Maternity leave is the leave from the office when a woman is on leave because she is about to have or has just had (or adopted), a baby. Under the Maternity Benefits Act of 1961, a women employee is entitled to maternity benefits at the rate of her average daily wage for the period of her absence, for a maximum period of 26 weeks(from 29 Mar 2017 earlier was 12 weeks) or as per the HR policy of the company. This article discusses Maternity Leave, Maternity Benefit Act, How duration of Maternity Leave is calculated, about wages one will get, about Earned leave during Maternity Leave. It also shows Maternity Leave in some Private companies in India, Maternity Leave across the world. Will long Maternity Leave be used as a excuse by employers to hire fewer women or fire them when they apply for Maternity leave.
Table of Contents
What are Maternity Leave benefits?
Maternity leave in India is a paid leave of absence from work that allows women employees the benefit of taking care of their newly born, and at the same time retain their jobs.
The objective of maternity leave and benefit is to protect the dignity of motherhood by providing for the full and healthy maintenance of a woman and her child when she has recently delivered or adopted a child.
- Women after 1 Apr 2017 are entitled to 26 weeks of maternity leave(earlier was 12 weeks) for which they will be paid.
- This Act is applicable to all organizations that employ 10 or more persons both in the private sector and public sector.
- The six-month maternity leave benefit is only applicable for two surviving children.
- Women who opt for a child through surrogacy or adopt a baby below three months will be entitled to only 12 weeks of maternity leave.
- For mothers with more than two children, the maternity benefits will only cover 12 weeks.
- How she takes those 26 weeks depends on her. She can take all her Maternity Leave after the birth of her child. She can start her Maternity leave anytime in 8 weeks before her due date.
- One gets Maternity Leave also for miscarriage or medical termination of pregnancy
- An employer cannot dismiss a woman for taking maternity leave and cannot serve a termination notice to a woman on maternity leave which expires before the maternity leave ends. Also, an employer can’t change the terms of service to the woman’s disadvantage during her maternity leave.
- Expenses for Maternity are often covered in insurance offered by the employer up to some amount. Those with ESIC get some financial benefits too
After the Maternity Leave
- Mothers may be allowed to work from home beyond the 26-week maternity leave period. Depending upon the nature of work, women employees may be able to avail this benefit on terms that are mutually agreed with the employer.
- Organizations with 50 employees will now have to mandatorily have crèches. Another option is for a few firms to set up a common facility within a prescribed distance.
- The employer will have to allow the mother to have four visits to the crèche which will include the interval of rest allowed to women employees.
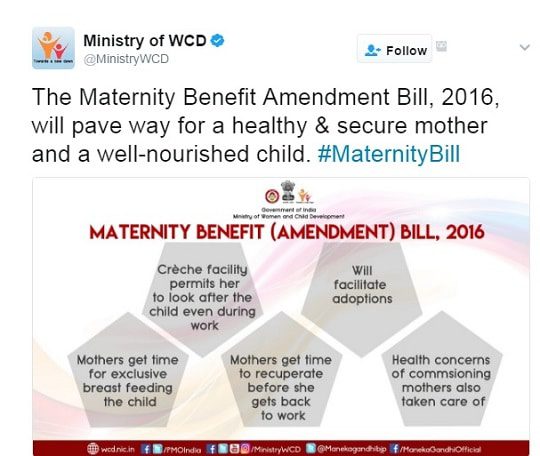
How are 26 weeks of Maternity Leave calculated?
According to the Maternity Benefits Act 1961, a women employee is entitled to 26 weeks of which not more than 8 weeks(earlier was 6 weeks)s shall precede the date of her expected delivery. How she takes those 26 weeks depends on her. She can take all her Maternity Leave after the birth of her child. She can start her Maternity leave anytime in 8 weeks before her due date.
- When a woman dies during this period, before delivering the child, the maternity benefit shall be payable only for the days up to and including the day of her death.
- When a woman, dies during her delivery or during the period immediately following the date of her delivery for which she is entitled for the maternity benefit, leaving behind in either case the child, the employer shall be liable for the maternity benefit for that entire period but if the child also dies during the said period, then, for the days up to and including the date of the death of the child
When can a women employee take Maternity Leave?
- In case of miscarriage or medical termination of pregnancy, a woman shall, on the production of such proof as may be prescribed, is entitled to leave with wages at the rate of maternity benefit, for a period of six weeks immediately following the day of her miscarriage or, as the case may be, her medical termination of pregnancy.
- In case of tubectomy operation, a woman, on the production of such proof as may be prescribed, is entitled to leave with wages at the rate of maternity benefit for a period of two weeks immediately following the day of her tubectomy operation.
- A woman suffering from illness arising out of pregnancy, delivery, premature birth of a child (Miscarriage, medical termination of pregnancy or tubectomy operation) be entitled, in addition to the period of absence allowed to her leave with wages at the rate of maternity benefit for a maximum period of one month.
- Maternity Leave is also allowed for having a Child through Adoption or Surrogacy
Does the employee pay for delivery charges?
Many companies also offer health insurance benefits often covering maternity also up to some predefined limit and usually up to two children.
It can also be claimed by a male employee for his wife’s hospitalization expenses.
The maternity benefit is available for normal as well as C-section deliveries.
After how long can one claim maternity benefits depends on the company’s policies. Many offer the benefits as soon as one joins the company. But please check your company policy
Most employer’s group insurance policies cover hospital charges up to a fixed amount and pre-and post-delivery hospital stay for up to 60 days. Some insurance companies also cover the pre-and post-delivery charges.
But such policies don’t cover routine monthly check-ups and medical termination within 12 weeks of pregnancy. You can claim these expenses along with your other Medical Bills if your company provides the benefits.
If you are not covered by your employer’s group insurance, you can avail of family insurance provided by many insurance companies. However, most of these insurance schemes require that you are with them for at least 24 months before the pregnancy, and have paid three premiums.
What are the wages that one gets for Maternity Leave?
The average daily wage means the average of her wages during the three-month period immediately before her maternity leave starts. The company will pay the full wages and not just the basic salary. Wages for Maternity Benefit includes DA, HRA, other cash allowances, incentive bonuses. But it does not include following:
1) any bonus other than incentive bonus
2) overtime earnings & any deduction or payment on a/c of fines
3) any contribution to any pension fund or provident fund or for the benefit of the woman under any law for the time being in force
4) any gratuity payable on the termination of service.
If you need it, the law allows for up to a month of sick leave if the illness or problem requiring leave is because of your pregnancy, delivery or premature birth. During this month, you are entitled to your usual wage. But you will need to submit proof of the illness.
Does one get Earned or Paid Leaves during Maternity Leave?
This is a grey area. Depends on the organization.
Many feel that Earned or Paid Leave is credited on account of an employee’s presence on the duty. But Maternity Leave is not considered as leave. It is a social benefit being provided through the Maternity Benefit Act for a period that is regarded leave irrespective of actual physical absence from duties. So a women employee will get Earned Leaves during her Maternity Leave.
But In many organizations, The entire period availed as maternity leave would be taken into account for the purpose of calculation of 240 days of continuous service which is the eligibility criterion for EL to be availed in the succeeding year. Yet, as the employee does not work actually during these days of maternity leave, she will not earn any leave on these 26 weeks
Our article covers various kinds of leaves Casual Leave, Earned Leave, Sick Leave: Leaves in India in detail
Medical Bonus during the Maternity Benefit.
A pregnant woman worker is entitled to a maternity benefit,in the form of a medical bonus, of Rs 1000 if no prenatal confinement and post-natal care are provided by the employer free of charge. It can be increased to a maximum limit of Rs 20,000.
The Central Government is authorized to increase the basic amount every three years. In August 2008, the amount of medical bonus was Rs 2500 which has been later raised in 2011 to Rs 3500. (Note: Bonus under the ESI Act is Rs 5000)
How to Claim Maternity Leave?
A woman employee is required to give her employer notice in writing/apply on the leaves portal asking for maternity leave and benefits.
The exact process depends on the HR policy of your company.
Discuss it with your manager as soon as you are pregnant. To plan the work during the pregnancy, transition plan before maternity
Can one extend the Maternity Leave?
If the employee becomes ill due to any of the illness arising out of pregnancy/delivery then she is entitled to an additional 30 days leave with wages under the Maternity Benefit Act. One needs to submit proof of illness and the employer has to agree to it.
If after Maternity leave if a women employee requires more days leave that can be adjusted with her available leave balance depending on company HR Leave Policy. Some companies allow women employee to club her Casual Leave(CL)/Sick Leave(SL) /Earned Leave(EL), which she has to her credit, with Maternity Leave. Many do not allow Sick Leave or Casual Leave to be clubbed with Maternity Leave.
Maternity Benefit Act
THE MATERNITY BENEFIT ACT, 1961 (53 OF 1961), is an act to regulate the employment of women in the private sector for a certain period before and after child birth and to provide for maternity benefit and certain other benefits. It became effective from 12 Dec 1961.
Earlier the Maternity benefit was for 12 weeks. On 29 Mar 2017 President signed the Maternity Benefit Amendment bill to extend the benefits to 26 weeks.You can read the act here.(pdf) and Amendment in 2017 here.
Under the Maternity Benefits Act of 1961, a women employee is entitled to maternity benefits at the rate of her average daily wage for the period of her absence, for a maximum period of 26 weeks(earlier was 12 weeks). She can claim Maternity Leave only if she has worked at least 80 days for her employer in the last 12 months. HR policies for Maternity Leave vary from company to company. Please check with the HR department of your company to find out more about its policy on maternity leave.
- The average daily wage means the average of her wages during the three-month period immediately before her maternity leave starts.
- The law also states that from 10 weeks before the women’s employee’s due date, she will not have to do arduous work, stand for long hours or be asked to do any other work that may cause problems. A working woman also has the right to ask for light jobs during pregnancy for eg., jobs that do not require long standing hours or work in sections where hazardous substances are not used as per the maternity benefit act.
- If a women employee miscarries, she is entitled to 12 weeks of leave and wages.
- India now qualifies among the 16 countries having the longest paid leave for new mothers. Ref: Lok Sabha Question
Maternity leave in Government Jobs
Women employed in government jobs in India get a six-month maternity leave as per the Central Civil Service (Leave) Rules 1972. The last circular in this regard was issued in 2008, when it was increased from four-and-a-half months. Moreover, women government employees are allowed to take childcare leave of up to two years in phases at any point till their child turns 18 years old. The Seventh Pay Commission recently recommended that only the first 365 days of leave should be granted with full pay, while the remaining 365 can be availed at 80 per cent of the salary. Memorandum from the Department of Personnel and training can be read here.
Alternatives to the Maternity Benefits Act
In lower-income jobs, the Employees’ State Insurance, a self-financing social security and health insurance scheme for workers, maybe an alternative source of maternity benefits. The ESI is due to employees earning Rs. 15,000 or less per month, with the employer contributing 4.75 percent and the employee contributing 1.75 percent. Those who qualify may receive maternity benefits under the ESI scheme instead of the Maternity Benefits Act. In order to be eligible for maternity benefit under ESI Act, 1948, an insured woman should have contributed/contribution payable for not less than 70 days in the last two consecutive contribution periods i.e. one year. ESIC website covers details of Maternity Benefit.
Can a women employee on probation apply for Maternity Leave?
Women on probation can apply for maternity leave if she meets following conditions.
- Every woman employee, whether employed directly or through a contractor, who has actually worked in the establishment for a period of at least 80 days during the 12 months immediately preceding the date of her expected delivery, is entitled to receive maternity benefit.
- The qualifying period of 80 days shall not apply to a woman who has immigrated into the State of Assam and was pregnant at the time of immigration.
- For calculating the number of days on which a woman has actually worked during the preceding 12 months, the days on which she has been laid off or was on holidays with wages shall also be counted.
- There is neither a wage ceiling for coverage under the Act nor there is any restriction as regards the type of work a woman is engaged in.
Employer and Maternity Leave Problems
Can an employer dismiss a women employee because she is pregnant?
An employer cannot terminate a women employee while she is expecting or is on maternity leave, This is unlawful. Most companies have policies preventing discrimination against pregnant women, but there have been cases of discrimination where women have been pressurised into giving up work. If you feel your employer is not applying the law properly, take legal advice. While you can go and complain to the labour department, but that rarely does much good. However, try to work out an amicable solution with HR.
If you do go and complain, you can no longer work for them as they will make life miserable for you after you join, and you will have a problem getting another job as you can not give a reference. You need to decide if you want to continue with such a company after you are ready to work again and take a decision on basis of that. At times it may simply be a good idea to say good bye to a bad company and move on, even if it is at a financial loss in the short term.
