Good and Services Tax (GST) was introduced on 1st July 2017 to normalize the tax regime of the country. This tax reform brought in multiple changes for businesses and the common man. This article explains GST for a common man, for business. It then talks about GST Invoice or Bill with GST Information such as GSTIN, CGST, IGST, HSN Codes, SAC Coes, UQC.
In case you are confused about what is GST, then let us tell you that it is the indirect tax levied on all goods and services. It is a multi-staged tax levied on the value added at every stage. Let us now check how this tax regime is affecting businesses and the common man.
Table of Contents
GST for common man
The primary area where GST has its direct impact is the prices of consumer goods and services. The prices of goods and services may change due to the effect of the tax. The government has brought in five tax brackets : 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%. All the consumer goods fall under these brackets and are taxed accordingly.
- The government has made sure that the articles of daily consumption like milk are being taxed at 0%.
- Commodities such as sugar, tea, and edible oils are being taxed as low as 5%.
- Goods like butter, computers, and dry fruits fall under 12% tax bracket
- capital goods, toothpaste, toiletries, and others fall under 18% tax bracket.
- Consumer durables such as air-conditioner and refrigerator fall in the 28% tax bracket. Small cars and high-end motorcycles are also a part of the 28% tax bracket with an additional cess of 1% or 3% (for small cars) and 15% (for motorcycles).
Similarly, for the services provided, different services fall under different tax brackets.
- Information Technology (IT) and financial services fall under the highest bracket of 18%
- Work contracts fall under the 12% bracket.
- Transport services fall under 5% bracket
- Services like hotel and lodging with tariff under INR 1,000 are not being taxed.
GST for business
GST functions on value addition. Taking an example of the manufacturing sector, if the value is being added or if the value of goods increases at any step, the tax will be levied on the same. If the raw material is converted to finished goods, the tax is levied on it.
GST is a destination-based tax. The tax is levied at the point where the goods and services are consumed. For example, if a product is manufactured in Gujarat and sold in Karnataka, the tax will be levied in the state of Karnataka.
A return is a document containing details of income which a taxpayer is required to file with the tax administrative authorities. This is used by tax authorities to calculate tax liability. Under GST, a registered dealer has to file GST returns that include:
- Purchases
- Sales
- Output GST (On sales)
- Input tax credit (GST paid on purchases)
To file GST returns, GST compliant sales and purchase invoices are required. The beauty of the system is that one has to manually enter details of one monthly return – GSTR-1. The other two returns – GSTR 2 & 3 will get auto-populated by deriving information from GSTR-1 filed by you and your vendors.
In the GST regime, any regular business has to file three monthly returns and one annual return. This amounts to 37 returns in a year. There are separate returns required to be filed by special cases such as composition dealers.
GST Invoice
Any dealer registered under state VAT law had a unique 11 digit TIN number assigned to him by state tax authorities. Similarly, service tax registration number was assigned to a service provider by Central Board of Excise and Customs (CBEC). Under GST regime, all these parties have come under one single authority and the different identification numbers are replaced by a single type of registration number for everyone Goods and Services Tax Identification Number or GSTIN
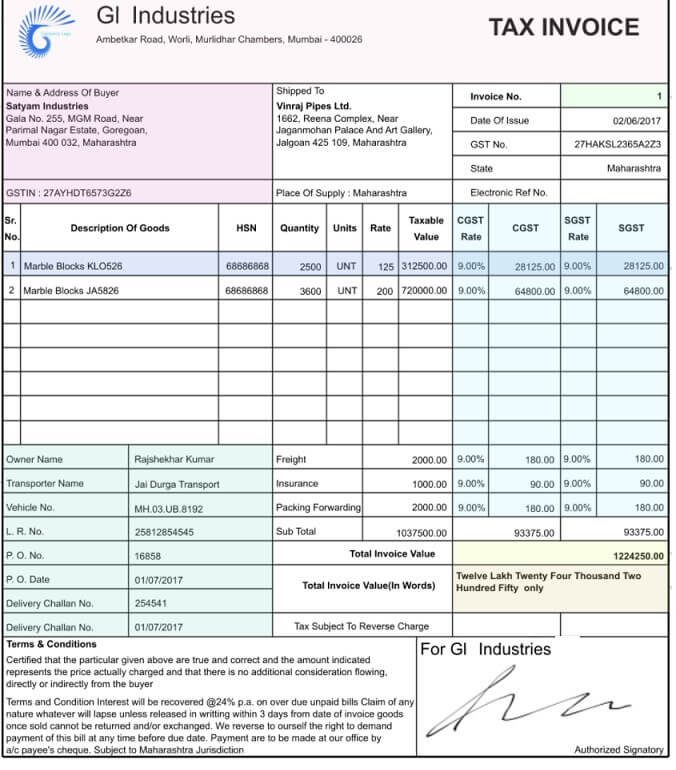
GST invoice is the invoice that is acquired by the assesses having GSTIN (Goods and Service Tax Identification Number). This invoice describes the rate of tax and the taxable amount over the interstate and intrastate sales/purchases. In case of any such purchases or sales, invoice tax bifurcation is to be done on CGST and SGST. In the case of inter-state sales, IGST will be applied.
