On 19 Aug 2015, RBI gave in-principle licences to eleven entities to launch payments banks. What are Payment Banks, What are different Kinds of Banks in India, what is the history of Banking in India are some of the questions that are covered in the article.
What are Payment Banks?
Payment banks are banks which will offer selected services as compared to full fledged banks. A payment bank can only receive deposits and provide remittances. It cannot carry out lending activities. This type of bank is targeted at migrant labourers, low income households, small businesses, and other unorganised sector entities to to help India reach its financial inclusion targets. These banks have to use the word Payment Bank in its name which will differentiate it from other banks.
While Airtel has launched its services, other players like Paytm, FINO PayTech and Aditya Birla Idea Payments Bank are looking to launch theirs by early 2017.
IndiaPost has become the third entity to receive a final license from the Central Bank to start its payment bank operations. Country’s largest telcom service provider Bharti Airtel and digital payments firm Paytm are the other two to have received the license while only Airtel has started operations so far. Operations are expected to start before March 31 and will be gradually rolled out in 650 districts using the network of 1.54 lakh post offices.
Airtel Payments Bank offers 7.25% interest on deposits in savings accounts. Large commercial banks such as State Bank of India and ICICI Bank Ltd offer 4% . Some banks offer interest on savings account in the range of 5.5-7.1%, depending on the deposit amount.
Table of Contents
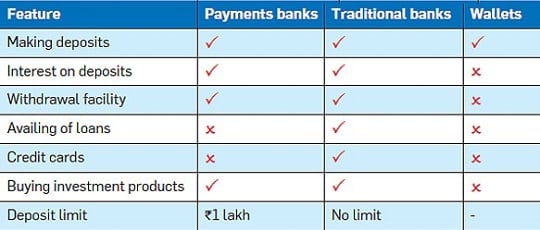
Difference between Payment Banks, Traditional Banks and EWallets
Payment Banks differ from both traditional banks and e-wallets in terms of services. Payments banks pay interest, can’t lend
Airtel Payment Bank
Finance minister Arun Jaitley formally launched Airtel Payments Bank Ltd on Friday in New Delhi. A joint venture between phone services provider Bharti Airtel Ltd and Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd, the payments bank went live with a network of 250,000 banking points. In the pilot phase, the bank added over 1 million customers.
Airtel Payments Bank offers 7.25% interest on deposits in savings accounts. Large commercial banks such as State Bank of India and ICICI Bank Ltd offer 4%. Some banks offer interest on savings account in the range of 5.5-7.1%, depending on the deposit amount.
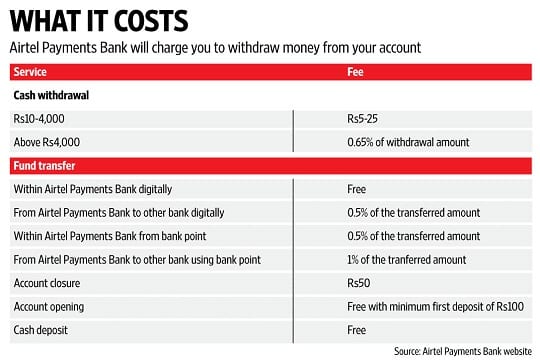
Cost associated with Airtel Payment Bank are given below
Why are Payment Banks important?
It’s a step to redefine banking in India. The Reserve Bank expects payment banks to target India’s migrant labourers, low-income households and small businesses, offering savings accounts and remittance services with a low transaction cost. Payments banks are therefore expected to create some disruption in the banking system and bring banking to the masses on a wider scale.
- It hopes payments banks will enable poorer citizens who transact only in cash to take their first step into formal banking. So For unbanked customers, a payments bank account will provide the much-needed access to banking services.
- It could be uneconomical for traditional banks to open branches in every village but the mobile phones coverage is a promising low-cost platform for quickly taking basic banking services to every rural citizen. A labourer working in a metro, today spends about half a day in a queue at the local bank branch to transfer money to his family in the village. With a payments bank account, he may be able to do it through his phone which need not even be a smart phone.
- The innovation is also expected to accelerate India’s journey into a cashless economy. The new payment banks will also make people less dependent on cash, even for small sums, and since a mobile wallet could be a bank account soon, this move could, over time, have a big impact on m-commerce.
For customers who already have bank accounts, a payments bank account can be an additional one from which they can carry out all their remittance and transactions electronically. They can avoid handling cash.
What the Payment banks can do?
- They can raise deposits of upto Rs. 1 lakh, and pay interest on these balances just like a savings bank account does.
- They can enable transfers and remittances through a mobile phone.