Penalty for the employer for not giving Maternity benefit to the employee
The act provides that, no employer shall dismiss, discharge or reduce or otherwise punish a woman employee during the period she is in receipt of maternity benefit. If an employer does not provide the maternity benefit, the employer may be fined. The fine, in this case, may extend up to Rs .5,000. Moreover, an employer may be held liable to pay as much as Rs.20,000 on failing to provide free medical care to expectant employees. For discharging or dismissing such a woman during or on account of her absence from work, the employer shall be punishable with imprisonment which shall not be less than 3 months, but it will extend to one year.
Also, the appropriate Government may appoint inspectors for the purposes of this Act defining their jurisdiction limits.
Complaint under Maternity Benefits Act 1961
The Central Industrial Relations Machinery (CIRM) in the Ministry of Labour is responsible for enforcing this Act. CIRM is an attached office of the Ministry and is also known as the Chief Labour Commissioner (Central) [CLC(C)] Organisation. The CIRM is headed by the Chief Labour Commissioner (Central).
No court inferior to that of a Metropolitan Magistrate or a Magistrate of the first class shall try any offense under this Act and no such complaint shall be filed after the expiry of one year from the date on which the offense is alleged to have been committed.
What are the implications of long maternity weeks of 26 weeks?
Giving women 26 weeks of paid maternity leave is a great, bold move that sends the right message, but six months is a long time in anyone’s career today. Right now, even going on three months of leave places several challenges on women when they want to get back to work. It can affect their career map. Even with the 12 weeks of Maternity leave, In India, many women(around 37%-48%) leave their job because of family responsibilities. Those who do return to work after maternity leave often ends up taking more childcare leaves to cope with the responsibilities of motherhood, and find that it affects promotion and appraisal prospects at work.
With an extended 14 weeks of maternity leave, from 12 weeks to 26 weeks, many fear that for six months, if other staff members learn to manage without the employee on leave, companies might wonder if that person is dispensable. Some fear women who work in more person-dependent roles, ones that require building relationships with clients, for instance, could face trouble getting re-absorbed by companies that are not progressive enough.
The excerpt of Overview of Maternity Leave is shown in the image below. Click here or on image to see the full overview.
Paternity leave
Paternity leave is paid or unpaid leave given to a male employee when a child is born. While paternity leave is authorized for government employees there is no law that instructs the private sector to make it obligatory.
Individual organizations decide whether or not they would like to extend the facility of Paternity Leave. There is no legal requirement in regards to granting Paternity Leave to anyone.
Thus, on the one hand, you have Cisco Systems (India) which grants its employees 12 weeks paternity leave and on the other, you have Infosys which offers 5 days of paid leave
Maternity Leave in some Private companies in India
Companies like Flipkart, Accenture, Godrej and HUL had been offering six months of maternity leave well before the amendment of the policy came into consideration.
- Bharti Airtel: increased maternity leave for women employees to 22 weeks, from 12 weeks. Airtel promised other benefits and flexible work options to ensure a smooth transition to full-time work and day care facilities.
- Flipkart: Offers an extended maternity leave of 24 weeks, Flipkart also encourages women employees to avail benefits of their flexible working hours (with full pay) for as long as four months after their maternity leave. If needed, women can also take a 1-year career break without pay at Flipkart.
- Microsoft : As of February 1, 2016, Microsoft India is offering 6 months maternity leave, extended from 3 months’ leave,to its women employees. The company is also offering 2 weeks paternity leave to new fathers. This is in addition to Microsoft India offering women employees the option of availing unpaid leave for up to three months and flexible work arrangements for up to two years. Additionally, to care for adopted children, mothers will be eligible for eight calendar weeks of paid leave, while fathers are eligible for two weeks of paid leave.
- Nestle: Nestle India has extended its maternity leave policy to 6 months, effective February 1, 2016, from the previous leave of 18 weeks, while granting adoption leave for six weeks with full pay and benefits for all permanent women employees. Besides, a paternity policy has been introduced with a leave of five working days with full pay and benefits for all permanent male employees.
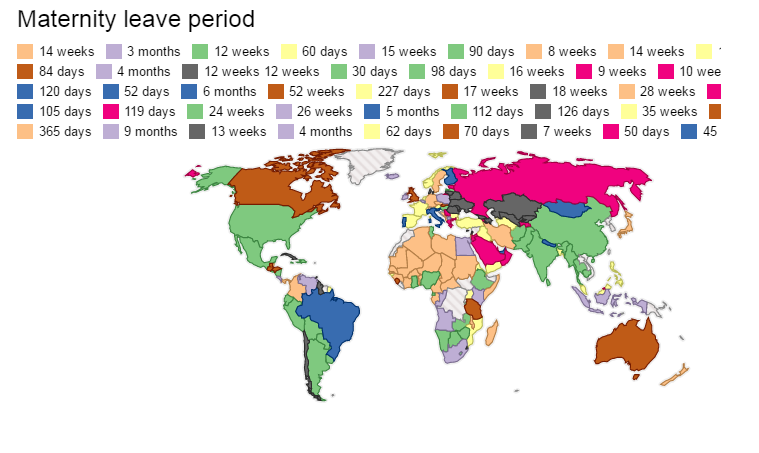
Maternity leave around the world
The International Labour Organisation recommends a minimum standard maternity leave of 14 weeks or more, though it encourages member states to increase it to at least 18 weeks. At 26 weeks, India is set to join the league of 42 countries where maternity leave exceeds 18 weeks. It, however, falls behind several East European, Central Asian and Scandinavian countries, which have the most generous national legislation for paid maternity leave.
At present India qualifies among the 16 countries having the longest paid leave for new mothers. The Maternity Leave in other countries is given below and a map of maternity leave is also shown.
- India: 26 weeks at full pay (Image is of 2015 so it does not reflect the updated status)
- UK or England: 39 weeks of paid leave
- China: 14 weeks, paid the average wage at the company
- US: 12 weeks, employers not obliged to pay anything
- Canada: 15 weeks paid leave; can take up to 52 weeks of leave
Related Articles:
- Casual Leave, Earned Leave, Sick Leave: Leaves in India
- What are Employee Stock Options (ESOP)
- Understanding Variable Pay
- Basics of Employee Provident Fund: EPF, EPS, EDLIS
- Salary, Net Salary, Gross Salary, Cost to Company: What is the difference
- Changing Jobs: Take Care Of Bank Account, Tax Liability
Do you think 26 weeks of Maternity Leave is OK? What should the organizations do to make women return to the job after maternity leave smoothly? Have you faced pressure from your employer on resigning when you have applied for maternity leave?

320 responses to “Maternity Leave :Duration, Wages,Maternity Benefit Act”
Thanks for sharing valuable information regarding maternity leave
Can you clarify references for the below excerpt from your article?
“Does one get Earned or Paid Leaves during Maternity Leave?
Earned or Paid Leave is credited on account of an employee’s presence on the duty. But Maternity Leave is not considered as leave. It is a social benefit being provided through the Maternity Benefit Act for a period that is regarded leave irrespective of actual physical absence from duties. So a women employee will get Earned Leaves during her Maternity Leave. “
This is a grey area. It depends on the organization.
Many feel that Maternity leave is a social benefit hence it should not be considered as Leave.
But In many organizations, The entire period availed as maternity leave would be taken into account for the purpose of calculation of 240 days of continuous service which is the eligibility criterion for EL to be availed in the succeeding year. Yet, as the employee does not work actually during these days of maternity leave, she will not earn any leave(PL) for the maternity leave period.
This information is really useful and it helps me a lot for clearing my doubts. Best of luck for your future posts.
I am joined duty on 08.12.2019 and taken maternity leave from 01.09.2020 to 29.02.2021, during the period my probation was declared (0n 08.12.2020). I want to know about the status of my Earned Leave
Could you please elaborate how a female employee is eligible for earning Earned leave during maternity?
The Factories Act and Shops and Establishment Act both say something in line with the below
” in the case of a female worker, maternity leave for any number of days not exceeding twelve(twenty six) weeks shall be deemed to be days on which the worker has worked in a factory for the purpose of computation of the period of 240 days or more, but he shall not earn leave for these days.”
and the Maternity Benefit ACT does not specify the earned leave part
I am applying for ESIC Maternity policy. I am applying in sep 2020. my baby arrived 15 sep 2020 I am join office after 6 month that is 1 march 2021 till now I am working am submitted my all document related policy but due to covid offices are closed. but noe I want to quit job because my baby care. so my question is if I quit my job then I able to get money of my policy.
Hi,
My name is Sachin, my friend is 8 month pregnant now and doctor given delivery date as april 5th. She want to apply for ESI maternity benefit, but when she visited esi hospital doctor told before one week of delivery only she can get letter from them. But as per the article before 11 weeks only she can apply for maternity benefit. Please clarify.
Thank you.
Very informative article and helpful. I liked the 2.8 topic content.
Thank you!
I have to consult esci doctor for maternity salary benefits but i can’t get it wht she wants to say i want to know about my salary benefits
ESIC provides 100% of average daily wages in cash up to 26 weeks in confinement and 6 week in case of miscarriage, during maternity leave and 12 weeks for commissioning mother and adopting mother.
What information are you looking for?
Hi Sir. I gave birth on 2nd July 2020.I have submitted all the documents on 5th August 2020.So how many days it will take for process. When I can expect automatic call & maternity payment.
Congratulations.
Due to covid no idea how long will it take.
Why don’t you get in touch
Hi I would like to apply for maternity leave as I’m 8 months pregnant but I found that my name in esic is different from Aadhar card and bank details when I approached regional esic office regarding this they said they can’t change the name as it is according to SSC memo. So Will there be any problem during payment if one letter is missing from my actual name as per bank details. Please reply me
It can.
Please contact your employer to correct the details.
Bank account details of existing Insured Person can be updated by employer by logging into the Employer portal and
accessing “Update particulars of Insured Person” link. Also, the employer needs to upload attested copy (with stamp &
signatureoftheEmployer)ofthefront page of cancelled cheque leaflet issued by Bank orthe pages of passbook showing the Name
of the Account Holder, Bank Name, Bank Branch and IFS Code. No two Insured Person can have same bank account number.
Hello sir /madam
my maternity leave payment only I got two months. 02/01/2020 to30/06/2020.march and April not credit .how I can resolve the problem
Speak to your employer about it.
My name is Geetha,
Am working in an organization from 01.12.2018.
Am 5 month pregnant due to the corona virus I do not want to go office. I have registered in esi but I didn’t consulted even once due to this virus am scared to go out.
I wanted to know can I claim maternity leave salary of 26weeks after delivery if I take leave from now onwards and if I not gone to esi hospital.
Please guide me
Congratulations Geeta and take care.
Check with your employer.
Usually, 26 weeks of leave can be taken at any time in discussion with the Employer.
But if you take now, you will not have much after the child is born so plan accordingly.
Will I get paid maternity leaves , without going edi hospitals
Under section 2.8. Maternity leave around the world, India shows 12 weeks of fully paid leave. Isn’t that 26 weeks?
Thanks for pointing out.
The article is of 2015.
We have updated the data but we have to find some good image to replace it.
Hello I wanted to asked whether medical bill possible to claim under esi ?
sir my meternity money is getting for me please check my case
It is best to discuss it with your employer
Sir I lost the esi form. Which i got from my organisation. So i didn’t took even photo in esi. Nw i am in maternity leave. How to claim my salary from esi….
thank forgiven all the information. it’s very helped me ESI registration form
Hai my delivery was on 3rd sep 2019 till know i have not applied for maternity leave can i apply know will get the benifet from esic
The ESI scheme provides maternity benefits at the rate of full wage subject to an insured woman’s contribution for at least 80 days in the preceding two consecutive contribution periods.
There are certain contributory conditions on the basis of which an insured woman can claim the said maternity benefit. It will be better if you visit your appropriate Branch Office of ESIC and obtain forms/guidance on the basis of which you can obtain maternity benefit.