According to the GST rules and regulations, all suppliers of goods or services are required to issue a tax invoice mandatorily, when the value of supply is over Rs.200. The tax invoice issued under GST is required to contain the following information:
- Name, address and GSTIN of the supplier.
- Invoice number not exceeding sixteen characters.
- Date of tax invoice.
- Name, address and GSTIN of the customer, if available.
- HSN code for goods or SAC code for services.
- Description of goods or services.
- Quantity supplied.
- The total value of supply.
- The taxable value of the supply.
- Rate and amount of GST
- Place of supply
Old bills with VAT
The structure of GSTIN or GST Identification Number
Every taxpayer will be assigned a state-wise PAN-based Goods and Services Taxpayer Identification Number ,GSTIN, which has 15 digits
- The first two digits of GSTIN represents the state code according to Indian Census 2011. Each state has a unique two digit code like “27” for Maharashtra and “10” for Bihar.
- The next ten digits of GSTIN are the PAN number of the taxpayer.
- 13th digit indicates the number of registrations an entity has within a state for the same PAN. It is alpha-numeric number (first 1-9 and then A-Z) and is assigned on the basis of the number of registrations a legal entity (having the same PAN) has within one state.For example, if a legal entity has single or one registration only within a state then it will be assigned the number “1” as 13th digit of the GSTIN. If the same legal entity gets another or second registration for a second business vertical within the same state, then the 13th digit of GSTIN assigned to this entity will become “2”. Similarly, if an entity has 11 registrations in the same state then it will be assigned letter “B” in the 13th place. This way up to 35 business verticals of any legal entity can be registered within a state using this system.
- The 14 digit currently is “Z” by default.
- The 15th is check code which is used for detection of errors.
The state codes are as below.
01-Jammu and Kashmir, 02-Himachal Pradesh, 03-Punjab, 04-Chandigarh, 05-Uttarakhand, 06-Haryana, 07-Delhi, 08-Rajastan, 09-UP, 10-Bihar, 11-Sikkim, 12-Arunachal Pradesh, 13-Nagaland, 14-Manipur, 15-Mizoram, 16-Tripura, 17-Meghalaya, 18-Assam, 19-West Bengal, 20-Jharkhand, 21-Orrissa, 22-Chattisgarh, 23-MP, 24-Gujarat, 25-Daman and Diu, 26-Dadar and Nagar Haveli, 27-Maharashtra, 28-Andhra Pradesh, 29-Karnataka, 30-Goa, 31-Lakshadweep, 32-Kerala, 33-Tamil Nadu, 34-Puducherry and 35-Anadaman and Nicobar Islands.
HSN Code in GST Invoice
HSN or Harmonized System of Nomenclature or The Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System is a multipurpose international product nomenclature developed by the World Customs Organization (WCO). HSN Code is an internationally accepted goods classification system used in over 200 countries. It was originally using 6-digit HSN codes to classify commodities for Customs and Central Excise. Later Customs and Central Excise added two more digits to make the codes more precise, resulting in an 8 digit classification. India has 2 more digits for a deeper classification
- The purpose of HSN codes is to make GST systematic and globally accepted.
- HSN codes remove the need to upload the detailed description of the goods. This will save time and make filing easier since GST returns are automated.
