Provident fund. As the name suggests, only eligible employees working in some organisation can subscribe to EPF through their employer, whereas a PPF account can be opened by any resident individual in India. Some more differences are given below
| Features | Public Provident Fund | Employee Provident Fund | Voluntary Provident Fund |
| Who can Invest? | Any Resident Indian, except NRIs | Any Resident Employed Individual | Any Resident Employed Individual |
| Min Period of Investment | 15 years | Up to retirement or resignation, whichever is earlier | Up to retirement or resignation, whichever is earlier |
| Employee Contribution on Basic + DA | N.A | 12% of Basic salary | Voluntary (Upto 100% of Basic) |
| Employer Contribution | N.A | 12% of Basic salary | N.A |
| Taxation on Maturity Returns | None | Tax Free | Tax Free |
| Tax Deduction | As per section 80 C | As per section 80 C | As per section 80 C |
| Maturity | Can be extended indefinitely by extending for 5 years each after that. | Can transfer account to new company till retirement. | Can transfer account to new company till retirement. |
| Maximum Loan amount | Partial withdrawals are permitted | Partial withdrawals are permitted | Partial withdrawals are permitted |
Comparison of the Interest rate of EPF and PPF
Video on VPF
This 5-minute video explains What is VPF?, Voluntary Provident Fund – Should one opt for it?
How well do you understand VPF?
Can you answer these questions about VPF? Drop in the comment, if you can
- Can VPF be availed by anyone?
- Is VPF Compulsory?
- I have a PPF account can I have VPF?
- How much can one contribute to VPF?
- Can one increase, decrease, stop VPF contribution?
- How much interest rate does VPF earn?
- Are there any tax benefits for VPF?
- What happens to VPF when you leave your job?
- When can you withdraw from VPF?
- What changes effective from 1 APr 2021 will affect the EPF & VPF?
Related Articles:
All About EPF,EPS,EDLIS, Employee Provident Fund
All About UAN or Universal Account Number of EPF
Salary, Net Salary, Gross Salary, Cost to Company: What is the difference
New Wage Code: Will Your Salary fall? How it affects EPF, Gratuity
- EPF Withdrawal:How to withdraw from EPF and EPS
- How to Correct EPF Details like Name,Father Name,Date of Joining
- Change Mobile Number in UAN if forgotten Password and Mobile Number Changed
Hope you have found this article helpful. Is VPF popular? Should one contribute to VPF? Have you contributed to VPF? Or you contribute to PPF? if given a choice would you choose VPF or PPF?

23 responses to “Voluntary Provident Fund, Difference between VPF, EPF and PPF”
Thanks for sharing, this article is extremely great and useful for users. Thanks and keep Sharing.
Dear Concern,
What Is The Mean Of VPF I Can’t Understand It VPF Is A Fund Or What Kindly Provide Me More Details About The VPF. There VPF OR EPF Functioning Different ? How Can I Apply For VPF Fund Please Give Me Suggestion. I Am A Employee Of Finance Sector but My Colleagues don’t No What Is VPF Please Help Me ASAP…….
In EPF, an employee has to contribute 12% of his basic pay towards his provident fund account. An equal amount is contributed by his employer. Apart from contributing the normal 12% of his basic pay, an employee may voluntarily choose to contribute more than 12% he can do so up to 100% of basic and D.A. This is called Voluntary Provident Fund. But the employer will contribute an amount matching only the 12%
Please read the article and let us know what your doubts.
We shall try to answer them
Dear Sir
X has a basic salary of Rs. 10000 and DA of Rs. 6000.
He opts for EPF.
Now my question is how much X is legally bound to contribute towards EPF?
is it 12% of Rs. 16000 or is it 12% of Rs. 15000.
regards
shivaniadream@gmail.com
12% contribute of Rs. 16000
8.33% Contribute of Rs. 15000
3.67 % Contribute of Rs. 15000
I want to register my premise in vpf with number of employee of 11 with consent of all employee can i duty bound after getting registration to deduct employees’ salary and deposit pf account for all 11 employee
Please reply
can I out in VPF? I have cover in VPF last 5 month
Technically it is feasible for organizations to start and stop VPF contribution during financial year but its an operational nightmare for them. Under special circumstances they may accept your request to start or stop contribution to Voluntary Provident Fund during FY.