As per procedure, you are also to report your self to the Doctor (Insurance Medical Officer) of the ESIC dispensary to which you are attached. The name of dispensary must have been indicated in your Identity Card. Necessary Certification is required to be obtained from said ESI Dispensary or ESI Hospital and submitted to the Branch Office of ESIC. On the basis of said certificates, the concerned Branch Office of ESIC will make you payment of maternity benefit based on your eligibility and entitlement.
how they calculate maternity salary
Sir, i am working 01 April 2018 and during the first half April 18 to Sept 18 i have working only 52 days but next 2nd half Oct-2018 to March-2019 i have working 108 days. And my LMP date is 26.06.2018 and my delivery is done on 13.03.2019. Sir, please tell me i am admissible for maternity leave or not? Because Branch office employee said me that i am not admissbile for 182 days maternity leave i.e. w.e.f. 13.3.2019 to 10.09.2019 because your benefit time period is 01.07.2019 to 10.09.2019. Please tell me the employee of branch office are saying right or wrong.
I joined in a hospital on June 6th 2019 and I found that I am 2 months pregnant on July 10th.currently I work in this hoapital and will continue until January before my due month. Hospital authority says I am not eligible to get maternity leave. I wanted to know am I eligible. Is it compulsory that I should complete 12 months in that hospital to be eligible for maternity leave Before delivery??
I found your article very informative and I totally love how the concepts are explained in this blog post. Thanks for sharing your insights. It helps a lot.
Premature birth ke baad बेबी कि death हो gyi 6 डेज में maturnity लीव कितने दिन कि milegi
Maternity Leave lene chahti hu but mere office wale bol rahe hai ki apko salary nhi dege bas 6 month holiday mil jayega … please mujhe bata dege kya aisa hota hai ya nhi .. mera esi main naam bhi likha hua hai …………… mujhe office wale thik se bata bhi nhi rahe .. please ap meri help kare
I work for a BPO, I’m working there for 2 yrs now and I’m on my 5th month of pregnancy, my HR and management are denying to give me my maternity benefits, due to my placenta issue I cant travel now to work and planning to go on my maternity leave but these people say I’ll eligible for my maternity benefits only if I complete my 8 month of pregnancy working with them and then only they’ll give me my maternity benefits. If I put my leaves now I’m not eligible for my benefits… harassing me to put down my papers on daily basis. TL taunts every now and then that company is favoring me by keeping me in the organization… no clue whom shall I approach for help.
i m 8 months pregnent now, my due date is on 10th august, my ESIC constribution is stopped in the month of March – 2019. April onwards company is not paying ESIC Contribution. Now, when i asked my HR Maternity paid leave for 6 months from the company ( as i am out of ESIC Now) she said that Esi will pay 6 months ML with Benefits. Kindly confirm whether i get 6 months paid leave from ESIC?????
Thank you.
Hi i am priya, now 6 months running pregnancy after 7 months can i take esi leave before delivery. If applicable please reply me. i want leave 2 months before delivery. how to take leave
Dear sir
i am gayathri working in private company from last 10 years, i am pregnant march 2018 and delivery baby girl on 10th dec-2018. some health complications i am taking leave from 1st sep-2018, i am apply maternity leave in our local esi they give leave from november-2018 to may-2019 (6month) but as per my company leave sep2018 to feb-2018 (6 months completed), they ask to join to my job. what can i do, if i will join my job, esi maternity benefit will claim or not. our hr also tells continue 6months pf not deposited to my account, my pf account will dead. please suggest me to get my maternity benefit.
regards
gayathri
February 14, 2019 at 4:00 PM
I am pregnent now 4 month is running and due date is on 11th august, can i apply esi leave before 2 months delivery? if i m not treated in esi despensary for monthly check up,whether i m eligble for esi leaves for 26 weeks with full pay? how to apply ESI Leave? If i will go to native for delivery is it possible to apply ESI Leave? please give me reply. Thank you.
I am pregnent now 4 month is running and due date is on 11th august, can i apply esi leave before 2 months? if i m not treated in esi despensary for monthly check up,whether i m eligble for esi leaves for 26 weeks with full pay? how to apply ESI Leave? please give me reply. Thank you.
Nice information,
I worked in a company for 8 years and I’m pregnant ,I’m in my 7 th month of pregnancy and still working in that Company..
I asked my HR about my maternity leave she said i wil just get my basic salary not full salary .on asking her why not full salary she replied every company has different policies in this government rule does not get applicable..
Please help me with the answer as per government government rule i should be liable for full pay or basic salary.
And also tell me if there is any law which says that it depends on Company policy..
Sir,I m working in a pvt school,for the past 3 three years.my maternity leave Start from28sep 2018 to 28 March2019.when I submitted all the documents from esic including my letter to my office, at that time they are not that much satisfied with that.They r not ready to give 6 months ML.March 28,2019my rejoining period,but yesterday (14_03_2019),I received a call from our school, they says that they terminated me from that school.sir what can I do?I don’t know? Sir please give me a correct reply
Congratulations on becoming a mother.
It is hard but very rewarding.
Sad to hear about your case.
It happens to many women.
You can raise the complaint against the school with the Regional EPFO office.
Question is do you want to go back to the school who doesn’t want you?
Can you find another school?
Hi, I am working in private company.i joined last year.i am 5th month Pregnant.if i resign current organisation then i will get maternity benefit or not. also i will be eligible for ESIC.
Hi,
I’m working in Wipro infotech mysore as a partner employee, my partner office is in Mumbai (Thinkapps solutions Pvt LTD), I’m on maternity leave now from September 17th, I gave birth to baby girl on 21st September.
I don’t have idea that ,to which esic should I submit all the documents, Mumbai or mysore. Could you please help me out this.
after all esi benefits i delivered my baby on jan 2,2018 and again within 5 months i have become pregnant again and my EDD is 7/03/2019.will i be able to get all benefits again from esi
I am working in a private school and have esi card.. If I applied for maternity benefits in esi the employer should pay the salary or not
Hi, now im on notice period, since i rejoined the office after maternity leave tat’s on 05th may 2018 there is been a harassment from the managers some or the other way, though they have issued termination notice when im on ML in between 6 to 7 month, i request to the management to extend my ML for 1 more month i’e 6month to 7 month, but they accepted it orally & send termination letter in 7th month ML, which im not aware, i came to know when they have called & informed me, so i rejoined on 05th may 2018 so some or the other problem from the management. so now given the resignation letter..
Now my gratuity will be considered maternity leave since im been working here from oct 2011 to till date in between i had been for ML leave for 2 times…. ( i have 2 kids now) so please let me know….
or excluding the ML days gratuity will be calculated….
Thank you so much,,, & Thanks for the reply, sorry its not 5th may 2019, its 5th may 2018 were i have already joined to the company, were after 6th month they have issued termination letter, which im not aware once i joined office then only i came to know it… now the problem is they are keep on torchering me, so i quite resigned the job on 29th sept 2018,, currently im on notice period,, so please let me know further…
I have taken meterninty leave from 27th sept 2018 & baby born on 1st oct 2018, i rejoined on 05th may 2018, coz of some health problem & other problem i could’t able to join the company in 6 months, so requested with the to extend the leave and joined on 05th may 2018, will i eligible to get maternity salary please let me know it.. since company is not willing to pay for the same. & some retention bonus rejecting to pay.
Congratulations on the baby.
Hope both you are your child are doing fine.
5th May 2019 is far.
Extending leave beyond 6 months depends on the employer.
So its best to talk to employer.
You should get 6 months maternity leave with full pay. You can talk about extending your leave later.
Thank you so much,,, & Thanks for the reply, sorry its not 5th may 2019, its 5th may 2018 were i have already joined to the company, were after 6th month they have issued termination letter, which im not aware once i joined office then only i came to know it… now the problem is they are keep on torchering me, so i quite resigned the job on 29th sept 2018,, currently im on notice period,, so please let me know further…
its 5th may 2018
Thank you so much,,, & Thanks for the reply, sorry its not 5th may 2019, its 5th may 2018 were i have already joined to the company, were after 6th month they have issued termination letter, which im not aware once i joined office then only i came to know it… now the problem is they are keep on torchering me, so i quite resigned the job on 29th sept 2018,, currently im on notice period,, so please let me know further… Thank you so much,,, & Thanks for the reply, sorry its not 5th may 2019, its 5th may 2018 were i have already joined to the company, were after 6th month they have issued termination letter, which im not aware once i joined office then only i came to know it… now the problem is they are keep on torchering me, so i quite resigned the job on 29th sept 2018,, currently im on notice period,, so please let me know further…
Hi, My wife joined as 2nd Grade teacher on 1st Oct 2018 in Rajasthan ( RPSC – Rajasthan public service commission) . We have 2 month daughter ( Delivery date 7th Aug ) . Please let us know where we will get maternity leave benefits or not as it’s very hard for woman to manage. If will not applicable for ML than suggest a way as we are in trouble .
As she has joined after the birth of the baby she is not eligible for maternity benefits
After meternity all the papers submitted which is required for 26weeks payment before 1month I submitted but I didn’t get maternity payment… After how many days I will be getting plz help??
How are claiming maternity through Maternity act or ESI?
Hi ,i am eligible for maternity leave,,now i am 7thmonth pregnent,to apply for maternity leave after delivery how many days we can apply for leave
Congratulations Lakshmi and best wishes for a smooth delivery and a healthy child.
According to the Maternity Benefits Act 1961, a women employee is entitled to 26 weeks of which not more than 8(earlier was 6 week)s shall precede the date of her expected delivery.
How she takes those 26 weeks depends on her. She can take all her Maternity Leave after the birth of her child. She can start her Maternity leave anytime in 8 weeks before her due date.
I am working private sector since 10 years now I am 6month pregnant, my due date is December middle shall I go to maternity leave 1st September, esi pays 26 weeks full salary or not
Are you covered under MAternity benefit or ESIC benefit?
If under ESIC benefit then please login to ESI website http://www.esic.in/EmployeePortal/login.aspx and check for entitlement benefits as shown in the image below.
Dear Sir/Madam,
I have taken maternity leave from 17th May 2019 to 17th November 2019 but I have been working in company after completion of maternity leave they are not taking back.
I need your suggestion
Hi,
I would like to know whether i will receive my salary during maternity period, as per my salary scale i’m excluded form ESIC. so only 26 weeks leave i receive or will i receive salary during this period from my company.??
Hi sir I work in electricity department Telangana my wife delivered baby girl 10 months ago , I don’t know about medical bonus at the time of delivery and later now I came to know about medical bonus can I apply now for medical bonus please let me know the procedure thank you
I AM 32 WEEK PREGNENT WHEN I AM TAKE A ESIC METERNITY LEAVE AND MY EDD IS 27/08/18
hi all,
I’m working as an HR of a pvt. company. This is regarding one of our staff who joined the company on 3/11/17. She got pregnant on 21/12/2017 and Her EDD is 28/09/2018. She is covered under ESI Act. Now, she has requested for 26 weeks of maternity leave under the MB Act with full pay.
Will she be eligible for maternity leave? Can she apply for Maternity under ESIC? What is the process? Kindly help
If she has contributed to ESIC she cannot claim under Maternity Benefit Act.
She can call following numbers
Toll free. 1800-11-2526 Medical Helpline: 1800-11-3839 Email: esic-hqrs[at]esic[dot]in
What are the conditions subject to which maternity benefit is payable are given below. She can login to ESIC website and check details.
The conditions for availing maternity benefit are as follows:
Payment of contribution for not less than 70 days in the immediately preceding two contribution periodsConfinement should actually occur or expected to occur in a benefit period relevant to the insured woman, i.e., if she actually confines or expected to confine before the start of the first benefit period, is not entitled to claim, even though, a part of the maternity leave will fall within her first benefit period. If an insured woman’s actual date or expected date of confinement, falls within her first benefit period, she will be entitled to maternity benefit even if a part of the maternity leave may fall before the start of the first benefit period. Upto 26 weeks in the case of normal delivery, upto 8 weeks in the case of mis-carriage. Extendable by 4 weeks on medical advice.Benefit payable at almost 100% of average daily wages. Benefit is paid only if the insured woman does not work for remuneration during the period for which benefit is claimed irrespective whether she received any leave wages also for the days of abstention or was on strike during the same period.
When ESI ML salary will be credited?
Hiii I hav taken maternity leave since Jan 20th and I got my delivery on 25th Feb so I hav my ESI card and I went to check up. after that I came to my native so not able to go fr ESI hospital now it’s 4th month fr my baby so how can I apply for maternity benefits. I was working in health department of nurse council. ll I get my maternity benefits now
my date of joining was 02-02-2017 and i was on maternity leave from 10-10-2017 ,my regional office I.e sec 29 in chandigarh says that i m eligible to goo on leave but after 6months they refuse to getting me the benefit(payment)as per the rule my 80days are completed on my job but they will tell me that your contribution days are not completed..please suggest me
Do you have Maternity Leave benefit or ESIC?