- A dealer or a service provider must provide HSN/SAC wise summary of sales in his GSTR-1 if his turnover falls in above slabs.
The HSN structure contains 21 sections, with 99 Chapters, about 1,244 headings, and 5,224 subheadings.
- Each Section is divided into Chapters. Each Chapter is divided into Headings. Each Heading is divided into Sub Headings.
- Section and Chapter titles describe broad categories of goods, while headings and subheadings describe products in detail.
With the HSN code acting as a universal classification for goods, the Indian Government has decided to adopt the use of HSN code for classification of goods under GST and levy of GST.
- The HSN code chapter is represented in the first two digits of the HSN code.
- The heading of the goods is represented in the third and fourth digit of the HSN code.
- The sub-heading of the goods is represented in the fifth and sixth digit of the HSN code.
Handkerchiefs made of Textile matters 621390
- First two digits (62) represent the chapter number for Articles of apparel and clothing accessories, not knitted or crocheted.
- Next two digits (13) represent the heading number for handkerchiefs.
- Finally, last two digits (90) is the product code for handkerchiefs made of other textile materials.
India has 2 more digits for a deeper classification.
- If the handkerchiefs are made from a man-made fibre, then the HSN code is 62.13.90.10.
- If the handkerchiefs are made from silk or waste from silk., then the HSN code is 62.13.90.90.
Services Accounting Code (SAC) in GST Invoice
Like goods, services are also classified uniformly for recognition, measurement and taxation. Codes for services are called Services Accounting Code or SAC.
For example, Legal documentation and certification services concerning patents, copyrights and other intellectual property rights is 998213
- The first two digits are same for all services i.e. 99
The next two digits (82) represent the major nature of service, in this case, legal services
The last two digits (13) represent detailed nature of service, i.e., legal documentation for patents etc.
Many small businesses might find it cumbersome to find and update HSN code for the goods supplied. Hence, to reduce the compliance burden of small businesses, the GST Council has relaxed the requirement for displaying HSN code on invoices based on the sales turnover. As per Notification , HSN code on the invoice can be displayed as follows:
- Entities having less than Rs.1.5 crores annual turnover in the preceding financial year will not be required to display HSN code on the invoice.
- Entities having Rs.1.5 crores to Rs.5 crores annual turnover in the preceding financial year will be required to display the first two digit (Chapter) of the HSN code on the invoice.
- Entities having more than Rs.5 crores annual turnover in the preceding financial year will be required to display the first two digit (Chapter) and chapter heading of the HSN code on the invoice. Thus, only entities having more than Rs.5 crores of annual turnover would be required to display 4 digit HSN code on the invoice.
UQC
UQC stands for Unique Quantity Code. In simple terms, it is a unit of measurement such as 1 kilogramme of wheat, 1 litre of oil etc. As per CGST Rules, any tax invoice, credit note, debit note must have UQC or quantity unit description. So 1 kilogramme of wheat has to be mentioned in the invoice as 1 KGS, 1 litre of oil as 1000 MLT, 100 metres of fabric as 100 MTR etc.
What are payments to be made under GST?
Under GST the tax to be paid is mainly divided into 3 :
- IGST – To be paid when interstate supply is made (paid to center)
- CGST – To be paid when making supply within the state (paid to center).
- SGST – To be paid when making supply within the state (paid to state)
| Sale of Goods | CGST | SGST | IGST |
| Goods sold from Delhi to Bombay | NO | NO | YES |
| Goods sold within Bombay | YES | YES | NO |
| Goods sold from Bombay to Pune | YES | YES | NO |
Apart from the above payments a dealer is required to make these payments:
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) – TDS is a mechanism by which tax is deducted by the dealer before making the payment to the supplier.
GST payment is to be made when the GSTR 3 is filed i.e by 20th of the next month.
Related articles
- GST Bill : Good and Services Tax
- GST India : How Will It Affect Common Man Finances?
- Bill,Invoice,Receipt and Voucher
The tax regime has its implications on all kinds of businesses whether it is manufacturing or e-commerce. The government has tried to bring all the businesses under the purview of the tax regime. Some have profited from the new system while others have seen a negative effect on their business due to increased prices. It was very important to simplify the taxation in India in order to bring all the taxes under one roof and harmonize the system. GST has provided a solution for the same.