Typically If you are planning to contribute to Voluntary Provident Fund then you need to inform your organization at the beginning of financial year. You cannot start contributing in between the FY. Secondly, once you opted then you cannot back out or stop your contribution during Financial Year. You have to compulsorily complete cycle of financial year.
So please verify with your organization and update us too!
Hi,
I have one query that, like VPF, is there any provisions of Voluntary Pension scheme. May be some of have poor pension, by voluntary payment, they can expect more pension after 60.
Thanks in advance.
Regards
Gangadhar
There are many options like Atal Pension Yojna or pension schemes of Insurance companies.
Do remember that pension is taxable.
One has to plan retirement and pension plans are one such way
Thank you for sharing information.
It is valuable post.
1) I am contributed from 10-11month can I apply for loan want to used that money, is it possible.
2) Can used this facility or is their any way to used that invest amount.
Great & very useful information on VPF indeed. Your work is highly appreciated…
Here goes my question:
I have opted for INR 1000/month as my VPF contribution for the past 5 years. I am working in an xyz organisation for the past 6 years. When I checked my EPF balance, It says your balance EE amount is INR 1,44,683 & ER amount is 56,433. I am aware of the fact that what is shown here is employee provident fund = ( employee 12% + 3.67% of employer share) excluding employee pension fund = remaining 8.33% of employer share. One thing that strikes my mind is, is my VPF contribution includes in my EE amount? if yes, then Employee share provided here should be > 12%. Please help me to understand this. Because if employee and employer contribution is same as per rule, then does this mean that my employer has to deposit equal amount as my VPF over month on month?? 🙂
Regards,
Syed Tajuddin
Please tell me min VPF
You run a great blog here and I really appreciate the good work you are doing…
I have a question
“In case one makes a premature withdrawal, before five years of continuous service and contributions in EPF as discussed in , one will have to pay tax.”
Does the phrase ‘five years of continuous service and contributions in EPF’ mean only a continuous service in a single organisation ?
Can a person who have switched companies but his contributions to EPF is continuous and to the same PF account withdraw a prt of his PF tax-free ?
Glad you liked our blog Saravana.
As discussed in our article Withdrawal from EPF,EPS
In case you are a member of recognized provident fund it depends on if contribution is over 5 years or not, including transfers from different companies. For ex: an employee who has worked with X company for say 3 years, then he resigned from that organisation and joined Y company, wherein he worked for 2 years, then resigned from there to join establishment for 2 years but during these 7 years of service he has not withdrawn but transferred his Employee provident fund, then we say continuous service of 7 years.
So five years of continuous service and contributions in EPF does not mean continuous service in a single organisation.
I am not sure if partial withdrawal is allowed from EPF. Let me verify and then get back to you.
Thanks for the information.
My question is – in case the employer doesn’t allow investment in “VPF”, is there any alternative way of investing in VPF?
Sorry Vishwanath I don’t think there is any other way to contribute to VPF but you can open PPF account.
shared information is really useful
thanks
-Raj
Thanks a lot Rajesh. Your words are very encouraging!
Can one make a one-time contribution of a large sum (say 5 Lakhs) to VPF in addition to the monthly VPF contribution?
From what I know or have read it is not possible to make one-time contribution of a large sum to VPF. Incase you come to know of something else please let us know too!
A deep and thorough article on VPF.
I joined a job in late 2010 and in year 2011-2012 I opted for VPF 2K per month along with EPF for 80C contribution but I was not aware of other details that you mentioned in this article. I think I made a good choice, as VPF is better and more convenient than PPF.
One thing I wish to point out, please update the information when referring/quoting
an old reference, like in table you mentioned for PPF limit as 70K while it has been enhanced to 100K
Thanks for an informative post.
Saumya
Thanks Saumya for pointing out the error – yes we had kept PPF limit as 70K only. We updated the interest to 8.6% but overlooked this.
We would suggest opening a PPF account also, if it fits in with your asset allocation as it falls under EEE.