- They can offer services such as automatic payments of bills, and purchases in cashless, chequeless transactions through a phone.
- They can issue debit cards and ATM cards usable on ATM networks of all banks.
- They can transfer money directly to bank accounts at nearly no cost being a part of the gateway that connects banks.
- They can provide forex cards to travellers, usable again as a debit or ATM card all over India.
- They can offer forex services at charges lower than banks.
- They can also offer card acceptance mechanisms to third parties such as the ‘Apple Pay.’
What the Payments banks cannot do?
- No NRI deposits should be accepted
- Cannot issue credit card
- Not allowed to set up subsidiaries to undertake non-banking financial services activities
- Other financial and non-financial services activities of the promoters should not be mingled with the working of payment banks
TimeLine of Payment Banks
- On 23 September 2013, Committee on Comprehensive Financial Services for Small Businesses and Low Income Households, headed by Nachiket Mor, was formed by the RBI.
- On 7 January 2014, the Nachiket Mor committee submitted its final report. Among its various recommendations, it recommended the formation of a new category of bank called payments bank.
- On 17 July 2014, the RBI released the draft guidelines for payment banks, seeking comments for interested entities and the general public.
- On 27 November, RBI released the final guidelines for payment banks
- On February 2015, RBI released the list of entities which had applied for a payments bank licence. There were 41 applicants. It was also announced that an external advisory committee (EAC) headed by Nachiket Mor would evaluate the licence applications.
- On 28 February 2015, during the presentation of the Budget it was announced that India Post will use its large network to run a payments bank.
- The external advisory committee headed by Nachiket Mor submitted its findings on 6 July 2015. The applicant entities were examined for their financial track record and governance issues.
- On 19 August 2015, the Reserve Bank of India gave in-principle licences to eleven entities to launch payments banks
Who has Reserve Bank granted in-principle approval to be a payment bank?
The RBI guidelines said that payment bank licenses would be granted to mobile firms, supermarket chains, and others, to cater to individuals and small businesses. Of the 41 companies and individuals that applied, only 11 have been selected. The one selected in alphabetic order are given below
- Aditya Birla Nuvo Ltd
- Airtel M Commerce Services Ltd
- Cholamandalam Distribution Services Ltd
- Department of Posts
- Fino PayTech Ltd
- National Securities Depository Ltd
- Reliance Industries Ltd
- Dilip Shantilal Shanghvi
- Vijay Shekhar Sharma (Paytm)
- Tech Mahindra Ltd
- Vodafone m-pesa Ltd
The companies that have been selected right now seem to be according to the RBI gudielines. The Department of Posts can reach every village, and connect farmers to banks. The phone companies in particular have large distribution networks throughout India, even in rural locations, and this will help as people will be able to easily convert cash into virtual money and vice versa example m-Pesa. Vijay Shekhar Sharma(Paytm) cash wallet is pretty popular due to its tie up with many taxi services and online sites. Many people use their telco’s wallets to pay their phone bills in exchange for discounts on the bill.
What will the Impact of Payment Banks on Regular banks?
The impact on private sector banks will be minimal because they have already made strong investments in technology. Also some of the private sector banks like Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd, Yes Bank Ltd and ICICI Bank Ltd have tied up with some of the companies that have got approval for setting up payment banks and hence will not be affected much.
RBI governor Raghuram Rajan, in an interaction with State Bank of India chairperson Arundhati Bhattacharya on 20 Aug 2015, made light of the threat to big banks from payment banks, and said instead they could act like feeder banks and make the larger banks more competitive.
But there could be an impact on small and medium public sector banks as incremental deposit growth and market share will see some impact from payment banks, especially in the rural and semi-urban areas.
In fact, competition for banks is only going to get tougher. RBI is going to announce small finance banks soon and is currently evaluating around 70 applications.
Are there Banks similar to Payment Banks in countries other than India?
Payment technologies have proved hugely popular in other developing countries. In Kenya, the most cited success story, Vodafone’s M-Pesa is used by two in three of adults to store money, make purchases and transfer funds to friends and relatives. In China, mobile apps have mushroomed and have started threatening the traditional banks, so much so that many customers have switched directly from cash transactions to banking through mobile apps.