Hi
I took maternity leave from office on March 19 but baby delivered on april 14. In esi office they consider 6 month from my delivered date approximately till oct13. Accordingly I will rejoin office on sep19. Whether I will get salary from both esi and my office. If it’s possible.
I have a one more doubt esi salary based on month or days.
You can get it from one only, either ESI or office
My wife is working in a pvt company and she is on her maternity leave from 10 march and she deleverd on 29 march. Is company liable to pay her entire salary as the hr department said she will receive her claim from esic.
yes, if esic deduct from her salary then they will pay for 6 month salary.
For this you have to go the ESI dispensary where Doctor and ANM will sign on Form 17,18. then you have to submit this form along with other form to ESI office(ask to your HR in which branch your registered). ESI branch manager will guide you other form.like form 19,cancel check ,receipt form etc.
Thanks for reply
Dear sir,
I am working in Land Records Department Maharashtra state.I am pregnant for three months . Recently I came to know that I am having two babies in my womb(twins).
So please late me know the rules for Maternity Leave and Child Care Leave if any.
hellow sir i joined in oct 6TH 2017,and i conceived on oct 16TH 2017 and my delivery date is july 23th 2018. iam i eligible for maternity leave and claim please let me know.
If someone has due date of later but delivers 4-6 week earlier, can the person start his/her leave at the later date and use the available earned leaves or medical leaves from the date of early delivery to the previous date of expected delivery?
I am currently in probationary period.. i reported on march 19th 2018. Now i applied for maternity leave. As per rules ahould work atleast 80days, but now can i get salary?
You should.
Its best to Ask your employer
Dear sir ,
My wife working for a private HR company which provides employees to some other company(3rd party) to work there . She has been working for there since June’16.She is taken her maternity leave from 20th Nov’17 to till 20th May’18. She gave birth to a child on 04th jan’18.we had submitted birth certificate and maternity leave form at ESI local office . They ask for signature from employer stating that during above said period there is no salary paid credited to my wife’s account. we have to sended to her parent company for signature.it will take some more days like 10 days or more. Her leave period has been ended on 20th may’18. And the reporting manager has been asking for join or resign for the job after 20th May’18. But we are unable to join because her office was so far from our house and baby also needs feeding . Hence we decided to resign the job. But we had problem with submtion of the leave form because it has been despatched to her parent company and we had to receive during this week .If my wife resignes the job after 20th May’18. Then she will get her maternity leave benefit/pay.or not eligible please help us.
She should get her maternity leave benefit.
Hey admin,
Thank you for this blog with the useful and very well explained solution about maternity leave.
I am working in Narayana Hrudayalaya Hospital (Bommasandra) as Shift Incharge (Nursing Incharge). Joined on 17th of August 2011 as a Staff Nurse.
In my case, Before going on maternity leave (a month before delivery date) we have submitted E-Pehchan Card to Nearby ESI office (Bommasandra, BLR, KA) along with all of the documents.
On 6/11/2017 we had a Baby boy, 🙂 and on 16th of Nov, again we went to ESI Office and submitted the form 18 (Regulation 88 – 89)
My joining date is May 6th, 2018. (Yay.., My HR has given 6-month leave)
As if now – I didn’t get any penny from my Company or ESI.
What will be the next step to get maternity benefits? How long – will it take time to get benefits?
I really appreciate you for the replays to visitors comment (80% bloggers won’t do that).
Keep up the good work mate.
Applied for a maternity salary in the month of January and still waiting for the salary from ESI Team. No response at all. Facing very difficult without salary. Request you to please help me with this Issue.
Please this is my humble request..
Congratulations on becoming a mother. Hope the baby and you are doing fine.
Sad to hear about your difficulties.
The procedure is as follows
Before delivery, visit your nearby/assigned ESI dispensary to get the required details. After delivery, they will ask you to visit the dispensary with child. Then, they will provide leave approval letter. You need to submit that leave approval letter to ESI Branch Office for process. After verification, the ESI will start paying your salary to your bank account.
Hi,
If I join a new company in March 2018, when should be the expected date of delivery to claim maternity leave for 26 weeks.
I read the sentence “The woman have worked for a continuous period of 80 days in twelve months immediately preceding the date of her expected delivery” many times, but not able to understand its meaning.
Could you please elaborate it in layman words.
Does it mean that if I deliver after March 2019, then only I can claim the said benefit?
Thanks
You shall be eligible for maternity leaves after 80 days of continuous employment means in case you joined a company in the month of 01 March 2018…you shall be eligible for maternity leaves 31 days of March + 30 days of April + 19 days of May.
After 19 May 2019 one shall be eligible for maternity leaves. The employment should be continuous (however approved leaves if any shall be counted for eligibility)
Now what i can i do? because now i am going Paldi Ahmedabad ESIC office not provide proper answer. d Before delivery 9 month ESIC Contribution require. is it any rules ? my ESIC Contribution 9 month complete in january 2018. i call ESIC help line number and he said 9 month ESIC Contribution not require any for maternity benfit. its only require days. As per the rule employee must be present as employer at a particular organization for more than 80 days and I have already completed more than 210 days in current organization.Please provide me any email id . because i have send email on ESIC main office as well state office but they are not reply me .
so please help me and provide any suggestion.
Currently I am employer for private limited company. My joining date is 8th march 2017. Right now, I am going through 9th month of pregnancy and doctor has given the expected date, which is 26 January. The ESIC deductions for 9 consecutive months will be done on January – 2018, so based on this I am eligible for the benefits of leaves for the maternity of 6 months provided by government but ESIC Paldi Ahmedabad branch is denying to provide the governmental benefit and they had said us that we are not eligible for such benefits. As per the rule employee must be present as employer at a particular organization for more than 80 days and I have already completed more than 210 days in current organization. So kindly let me know whether I am eligible for the governmental benefits of maternity leave for 6 months or not. Currently I am not on leave, I am going to work office on regular basis. Do the needful for providing the support and respond for this query as soon as possible.
Do you have ESIC Pehchan Card duly issued by appropriate Branch Office?You can also check whether other employees possess ESIC Pehchan Card or not.
In order to be eligible for maternity benefit under ESI Act, 1948, an insured woman should have contributed/contribution payable for not less than 70 days in last two consecutive contribution periods i.e. one year.
Why us the ESIC Paldi Ahmedabad branch denying it?
Now what can i do? And i am go to the ESIC office he does not provide answer ? regarding this situation? so please in this situation i am eligible for ESIC benefit ? and if I am eligible. so,please provide information and help me .
Now what i can i do? because now i am going Paldi Ahmedabad ESIC office not provide proper answer. d Before delivery 9 month ESIC Contribution require. is it any rules ? my ESIC Contribution 9 month complete in january 2018. i call ESIC help line number and he said 9 month ESIC Contribution not require any for maternity benfit. its only require days. As per the rule employee must be present as employer at a particular organization for more than 80 days and I have already completed more than 210 days in current organization.
so please help me and provide any suggestion.
Please provide me any email id . because i have send email on ESIC main office as well state office but they are not reply me .
please reply me. and yes i have my esic pahechan card. if requried i will send my esic number.
I am 7th month pregnant and i am working on a contract basis in jaipur. My contract will be finished on 31st March 2018. So if i am taking maternity leave from February 2018 and my employer is not extending my contract then how will i get the maternity leave benefit.
Are you under Maternity benefit act/ ESI act?
If you are applying for Maternity benefits while in contract then you should get Maternity benefits.
Your employer might not be extending it for trying to save on maternity benefits.
The best way is to speak it to the employer.
You can show link to the following article Temprorary, Ad Hoc And Contract Staff Also Entitled To Maternity Leave: CAT
My delivery date is October 12 I gave the esi form to esi office they told me amount will credit as soon but still I not get my esi benefits in how many days esi amount will be credited
Hi
I am 19 weeks and working in an advertising firm in Chandigarh. I had joined the company in January 2017 and have already informed the HR about my pregnancy in written when I was 16 weeks pregnant. But now, they are making excuses and putting allegations on me regarding my performance at work. Now all of a sudden, I have become a bottom performer for them and they have increased work pressure and targets to meet with a condition that those who will not meet the targets will not be given any incentive and/or shall be terminated from the job in case of poor performance. So that they don’t have to give me Maternity Benefits as per MB Act. I don’t expect any help or support from HR as everyone wants to save their job.
So, I just want to know can they terminate me on these grounds of not achieving targets or performing poor even after knowing that I am pregnant?
Please help & suggest what should I do in this case?
First congratulations on your motherhood.
Try to be happy for your child
Coming to the question there have been cases where to avoid paying the maternity benefits many companies do what you are facing or something similar
You can complain to regional labour office
But you have to look at the big picture, do you want to work in such company?
Will they be supportive of you after your child’s birth.
Think coolly, take input from your seniors and discuss with your family
Hello
My company is not giving only 3 months they are not giving 6month leave what we can do in this case
Hi
My organization is not ready to give 6month maternity leave it are saying we will give only 3 months .
Please can you help what we can do .
Show him the recent notification reg. Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Act, 2016 which has been notified in March, 2017.
They have to provide the leaves on salary. It is mandatory and it is applicable on any company employing more than 10 employees.
Technically As per maternity benefit act, the employer can be punished under, if he/she denies maternity benefits to women employees and that includes imprisonment for three months or fine up to Rs. 5000 or both.
You can Register a complaint against company with relevant department of labour ministry or file a court case.
It depends on how do you want to proceed?
Hi
As my office is not giving 6month there are saying we will not give we will only give 3 months
In such case what we can do.
Hi,
I am working in private sector, how many weeks the baby has to be old to take the ML, ie. how many weeks before the delivery date we can start avail the ML?
Congratulations and best wishes.
A women can start her Maternity leave anytime in 8 weeks before her due date.
Hi,
I have delivered a baby on Aug 11th 2017. I am an Asst. Prof in an Engineering college in Hyd. But my college is not ready to give me leave for more than 3 months inspite of the govt rule. i cannot leave my job due to my financial conditions as my baby was underweight when he was born, doctors has advised me to continue with the mothers milk he is now slowly gaining weight. i cannot leave my baby and continue the job i am feeling very helpless. Please advise.
Thank You
I am working in a private company. I have delivered a baby on 1.6.2017. One month prior to that date I commenced my MB leave. After completing 6 months leave including that one month I have to join on 25.11.2017. Accordingly I joined on 25.11.2017 and worked for 3 days. Now I want to resign from the service. My company is asking me to deposit 6 months salary paid to me towards MB leave. Please advise me whether I have to deposit that amount.
I m working with P ltd company since 2 & half year. They are providing ESI facility also & Now I m 9 month pregnant. SoI am applying for maternity leave from 1 December 2017.So i have some queries.
1) Can I get total 26 Week maternity leave. If yes then my employer will provide total maternity benefit payment or ESI only provide. Are they providing total salary which is my current salary ??
Also the salary is getting on monthly basis or they are providing after 26 week leave completion.
2) What is the procedure to claim maternity benefit. As my company doesn’t provide benefit to any one before. I m the first one to whom they are providing ESI benefit. So I have complete all procedure to own.
Kindly help me.
How many days prior to the date of expected delivery can one avail maternity leave? Is there any provision to avail the leave 04 months prior to the expected date of delivery?
According to the Maternity Benefits Act 1961, a women employee is entitled to 26 weeks of which not more than8(earlier was 6 week)s shall precede the date of her expected delivery.
How she takes those 26 weeks depends on her. She can take all her Maternity Leave after the birth of her child. She can start her Maternity leave anytime in 8 weeks before her due date.
Greetings,
I am working into MNC level 5 company from August-2016. I took my first maternity leave on 16th Apr 2018 to Oct 2018. I rejoined my work from Nov2018 and i applied for my 2nd maternity leave dated 31st Oct and my maternity leave ends 30th April 2020. I got delivered my 2nd baby born on 1st Nov 2019 (1st of my ML starred). Unexpectedly my elders was moved to native places and no one is there to take care of Kids. I and my husband take a decision to resign my job to take care of my kids.
So I went to my office dated 1st week of March 2020. Informed about my situation and everything, my Manager and HR asked me to send an Resignation email. Immediately I resigned my job.
HR confirmed they are going to consider my resignation as a normal way, they are going to deduct my basis salary for notice period, then they will give documents.
From that day I keep on doing follow-up with my HR and Reporting Manager but no one is not respondig I keep on sending emails to them to provide my relieving and experience documents.
Finally I got documents from HR today and he mentioned my resignation date and reliving date same day (Feb-2020)
In experiance Letter they mentioned aug-2016 to Oct-2019. They was not included this 4months in experience letter.