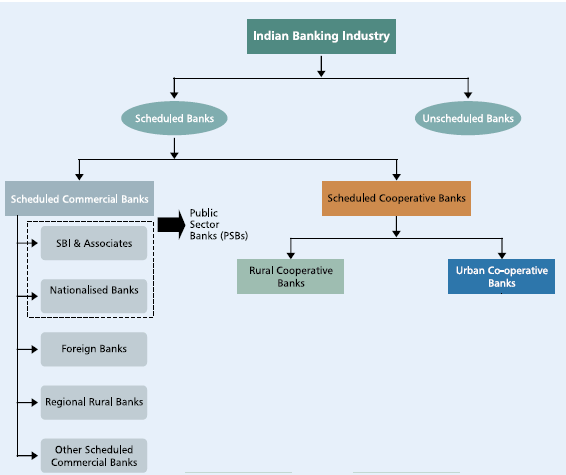
Banks In India
The Indian banking sector is fragmented, with 46 commercial banks including 27 public sector banks, jostling for business with dozens of foreign banks as well as rural and co-operative lenders. The following image shows List of Banks under various categories refer to RBI Banks in India and Wikipedia List of Banks in India
History of Banking in India
Banking industry in India goes back to the 18th century when two banks the General Bank of India and Bank of Hindustan operated under the British rule. These banks are no longer operational. Around 1796, three important presidency banks were established. The Indian government owned its first bank the State Bank of India (SBI). It was formed after the merger of Bank of Bengal. SBI is still functional today.
For more details refer to our article
Related Articles:
- What are Mobile Wallets or Digital Wallets
- Different ways of Banking:Internet,Mobile
- Interest on Saving Bank Account : Tax, 80TTA
- What do we want from Bank : Is Social Banking the way to go?
- What is Auto Sweep Bank Account?
- JAM Trinity: Jan Dhan Yojana, Aadhaar and Mobile number
What do you think of Payment Banks. What changes do you want in Banking, what form of Banking do you use, internet,mobile,social,

15 responses to “Payment Banks,Types of Banks in India, History of Banking in India”
Hi
B. Tech engineering passout
Chethan R tataguni Tataguni post
Hi Sir,
My uncle’s dividend warrants are getting deposited in the India Investor Fund. Can you please help us with it. Is there a way to get that money back? The reason they give is that the person doesn’t exists on the particular address, even though we sent them the mail, that we stay on the same address as mentioned in the Karvy’s record?
Regards,
Kinshuk
The mutual Fund houses issue dividends on a regular basis. Earlier, they used to issue cheques and send them to Unitholders’ addresses. Investors who have not updated their communication addresses or bank account details might not have claimed the dividend cheques.
The mutual funds keep the unclaimed dividends for three months. After that, they are reinvested in the money markets.
The Mutual Fund houses can invest these amounts for three years. After that they have to transfer the gains made on these re-investments to Investor Education fund.
Investor can claim the dividend money anytime. The principal amount with gains earned in 3 years will be paid back.
They may charge upto 0.5% on the dividend amount when the unitholder claims the dividend.
How to Claim? – You should have the folio no. of the mutual fund investment. Approach the mutual fund house with folio no. If the investor is no more then the nominee has to submit the required proof of legal heir documents.
Please approach the Mutual Fund again. DO the KYC .We suggest you make use of the ECS facility and get dividends and redemption proceeds directly credited in your bank account.
Hi Sir,
My uncle’s dividend warrants are getting deposited in the India Investor Fund. Can you please help us with it. Is there a way to get that money back? The reason they give is that the person doesn’t exists on the particular address, even though we sent them the mail, that we stay on the same address as mentioned in the Karvy’s record?
Regards,
Kinshuk
The mutual Fund houses issue dividends on a regular basis. Earlier, they used to issue cheques and send them to Unitholders’ addresses. Investors who have not updated their communication addresses or bank account details might not have claimed the dividend cheques.
The mutual funds keep the unclaimed dividends for three months. After that, they are reinvested in the money markets.
The Mutual Fund houses can invest these amounts for three years. After that they have to transfer the gains made on these re-investments to Investor Education fund.
Investor can claim the dividend money anytime. The principal amount with gains earned in 3 years will be paid back.
They may charge upto 0.5% on the dividend amount when the unitholder claims the dividend.
How to Claim? – You should have the folio no. of the mutual fund investment. Approach the mutual fund house with folio no. If the investor is no more then the nominee has to submit the required proof of legal heir documents.
Please approach the Mutual Fund again. DO the KYC .We suggest you make use of the ECS facility and get dividends and redemption proceeds directly credited in your bank account.
Very well explained!!
Very well explained!!
I always find your blog full of useful information that are not known to general public at great depth…. Thanks again for sharing such an informative article….
Thanks Debopam for your comment
I always find your blog full of useful information that are not known to general public at great depth…. Thanks again for sharing such an informative article….
Thanks Debopam for your comment