I’m facing too many mental pressure with HR department because of maternity reason they was never processed my salary increment from July-2017 to till date. I’m working with 100% performance without increment HR told I’m not eligible for salry increament because of Long Leave.
Out of 6months I received 3montha maternity salary. 4th month I informed about resignation they are not processed salary from 4th month and considered my last relieving date as my resignation date.
Now they was given relieving letter with separate date and in experience in letter not added four months used maternity leaves.
Iam permanent employee with company from last 4years. I resigned middle of maternity leave, this maternity days not added as working days or experience! Is this correct ??
Please advise for all this I’m on mentally disturbed and feel like end my life.
Greetings,
I am working into MNC level 5 company from August-2016. I took my first maternity leave on 16th Apr 2018 to Oct 2018. I rejoined my work from Nov2018 and i applied for my 2nd maternity leave dated 31st Oct and my maternity leave ends 30th April 2020. I got delivered my 2nd baby born on 1st Nov 2019 (1st of my ML starred). Unexpectedly my elders was moved to native places and no one is there to take care of Kids. I and my husband take a decision to resign my job to take care of my kids.
So I went to my office dated 1st week of March 2020. Informed about my situation and everything, my Manager and HR asked me to send an Resignation email. Immediately I resigned my job.
HR confirmed they are going to consider my resignation as a normal way, they are going to deduct my basis salary for notice period, then they will give documents.
From that day I keep on doing follow-up with my HR and Reporting Manager but no one is not respondig I keep on sending emails to them to provide my relieving and experience documents.
Finally I got documents from HR today and he mentioned my resignation date and reliving date same day (Feb-2020)
In experiance Letter they mentioned aug-2016 to Oct-2019. They was not included this 4months in experience letter.
I’m facing too many mental pressure with HR department because of maternity reason they was never processed my salary increment from July-2017 to till date. I’m working with 100% performance without increment HR told I’m not eligible for salry increament because of Long Leave.
Out of 6months I received 3montha maternity salary. 4th month I informed about resignation they are not processed salary from 4th month and considered my last relieving date as my resignation date.
Now they was given relieving letter with separate date and in experience in letter not added four months used maternity leaves.
Iam permanent employee with company from last 4years. I resigned middle of maternity leave, this maternity days not added as working days or experience! Is this correct ??
Please advise for all this I’m on mentally disturbed and feel like end my life.
In the entire notification, there is no clarity on when to pay the payment to the pregnant female employee. Should the employer need to pay on the day when the employee rejoins after delivery? Or needed to pay monthly as ongoing salary? Second, what if the employee don’t continue after delivery? Can you please provide clarity on that?
Useful information.
For any ESI Registration, go through http://www.aanoorhr.com/esi-services
1. plz tell me whether a women in govt. sector after maternity leave bring her child with her at her work place ? because there is no one to take care her child.
2. can she bring her child with a bai/her maid ? so that while working, her maid can take care her child .
NICE..
Click here for ESI Registration ,
Hi I’m working in private sector. I have worked till 9th month of pregnancy started. Before going to maternity leave I have mailed them that for maternity benefits and ill rejoin after 6months maternity. And they also replied that they will do as per norms for maternity benefit. But they paid two months and after they denied to pay my salary. Kindly confirm what step I have to take.
Hi.
This is samrin, I am 7 month Pregnant and i am working in a private organization from past-4 years. But, my organization has recently started ESIC facility from June-2017 . my due date is Jan-25-2018.
would i be eligible for any facility
Congratulations Samrin and Best wishes for future. Hope you are taking care of your self.
Please verify with your employer. You may be able to claim the ESI benefit.
If not ESI then you are still eligible for the benefit under the Maternity Act.
To claim ESI benefit?
Employees covered under the ESI Act, are required to pay contributions towards the scheme on a monthly basis. A contribution period means a six
month time span from 1st April to 30th September and 1st October to 31st March
Minimum 80 days in the immediately preceding two consecutive contribution periods is a must.
To qualify for this benefit, contributions should have been payable for atleast 78 days in the relevant contribution period.
The Maximum duration for availing sickness Benefit is 91 days in two consecutive benefit periods
If you somehow are not covered by ESI Act then you can state Section 5A of the State Maternity Benefit Act 1961.
However, according to Section 5A of the State Maternity Benefit Act 1961, a women employee continues to be entitled to Maternity Benefit under the Maternity Benefit Act notwithstanding the application of ESI Act to her, until she becomes qualified to claim Maternity benefit under Section 50 of the ESI Act and Rule 56 of ESI (Central) Rules1950. Under Section 5(2) of the Maternity Benefit Act, a woman worker entitled to payment of Maternity benefit if she has worked in an establishment covered by the Act for a period of 70 days in the twelve months immediately preceding the expected delivery. The period of seventy days is made up of days on which she is actually worked and the days of lay-off and paid holidays during the period of said 12 months.
So she can claim the Maternity Benefit from the Company under the State Maternity Benefit Act, 1961.
Please update us on what your employer says
I believe this web site holds very good pent subject matter articles.
I started my leaves on April 1 2017 and after 6 months my joining date was Sept 30th.
Sept 30, Oct 1 and Oct 2 was official holiday as it was Saturday, Sunday and National holiday.
So I joined back on Oct 3, 2017.My salary is deducted for Sept 30.
Is it right/justified?
I am working as a staff nurse in a private sector for about 5 years. I am paid ESI from january 2017 to September 2017. whether I get maternity benefits? If yes, whether it will be paid and how many weeks I may get.
Congratulations. Please take care of your health.
The conditions for availing maternity benefit under ESIC are as follows:
Payment of contribution for not less than 70 days in the immediately preceding two contribution periods.
Confinement should actually occur or expected to occur in a benefit period relevant to the insured woman, i.e.,
if she actually confines or expected to confine before the start of the first benefit period, is not entitled to claim,
even though, a part of the maternity leave will fall within her first benefit period.
If an insured woman’s actual date or expected date of confinement, falls within her first benefit period, she will
be entitled to maternity benefit even if a part of the maternity leave may fall before the start of the first
benefit period.
Upto 12 weeks in the case of normal delivery, upto 6 weeks in the case of mis-carriage. Extendable by 4 weeks
on medical advice.
Benefit payable at almost 100% of average daily wages.
Benefit is paid only if the insured woman does not work for remuneration during the period for which benefit is
claimed irrespective whether she received any leave wages also for the days of abstention or was on strike
during the same period.
Hello I am working with the company since 25th july 2016. Now I am pregnant and my due date is 11 Jan 2018.
Can i get ESIC benefit and also i want to go for maternity leave from October 2017.
Please suggest can i take leave from october or from November?
Ananya congratulations and best wishes for a happy delivery and motherhood.
Is your office covered under ESIC or Maternity Benefit?
A women employee who has a payment of contribution for 70 days in one or two consecutive periods (i.e either from April-Sept or Oct-Mar contribution period) is eligible for ESI maternity benefit.
The ESI Scheme is administered by a corporate body called the ‘Employees’ State Insurance Corporation’ (ESIC), which has members representing Employers, Employees, the Central Government, State Government, Medical Profession and the Parliament.
Hello thank you for all the inputs so far, but I do have a query!
My friend works in a private educational institution on a contractual basis. Her contract gets renewed every year and she gets a consolidated amount as salary (no pay scale, no PF). She has already worked there for 3 years.
She is due this December and the head of her institute told her the institute policy is only 3 months leave without any pay ….
It seems quite unfair…that such laws have been passed to safeguard women and my friend’s workplace has such a discouraging policy for would-be mothers
She is quite stressed that she will have to go without pay for 3 months?
What do you recommend? Thanks
That’s a tricky situation to be in.
By law, she is allowed to maternity leave of 6 months even though she is a contract employee.
She can raise a complaint but then it might spoil her relationship with the employer.
What if she does not get the contract again?
Hi,
I am working with a setup company from Apr 2016 (worked 11 months)
They have opened new company in Mar 2017 & transfer all employees to new one.
Now I am working in this new company i.e., for 6 months.
As a setup company they don’t any such case. As i am the first case.
My due date is 20 Jan 2017
Pls advise me regard Maternity Leaves as it is private sector how much leaves are there? How to deal with the employer.
How should i approach for maternity leave.
Pls help.
How many employees does your company have?
Maternity benefits to workers in the private sector are regulated under Employees’ State Insurance (ESI) Act, 1948 and Maternity Benefit (MB) Act, 1961. A women employee can claim Maternity Leave only if she has worked at least 80 days for her employer in the last 12 months.
So please approach your management and discuss with them.
Hi, i had been through a misscarriage (12 weeks) in my second pregnanacy and I had taken 45 days leave benefit. Now I m again pregnant please help me to know whether I am eligible for 26 weeks maternity leave or not as per new law
Yes you can.
Increase in Maternity Leave: Maternity leave for Eligible Employees has been increased to 26 weeks in case of women having less than two surviving children
Best of Luck and Take care
What is the legal proof / Labour or Legal court has order in favour of the following questions.
Question: Does get Earned or Paid Leaves during Maternity Leave?
As per Factories act 1948 , Annual leave with wages chapter, Section 78 it states that Maternity leave shall be considered for computation of 240 days, eligibility period to avail the annual leave with wages, but states that the period of such Maternity leave shall not be considered for providing the annual leave with wages.
Thus what is the legal proof for this?
As per the section 25 B of Industrial Disputes Act, a female employee will be treated as if she is putting her attendance on daily basis during the period of maternity leave. hence she will get Earned Leave/Paid Leave. You can read about Industrial Disputes Act here
Is there any helpline number for asking questions
You can try twitter https://twitter.com/LabourMinistry for your queries. Twitter is fast
Is maternity leave only for people who are covered under ESI? I mean who gets salary less than 21000?
Maternity Leave in India comes under two acts: The Maternity Benefits Act & ESI
The Maternity Benefits Act applies to every factory, mine and plantation, and any shop or establishment which has had ten or more employees on any given day over the preceding year.
Employees must also have worked in the establishment for 80 days in the 12 months preceding the date of delivery. They should inform their employer of the leave period at least seven weeks before the delivery date, and name the person to whom payment should be made in the case of absence or death.
Employees’ State Insurance, a self-financing social security and health insurance scheme for workers, The ESI is due to employees earnin (Rs 21,000 from 1 Jul 2017/Rs 15,000 or less per month, with the employer contributing 4.75 percent and the employee contributing 1.75 percent. Those who qualify may receive maternity benefits under the ESI scheme instead of the Maternity Benefits Act.
CAN I APPLY FOR MATERNITY LEAVE BEFORE 1 YEAR OF OLD JOB?
I HAD JOINED AS A CLASS 1 OFFICE IN COMMUNITY HEALTH CENTER AS A FULL TIME GYNECOLOGIST ON 2/102016.
NOW I AM ELIGIBLE FOR MATERNITY LEAVE OF 26 WEEKS.
Hi,
My Due Date is 22 Sep 2017, and I want to apply 8 weeks of prenatal leave. so how should I calculate 8 weeks?
If as per new Policy I take 6 Months (26 Weeks) as 180 Days (6 * 30) Maternity Leave. Then what will be the calculation if 8 Weeks Prenatal?
Is it= 8 * 5 (working Days in week)= 40 Days back calculated from 22 Sep 2017?
Or 2 Months: 2*30= 60 Days back calculated from 22 Sep 2017?
Please reply
It is continuous days, not working days. So 8 weeks = 2 months. You can take pre natal leaves from 23 Jul 2017. But then you would have only 4 months leave after delivery.
Hi,
As per new Maternity benefit act, is holidays and weekends are included in Maternity Leave?
Ex: If I take Maternity Leave from 01 Aug 2017 then, 26 weeks (180 Days) will include weekends and holidays also? or how it will be calculated. 01 Aug 2017+180 Days (Incl. Weekend & Holidays)= 27 Jan 2018, or 1 Aug 2017+180 Days (Exclu. Weekend & Holiday)= 6 Feb 2018???
Generally, all kind of holidays like a national holiday, Sunday arriving in between the maternity leave are included in it. Even the government applies the same rule for their employees in respect to maternity leave. You must contact the Human Resource department of your company in order to confirm and know the rules of maternity leave and their applicability.
So maternity leave would be
01 Aug 2017+180 Days (Incl. Weekend & Holidays)= 27 Jan 2018
27th Jan 2018 is Saturday and official holiday. 28th is also Holiday.
So does that mean I have to join on 29th Jan? Since it is a long leave, will these 2 days also be counted as holidays and salary deduction will happen?
Is it mandatory to deliver the baby in ESI hospital for taking the benefit of maternity leave or can we deliver the baby in private hospital ?
In order to be eligible for maternity benefit under ESI Act, 1948, an insured woman should have contributed/contribution payable for not less than 70 days in last two consecutive contribution periods i.e. one year. Section 56(1).
You can Go to local ESI dispensary and get the case referred to approved hospital or even super specialty hospital.
If you want to take the benefits from ESIC then you have to follow the procedure of ESIC
– You have to show to ESIC that you have admitted in private hospital as it was an emergency with no time to search the ESIC hospital.
– Intimation to ESIC after you get admitted to the hospital
– After discharge from the hospital, you have to give admission card along with all the bills till discharge from the hospital and submit to ESIC.
My wife is 32 weeks pregnant AND SHE IS UNDER ESI. I want to know that IS IT MANDATORY TO DELIVER THE BABY IN ESI HOSPITAL FOR TAKING BENEFIT OF MATERNITY LEAVE OR CAN MY WIFE DELIVER IN PRIVATE HOSPITAL?
IF DELIVERY WILL BE IN PRIVATE HOSPITAL THEN CAN MY WIFE ELIGIBLE FOR MATERNITY LEAVE OR NOT?
Sir,
My wife is now with her 30 days baby. She got the appointment letter for joining central govt job on 25th of June. Can she maternity leave and if so for how many months.
Please specify the clause and rule of the same.
Every female employee is entitled to receive maternity benefit if she works for a continuous period of 80 days in the twelve months immediately preceding the date of her expected delivery.
Hello sir.
Mene 8 years ek company me kaam kiya jaha mera esi cut hota tha than meri shadi ho gyi or mene job chhod di fi dobara job ki 2 saal but vaha esi nhi facilities nhi thi uske baad mene 6 month job ki jaha esi tha or mene vahi card continuoue kiya …due to high bp mera caesarian se
7 month me premature baby ho gya…so mujhe company ne 3 month baad nhi liya ….to kya sir mujhe maternity leaves k pese milenge ya nhi….thanks
Hello sir.
Mene 8 years ek company me kaam kiya jaha mera esi cut hota tha than meri shadi ho gyi or mene job chhod di fi dobara job ki 2 saal but vaha esi nhi facilities nhi thi uske baad mene 6 month job ki jaha esi tha…due to high bp mera caesarian se
7 month me premature baby ho gya…so mujhe company ne 3 month baad nhi liya ….to kya sir mujhe maternity leaves k pese milenge ya nhi….thanks
Hi,
My wife is working in SKP tricor pvt ltd, pune
The company said they will not allow her to take ML, they are asking her to resign and rejoin after delivering baby, she is been working there for 5 years now. Please provide the suggestions.
Its is not legal for Company not to give Maternity Leave.
You can raise the issue in social media but be careful.
Similar case Sacked for maternity leave: Ministry starts looking into complaint
I was on ml from feb 11 2017 and my hr didnt give 26 weeks ml . Can you let me know how to proceed on this
Congratulations on becoming a mother. Sad to hear about your HR not giving your due maternity leave.
You can take an offensive attitude. You can threaten to go to social media(twitter.com/socialepfo or facebook.com/socialepfo) and bring a case.
But remember that you have to go back and work there.
So try to get a middle way.
Try to understand is Company going through difficult times
Try to talk to your manager
Try to ask HR why are they not giving 26 weeks of Maternity leave if it’s sanctioned by the govt.
I have a doubt regarding maternity leave. My baby was born on 3rd jan 2017. I informed HR to apply sick leave and then earned leave, once both finishes, then only start the ML, so that I can get the benefit of 26 weeks once it get into effect. But HR says ML starts from date of delivery. Is he correct on this. If I apply SL and EL before ML then my ML completes in April 2017. Please suggest can I get the 26 weeks benefit. I need it because my baby is premature and he was in NICU for two months. So in any circumstances I cannot join back. I need leaves at least for 8 months. Please suggest.
Pramila HR is right as the ML starts from date of delivery or 6/8 weeks before if one takes it before the due date.
Counting from 3 Jan 2017 when maternity leave was for 3 months you were on maternity leave on 1 Apr 2017 so you would get 6 months and not 3 months.
After completion of ML you can apply for Sick Leave and Earned leave.
Congratulations on becoming mother and best wishes for your baby.
Please let me know what type of maternity leave can be provided as per ESIC …???
i am 5 months pregnant and will go on materrnity leave in oct 2017 to march 2017 and i am covered under esi as my salary is 20000 in this case who will pay the salary company or esi dept and what is the process they will pay me on monthly basis or they will pay e the total six month salary amount after six month of maternity leave
Hello M. Leave expert, I am HR in Bangalore and need your advise.
Currently we have a female employee is pregnant and will deliver baby approx. Oct 15th, 2017. As we know “Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Act, 2017 is effective from April 1st 2017. Prenatal Leave 8 weeks & Post Delivery 18 weeks are total 182 days.
Her M. Leave plan: (1) First 4 months – from Sep 1st to Dec 31, 2017. It looks ok. (2) last 2 months should be like this from Jan 1st to Feb 28th, 2018 maternity leave, BUT she plans to slip into 4 months (from Jan 1st to Apr 30th, 2018) by half day afternoon M. Leave and half day morning to office to work. Is it against to law / Maternity Benefit in Department of Labor, Government of Karnataka?
Female employees need to proper rest and also take care of her new born baby/babies during maternity leave & benefits. They should not go office working.
Hello,
My sister is a single woman. She is a College Professor in a government College and is planning to have a baby through IVF. Is she entitled to receive the maternity leave or can she be barred on the grounds that she isn’t married? I know that sole guardianship of single mothers have been recognised by Supreme Court but am not clear whether she can apply for maternity leave or not.
We’re in dire need of advice .
Thank You
She will be becoming pregnant and be delivering a child so she is entitled to 26 weeks of maternity leave.
Best of luck to your sister and hope she enjoys motherhood
Hi this is harish, my wife is working for a government organisation, as a staff nurse for more than 11 years, she has completed 26 weeks of her maternity leaves with the second baby, is she entitled for the extra 15 days of leave
How much maternity leave can be given to a woman whose baby died 10 days after delivery in her 27th week of pregnancy which she delivered normally. Is it26 weeks, 12weeks or 6weeks. She is having no surviving child at the moment.
How does the employer have to pay the employee during her maternity leave ? Is the employer required to pay her monthly salary each month or does it have to be paid after certain duration ? Is the employee entitled for entire 26 weeks of paid maternity leave ? If yes, when does she receive the payment ?
The employer pays the salary of the employee on maternity leave as usual at the month end.
I AM IN A DAILY WAGES GOVT SERVANT MY METRENITY LEAVE
Hi..I delivered on March 23..I am on maternity leave from March 24 till June 17 as per earlier 84days law.
Am I eligible for 26 weeks maternity leave..Please reply
Congratulations. Hope you and baby are doing fine.
Yes you are eligible for 26 weeks maternity leave.
Hi i have joined office after maternity leave.. and my HR is asking me to sign a bond of 1 year. I have bin with this company for 3 years. Is it lawful to ask to sign a bond after joining back from Maternity leave.
Hi , what is the minimum number days any woman should work in an company to avail the maternity benefit of 6 months. In some docs it is 80 and in some other 160 days.. which one is correct?
I was in 3rd week of maternity leave às on April 1 2017. My employer not providing 26 weeks of maternity leaves. I mailed them the govt clarification as well. Please suggest what can be done?
It is a difficult situation to be in.
You can sue the employer , threaten to report it to Labour department, tweet or write on facebook.
But handle the situation carefully.
You would need your employer support when you rejoin work.
hi..my wife draws more than 15000 ..but she is included in esi from jan 2017…she is in maternity leave from march…the company says from april the esi will pay the salary..but esi people say she is not eligible for leave benefits…who is responsible for the salary now
hii,
my due date is in august , can i give the 26 week maternity leave?
is there i m applicable for 26 week maternity leave?
Hi,
Is the 26 weeks of maternity leave includes 8 weeks of Prenatal leave or this is additional?
Please reply.
Yes 26 weeks of Maternity Leave includes 8 week of Prenatal leaves.
You get 26 weeks of Maternity Leave. You can decide how much pre natal leaves you want.
hi..my wife draws more than 15000 ..but she is included in esi from jan 2017…she is in maternity leave from march…the company says from april the esi will pay the salary..but esi people say she is not eligible for leave benefits…who is responsible for the salary now
For entitlement to maternity benefit, the insured woman should have contributed for not less than seventy days in the immediately preceding two consecutive contribution periods prior to actual or expected date of confinement as the case may be.
There are two contribution periods each of six months duration and two corresponding benefit periods also of six months duration as under.
Contribution Period Cash Benefit Period
1st April to 30th Sept. 1st Jan of the following year to 30th June
1st Oct to 31st March of the year following. 1st July to 31st December.
Hi. My due date is mid of July 2017. But due to medical conditions I’m advised bed rest May onwards. In which period do I fall? My employer still follows 3 months maternity leaves because as per them there is no update in the UP state labour laws of the new act!
A company either follows Maternity Benefit act or ESI act.
You can clarify this by raising your question at twitter.com/socialepfo or facebook.com/socialepfo
Hi i have joined office after maternity leave.. and my HR is asking me to sign a bond of 1 year. I have bin with this company for 3 years. Is it lawful to ask to sign a bond after joining back from Maternity leave.
That’s not legal.
But many companies do have bond for 6 months or so.
Hi,
My maternity leave has expired on 5th march 2017 Am I applicable this new amendment?? Now I am on Lop.
Sadly no. Only those who were on maternity leave as on 1 Apr would get 26 weeks.
Hi,
Hi,
My maternity leave has expired on 5th March 2017 and as per additional benefits I and entitled to avail LWP for 2 months. Will I not be benefited under this new amendment??
Hi, My maternity leave duration was 19Dec’16 to 19mar’17. I have delivered baby on 24th Jan 2017, my ML already exhausted and now i am on LOP leave for 3 months. Is the new rule of 26 weeks ML is applicable to me nw?
Sorry it is not applicable to you. As per Govt. clarification here Those who are on maternity leave as on 1 Apr would get 26 weeks
Hi,
My maternity leave got exhausted on April 9, had put in a mail for extension…have not joined back yet. My employer came back on my extension mail today and has denied me any extended leave. Is this offensive as per law?
Yes as per Govt clarification Those who are on maternity leave as on 1 Apr would get 26 weeks
It’s a difficult situation as the employer would have to pay for additional 14 weeks and many small companies do not like it.
So handle with care.
Hi,
My due date is on 28th May 2017, so my employer is saying that you have already lapsed your 4weeks of maternity leave as it needs to be claimed 8weeks before the expected due date. Need some clarification will my 4 weeks of leave be exhausted
He is totally wrong.
It is up to a woman (in consultation with her doctor) to decide when she needs to take maternity leave.
A woman can take her maternity leave starting 8 weeks before due date. Not before that.
I personally worked till 4 days before my due date and took 12 weeks after that which was maternity rule then.
As we have said in the article
According to the Maternity Benefits Act 1961, a women employee is entitled to 26 weeks of which not more than 8(earlier was 6 week)s shall precede the date of her expected delivery. How she takes those 26 weeks depends on her. She can take all her Maternity Leave after the birth of her child. She can start her Maternity leave anytime in 8 weeks before her due date.
You can show the maternity act page 5 1*[(3) to your employer.
The maximum period for which any woman shall be entitled to maternity benefit shall be twelve weeks of which not more than six weeks shall precede the date of her expected delivery:]
Hi
My due date is on June 3rd 2017.im planing to take maternity leave from may 1st.My company is saying there is no GO passed by government.they say they are waiting for final GO..
Can you help me
Is there a GO (government order)so that I can send to my company
Govt clarification is here
I am 23rd week pregnant and i want to take meternity leave from 1st may2017 should i take meternity leave from may for 26 week leave?
You can start your Maternity leave anytime in 8 weeks before your due date.
So you should be about 32 weeks pregnant to claim your Maternity Leave.
If you are having problems then you can speak to your Manager and HR is they would allow work from home.
My company has not implement the amendment yet. Why is it taking so long? I m sure in July and can take leave as per the new amendment in may. But they say they have not implemented the amendment yet. What can be done?
You can wait as it’s some time till July.
For company perspective they have to pay 26 weeks of paid leave hence they would be reluctant to bring in the change.
Hi,I m currently on maternity leave which will be exhausted on 25th April 2017 as per 12 weeks maternity leave policy.
But as per the new maternity leave policy those who are on maternity leave as on 1st April 2017 are eligible for the extended (26 weeks) leave benefit.I have spoken with my HR and also shared the circular issued by the labour ministry regarding the same but the HR said that the extended leave policy is applicable only after 1st April 2017.So kindly suggest what should be done now.
Tricky situation.Please be calm while addressing it.
The law is applicable for those who are on Maternity leave on 1 Aprl 2017.
But you don’t want to upset the employer too.
You can ask question on EPF twitter at https://twitter.com/socialepfo
or facebook https://www.facebook.com/socialepfo
and forward the reply to HR.
Hi,Thanks for the reply.But how will forwarding the reply from the link mentioned above will help in changing the mind of the employer as they are very adamant on it.Also can I complain the labour department for the same?
You can but handle with care. It’s a difficult situation as the employer would have to pay for additional 14 weeks and many small companies do not like it.
If you raise with the labour department then you can jeopardise your career. The company may fire you in the worst case or make life difficult for you.
So please handle it cooly.
Did you get any solution in your case?
I delivered a baby on 24 Nov 2016. My maternity leave got exhausted on 26 Feb 2016 and since then I am on Loss of pay till today. I have not rejoined office. According to the latest amendment, which was on 12 April 2017, will I be eligible for 26 week maternity leave?
Congratulations Sunaina. Hope you and baby are doing fine.
Technically your Maternity Leave ended on 26 Feb. So the rule does not apply to you.
You can still talk to your employer.
hai i need a clarification can anyone please help me out.?
i am 8 months pregnant now my due date is on May 7th 2017 and i started working in nmit from jan 18th 2017 and they are deducting for esi from that month in my salary am i eligible for 24 weeks maternity benefit with paid leave or not ?????
please reply….
As per ESI Act “an insured woman shall be qualified to claim maternity benefit for a confinement occurring or expected to occur in a benefit
period, if the contributions in respect of her were payable for not less than seventy daysin the immediately
preceding two consecutive one or two contribution periods”
From 18 Jan 2017 to 8 May 2017 you would have contributed for 110 days.
Contribution period in ESI is Apr to Sep and Oct to Mar.
You meet both the requirements so you are eligible for 26 weeks(not 24 weeks).
Please verify with your ESI dispensary.
You need to visit your ESI dispensary, obtain certification from IMO concerned and submit the same to your ESIC Branch Office.
Thank you sir… I need a little clarification regarding the second part of my doubt.
Is there any rule which says that maternity leave should be availed starting from the day of hospitalization for safe confinement?
If there is any circular or gazette which states that I could avail my whole maternity leave of 84 days starting from the day of delivery, and it is not mandatory to start it from a preceding date, can you please upload it or mail it to me?
Also who decides regarding the date of starting and completing the maternal leave? The employee i.e Me, or the Gynaecologist who conducted my delivery, or the management of the place in which I work? Kindly give me any legal reference to prove this also.
Thank you in advance.
Hi… I completed my maternity leave on mar 30 2017 and joined on mar 31 st 2017. Will i get extended leave of 26 wks as per the new amendment?
Also another doubt. I had requested to issue me maternity leave from the date of delivery.i.e. jan 8 2017. But the gynaec told as per rule it is to be issued from the date of hospitalization i.e. jan 6 2017. Is there any such rule? I had several other types of leaves remaining which i couldve taken until date of delivery.
And if my maternity leave was calculated from the date which i requested, my joining date would have been april 3rd. Would that have made any difference??
Sorry as per the new law as you joined before 1 Apr you will not be able to claim 26 weeks of maternity leave.
You can talk to your organization and see if they can adjust the dates.
Sir,my maternity leave ended on 3rd April 2017,now I am on LWP ,am I entitled for this benefit..as my ESI deduction starts from the month of January..
ESI Maternity Leave has been increased to 26 weeks from 12 weeks. Tweet from Labour Minister.
For companies covered under Maternity Benefit Act those women who were on maternity leave on 1 Apr are eligible for extended Maternity leave.
Regarding ESIC its not clear.
Please ask your employer and let us know.
We will also try to get more information on it.
Thank you for the reply. I need clarification regarding the second part of my doubt.
Is there any circular or gazette which states that maternity leave can be taken starting on any day which I wish… whether it is before delivery or on the date of delivery? If so, please upload it or email it to me.
Is there any rule which says maternity leave should be calculated from the date of hospitalization for safe confinement?? Who decides the starting date of my maternity leave? I, or the Gynaecology doctor who conducted my delivery, or the management of the place in which I work?
Thank you so much in advance……
According to the Maternity Benefits Act 1961, a women employee is entitled to 26 weeks of which not more than8(earlier was 6 week)s shall precede the date of her expected delivery. How she takes those 26 weeks depends on her. She can take all her Maternity Leave after the birth of her child. She can start her Maternity leave anytime in 8 weeks before her due date.
You have to inform your employer that you will be on maternity leave from so and so date.
You can read the Maternity Benefit act here.
Hi… I discussed the previously mentioned issues with my HR.
The HR told that the clarification letter on maternity benefit by the Ministry of Labour and Employment dated April 12 2017 is not legally valid as it is not published in the Gazette. So, all those who deliver after April 1, 2017 will only get the extended benefit of the amendment. Is it so?
No. Govt has clearly stated that Bill is effective from 1 Apr 2017.
For questions raised on social media they came up with clarifications such as Those who are on maternity leave as on 1 Apr would get 26 weeks.
If you have a doubt please raise it o social media twitter.com/socialepfo or facebook.com/socialepfo
Hi,
I delivered my baby on 13th march 2017 and my maternity leaves got finished on 10th april 2017(84 days maternity leaves). I requested my HR to extend my maternity leaves as per new law but he did not and said its effected from 1st april so you are not eligible. he gave me LOP(leaves without pay) from 11th april for 6 weeks. So currently i am on LOP leaves.
So Still am i eligible for 6 months maternity leaves as my ML got over on 10th april but i am on LOP ? Please do reply
As you were on maternity leave on 1 Apr 2017 when Maternity law came into effect, you are eligible for 14 more weeks. Please pass the official gazette notification here
We delivered in Dec 16 and my wife is on Mat leave currently. The Mat leave in her org is 22 weeks. Will the amendment be applicable to her? as per the article i understand yes since she is on mat leave as the time of the amendment viz 1st April however what i hear is since the org already offers add mat leave of 4 weeks this may not be applicable.. can you please confirm
I delivered my baby in feb 2nd and my maternity leave will be ending by April last week. Please confirm am I eligible for 6 months paid leave since the new law applies to who are in midst of their 12 weeks leave. Please confirm so that I can talk to my HR
Yes all the women who are on maternity leave on 1 Apr 2017 will be eligible for 26 weeks of maternity leave. Please talk to your HR
Earlier the maternity leave was for 84 days. Companies can give more than that.
Now a company has to give min of 26 weeks. It is a law now.
So she should get extra 4 weeks. Please ask her to talk to her HR
Hi, I am 9 months pregnant and going to deliver in the month of may, my query is, when I enquired with my HR department about this extended law of ML benefits, they are saying, as such, they didn’t receive any written information till date, so I am eligible for only 84 days leave. Please guide what should I do to avail 6 months leave benefits.
Congratulations and best wishes.
Those who will be delivering after 1 Apr 2017 are entitled to 26 weeks maternity leave. The Maternity leave of 26 weeks has become a law from 1 Apr 2017. Your company has to give you 26 weeks maternity leave.
Those who are on maternity leave as on 1 Apr would get 26 weeks. Clarification by the Govt on 12 Apr 2017 is given below. For full notice you can read here which you can forward to your HR.
Hi,
my wife is 4 months pregnant can i get medical benefits from ESI ?
hi i am working with jsb group and my 7th month will be started and my expected delivery time is around in june end so when can i gwt leave for my companies and how much time…its 26 weaks
You can take 26 weeks of maternity leave with 8 weeks before the due date
i had dekeivered baby on 17 november 2016.Can i take 6 month maternity leave m still on leave taking earned leave pls confirmed bcoz now m going to without oay lwave
No as your maternity leave even if 12 weeks taken from Nov 16 would be over by Feb 17.
But please clarify with your HR.
in bemoney aware it also mentioned newly mother who already exausted 4 month maternity leave also avail six month leave automatically
We have mentioned
Those who will be delivering after 1 Apr 2017 are entitled to 26 weeks maternity leave.
But it is not clear whether women who are in the midst of their 12-week maternity leave (under the un-amended law), will be entitled to extend their leave to 26 weeks. Clarification is awaited for following scenarios
Hi ,i had deliverd on 4th april 17,and i was on leave from 13 th march.can i eligible to get 26 week leave?pls reply.
Yes, you are eligible for 26 weeks. Those who are on maternity leave as on 1 Apr would get 26 weeks. Clarification by the Govt on 12 Apr 2017 is given below. For full notice you can read here
I delivered on 23rd January and my maternity leave will be ending on 23rd April as per old rule of 90 days. Will I get extended maternity leave of 26 week. Since i am a nursing mother and upto 6 month i have to breastfeed my baby I should get extended ML.
Yes as you are on Maternity Leave on 1 Apr you will get total of 26 weeks of maternity leave.
m also going on now laeve and in all mention six month breastfeed reuired for baby then according to this our maternity leave should also be six months bcoz my baby covers six month in may end
You will get 26 weeks or 6 months of maternity leave.
Then on joining the employer has to provide a creche where you can visit to breastfeed your child. (This will come into effect from 1 Jul 2017)
Hi,
my wife is 4 months pregnant can i get medical benefits from ESI ?
ESI is an alternative to the Maternity Benefit Act.
The ESI is due to employees earning Rs. 15,000 or less per month, with the employer contributing 4.75 percent and the employee contributing 1.75 percent. Those who qualify may receive maternity benefits under the ESI scheme instead of the Maternity Benefits Act. In order to be eligible for maternity benefit under ESI Act, 1948, an insured woman should have contributed/contribution payable for not less than 70 days in last two consecutive contribution periods i.e. one year. ESIC website covers details of Maternity Benefit.
Hi,
My maternity leave has expired on 6th April 2017 and as per additional benefits I and entitled to avail LWP for 3 months. Will I not be benefited under this new amendment as my company claims that the law is only applicable to women who avail maternity leave on or after 1st April?
The latest information about the act says that it is effective from 1 Apr 2017. They have still not clarified whether it is for those who are already on maternity leave on 1 Apr 2017 are eligible or not. Wait for few more days. We should be getting clarification on that too.
There is amendment on working from home which will be effective from 1 Jul 2017.
I m expecting delivery in sep 17. It is my 4th month prenatal. Right now I am travelling 33 Kms Morning and 33 Kms evening via uber cabs. due to long travel hours I asked my manager for work from home option in my company. My leaves are over. They are saying to take LWP if you do not want to travel. Is there any provision in policy so that I can convince them for the Work from home option during prenatal period. Please reply.
Sad to hear about your state.
You can take Maternity Leave 8 weeks before the due date as per the maternity Act.
Before and after that depends on your company.
Work from home option again depends on your company.
You can talk to a senior women manager and try to put your point across.
Do take care of your health, traffic sucks!
Hi I am currently 17 weeks pregnant. Due to some complications I am opting work from home option and planning to go on leave after 7th month.i.e begining of July month. My due date comes in September. So am I eligible to apply maternity leave two months before due date?
Hi I delivered my baby in feb 2 and my maternity leave will be ending this month. Please confirm that am I eligible for 6 month maternity leave since the president also okays the new bill
Please reply I am working in an IT company
Congrats. Hope you and your baby doing fine.
The bill has come into effect from 1 Apr 2017.
Companies are waiting for clarification whether iwomen who are in the midst of their 12-week maternity leave (under the un-amended law), will be entitled to extend their leave to 26 weeks
Check with your Company.
The appointed date for enforcing the amended maternity benefit has not yet been notified. The amended Act is notified on 28th March,2017.In the amended Act it is stated that for date of commencement separate notification is required.
Secondly in Rule 56A it is clearly said that medical bonus is RS.5000. I think, the information given by you is inadequate and erroneous
Thanks for information. We have updated the article.
Hi, I got job in bank of abroad through ibps.present I am 3 rd month pregnant,at the time of joining I may be in 7 th month..when can I apply maternity leave.can I get leave in probation period.
My wife delivered a baby on 7th March 2017 and is on maternity leave. Since now that President too has signed / approved the law will she be eligible to extend her maternity leave.
Congratulations. Hope your wife and child are doing fine.
Yes she would be eligible for 6 months maternity leave.
After a week she should get in touch with the company, as many companies will be discussing it this week and coming out with the policy
Sry sir im joined in the month of December 2016
It does not matter when you join. If your company has the maternity leave policy of 6 months you will get it
Sir,
Im joined in one private company in the month of December 2017. Present im 8months pregnant. Are I eligible for Esic maternity leave.
Hi,
I have delivered a baby who is 6 months now and i was not eligible for the 6 months maternity leave. So i have started working now and i am not getting nursing breaks where i can feed my baby. As per the Maternity Act, nursing breaks should be provided until the baby is 15 months old. As my company is not providing nursing breaks. How do i proceed further.
Talk to your company.
As the maternity bill is still not passed by the President many companies are waiting to make changes.
hi
i am working in cognizant and i delievered baby on 1st nov 2016..my maternity leave ends today ie 21/mar/2017..am i eligible for 6 months leave?when i spoke to HR team they are saying leadership team needs to decide..Please let me know whether am i eligible or not?
Thanks
Saranyah
Bill has not been signed by the President.
So it depends on the company actually.
Bill has been signed now..Will I get my maternity leave?
Yes you should get it
HI
I am working in cognizant..i delivered baby on nov 1st 2016..am i eligible for 6 months paid leave?
Thanks
Saranyah
my maternity leave expires today..it would be helpful if u give info
Hi im swathy im now 7 months my delivery date has on may im working in a private company will i get 6 months leave if not what should i do for that leavee plzz give the information
The bill has been passed by both Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha. It is waiting for President’s signature which we hope will happen soon.
So We think you would be able to get 6 months leave
Hi, I have applied my maternity leave on dec 19, 2016 and my delivery due date jan 27 2017. whether it is applicable for 24 weeks maternity leave with pay or not
Congratulations. Hope you and the baby are doing fine.
You have to ask your company. Many companies have already made changes but some are waiting for the President to sign the bill and then implement it.
According to this blog they have mentioned who are still in their maternity leave within 3months will also be eligible for new 6monts leave. But I did not find any update about tis in any gov website.
Hi am 7 months pregnant and my due date is on June 2017. And I work in private concern. Whenever I go and ask them they used to say we wil get back to you in two days. Once if the bill get passed and sure private concern as to provide pregnant women with paid 26 weeks. Can you please say me whether am I applicable for it?
It should be applicable to you.
Govt has still not come out with any deadline but your company should bring into effect very soon.
Hi,
I am 3 month pregnant woman. I working in private company, it’s an export house and I am working as a merchandiser. My company gives 3 month maternity leave. But I have a doubt that they would pressure me to resign the job when they have to give me 26 weeks paid leave. also I want to know that I am eligible for 26 weeks paid maternity leave now.
Hi I delivered on Nov 30 2026 maternity leave ended on Feb 19, 2017. If this bill passed am I eligible for 26weeks leave benefits or not?
Congratulations hope you and your child are doing fine.
Sadly no.
You can talk to your HR about it. Most of the companies want to retain their good employee.
the women who had delivered after 20 January 2017 can applicable for 26 week maternity leave before that only 12 weeks
Thanks for Info.
How did you get the date as 20 Jan ?
Hi,
I m 7 month pregnant women. I working in private company.it’s an reputated export house.and I m working as a merchandiser. my company is not giving me any merternity leave.other than that they are pressuring me to resign the job. In this case what should I do,which is legal and helpful for me.
kindly advice how much I m eligible for take leave.
You can take legal action but it would be long and troublesome. Even if you win Would you like to work in the company where you are not welcomed?
You can read about similar story in Times of India Woman says sacked for seeking maternity leave
Along with the cesarian operation, tubectomy has also done. while claiming maternity leave of 84days whether we can claim 1 week additional leave.
Now i am pregnant & 6 Months.My delivery date 06.05.2017
Iam eligible for 6 months maternity leave. please confirm.
Please check with your company. Many companies have started giving 6 months of leave.
Can you please tell me how to apply for maternity leave. I have completed 5 months.
hello i dont know how to apply esic maternity benefits i have completed 6month and my delivery date is may 2017 so plz can u suggest me how can i apply online
and how can i get my maternity paid wages.is there any from for maternity paid wages.so plz suggest me
Thank you
Hello,
As I am in my 8th Month of my pregnancy. My due is by March 10, 2017. My company provides me with 84days of paid leave. Will I be eligible for 6months of paid maternity leave. Only the conversation is going on and on, but we have not received any confirmation for 6months leave. Why don’t this take place at the earliest. So, every women employee will be benefited. Also if we want to extend the leave on later part I don’t think our employer will consider. Please advise on priority.
The amendments to the act has not been approved by president yet so there is no official confirmation. This may get approved in winter season. Hope you will get a 6 months leave.
Have health and happy child..
Thank you
i am employ in a private organization. i am 8 weeks pregnant. my project is going to be complete in the end of march. i applied for maternity benefits. can i take the maternity leaves in the starting month of pregnancy. because i have some complications.
“As per the maternity Law, 45 days’ salary is given when you go on Maternity Leave i.e. 30 days in first month and 15 days’ salary in following month. Rest 45 days’ salary will be credited in your account once you rejoin the company.
For this reason, you have received half of your salary in this month as you have already received 30 days salary in previous month.”
Above is reply from a company for paying half salary during maternity leave. Please help if this is valid in maternity law.
Hi,
we have a case where a woman delivered in the 8th month of pregnancy and the child died after 2 days. Is she eligible for the maternity leave of 12 weeks…?
now i am pregnant my delivery date21.2.2017
so i can get 6 month leave
Congratulations and Best wishes.
Law for extending Maternity Leave has NOT been approved.
But many organizations have started giving 6 months leave.
Please discuss it with your employer.
Hi,
I work for a public sector bank for almost 2 years .In our bank maternity leave is for 6 months. On the month of june 2016 I was transferred to a completely different place from my husband’s place and I had to stay alone. My pregnancy got detected in the month of July2016 and since it had some serious complications I had to be on bed rest for my entire period of pregnancy. Hence I was in loss of pay from the month of August 2016 as all my leaves were exhausted.On an extremely emergency situation I had came down to my home town for my health issues and since traveling was not allowed at this condition I could not join my duty. Each and every month I have submitted my medical certificate certifying my current health condition to my employer without fail. My sudden movement to my home town was also approved by my employer at that time.Now when I am applying for maternity leave from 1st of january 2017 since my deliver is due in march 2017 they are not allowing me to apply stating a reason that LOP cannot be combined with maternity. And I can apply maternity leave only when I can join service. I have again submitted a fresh set of medical reports and doctor’s certificate clearly mentioning my inability to move. But still my Hr is completely denying me from applying. I just want to know am I not eligible for maternity leave even if my Loss of pay is completely due to pregnancy related complications. An what are the legal options I have. Since I am sick and tried of begging for the leave in front of my HR people.
Now I am pregnant my delivery date 1 march 2017. So I want maternity leave but company not allow to me materiity benefits….pls give me solution
Hi, Good to read about this article. As recently my wife’s employer denied her of maternity benefits. We have given the written notice much before the due date still were denied of. Now we are blessed with baby and still the situation is same. She was with organization for one and half years and even after regular chasing, the company sticks to the stand that since it was not part of offer letter or appointment letter hence it can not be asked for. What would be right course of action?
I am 6 mnths pregnant. planning to take maternity leave from April 2017. my company allows 3 months leave.
till now 26 weeks maternity leave is not a rule. is there any possibility to get 6 months maternity leave for me?
It all depends on the company.
Lets keep fingers crossed and hope that 6 month maternity is made a rule.
Is this bill is expected to be approved by President in a short time or this is also keeps rolling for years and needs strikes to be done to get this pass.
Really waiting for something good will happen by understanding the women responsibilities and her health consideration without affecting her financial income.
big ads in all news papers. but not yet become law. They are only giving only 84 days leave. My wife worked in Finance company up to 9 months. They didn’t given bonus also.
we do not know when will this become law.
Bonus amendment act is also hope and pain to Women who are pregnant and new mothers.
ESIC people asking C-section women also attend to get this leave personally with in 28 days of Delivery.
My wife travel with baby 500 km from to Hydeabad to get this leave.
Now days wife and husband without working as employee not giving good life their children.
ESIC people also asking Birth Certificate of the baby.
in Online they asking only Form 18 and Form 10
But ESIC people asking Form 18 , Medical Certificate, Declaration letter, Birth Certificate, Delivery Summary, Temporary Identification Certificate,Bank Pass book xerox or cancel Cheque OR Latest Bank State ment with IFSC Code, Form 10 With filled by HR after leave completed”.
These are not up dated in online ESIC portal.
Some state Governments giving Maternity Leave for 270 days( Tamil Nadu).
by
murali
9553683789
when will this amendment will become as a law as its it is not yet signed by president till now since it has been announced. And most of companies are not accepting the change as their is no nod by president.
so do you have any idea about the it becoming as act?????
Now I am pregnant my delivery date 27 November 2016. So I can get six month leave
Congratulations and Best wishes.
Regarding 6 months of maternity leave Please check with your HR. Maternity leave of 6 months is not a law till now.
Now i am pregnant & 8 Months.My delivery date 17.01.2017
Iam eligible for 6 months maternity leave. please confirm.
Hello,
I gave birth to my child on 01-08-16 and was on maternity leave till now. My company provides 3 month maternity leave but i’ll be not able to join till 6 month due to breastfeeding. I am fine with LWP, just need to know- Do i have to return my salary which was given to me during ML? Also, if they want me to serve notice period, may i ask work from home facility?
Hi,
I had applied for leave in October,2015 from 15Feb2016 to 1 August 2016. My employer had taken resign from me on 13Feb(last working day) and had not approved maternity leave. Upon joining again they considered it as rejoining, my previous experience in same company was not considered . Currently I am working in same company on same salary and designation due to job location and career gap. Also they provided me new job offer letter.
What action should I take against my employer?
Pls help to know wen bil will passed and this will implement in other companies who are depending upon bill or GO.
Sure will update.
I have not been paid by my employer during my maternity break . What action can I take against my employer.
It is illegal.You are eligible for Maternity Leave of 84 days with full pay and also you are entitle for Maternity Bonus after submitting the forms as per the provision of Maternity Benefit Act.
It is a difficult matter for it affects your career. It is very difficult for an employee to get its lawful dues when the company is bent upon denying it.
What is your location (in India or overseas) and where is the registered office of the company ?
Whether the client company where you are/were working is a foreign company, incorporated in another country other than India ??
Try to find out whether other women were also denied maternity leave.
Try to speak to HR, put claim in writing and ask him to write his comments on it (whether benefits will be given or not as per Maternity Benefit Act).
You can say you would be going to Labour office or use social media .
now i am pregnant my delivery date 26.12.2016
so i can get 6 month leave?
Congratulations and have a safe delivery.
You have to check with your office. Many offices organisations have moved to 6 months.
In Aug 2016, The Cabinet note prepared by the Labour ministry to amend the Maternity Benefit Act, 1961, increases maternity leaves from present 12 weeks to 26 weeks. The Rajya Sabha passed the bill in question on 18th Aug 2016, ensuring that paid maternity leave is extended from 12 to 26 weeks for mothers Although this is a huge step towards a historic step, it still needs to be passed by Lok Sabha and the approved by the President before it becomes a law, which may take time.
still i have a doubt is really increased from 3 months to 6 months
If someone is getting salary less then 15000 then who is going to pay the salary during the maternity period company or ESI.
Is there any govt circular about 26weeks maternity leaves or from where we can get/download that document to show it to our employer for an approval of maternity leaves as some emoloyers are not ready to saction 26 weeks maternity leaves.
The Rajya Sabha passed the bill in question on 18 Aug 2016, ensuring that paid maternity leave is extended from 12 to 26 weeks for mothers with 2 surviving children and 12 weeks for mothers with more than 2 children. It also takes into account mothers who adopt children and mandate child care facilities in organisations with more than 50 women employees.
Although this is a huge step towards a historic step, it still needs to be passed by Lok Sabha and the approved by the President before it becomes a law, which may take time
Hi All,
Usually mother should feed the child minimum of 6 Months. So we cant have exactly 6 months of Leave. The Women employees should get 8 Months of Maternity Leave.
Lets take it in small steps. Lets enjoy Increase from 3 months to 6 months .