What are the different types of leaves that an employee in India can avail of? Employees, across all industries in India, are entitled to a certain number of leaves per year aside from the holidays and days off. The number and type of leave depend on the industry, employer, and state you are in under the Factories Act and State’s shop and establishment act. Every state has different leave entitlement and leaves policies which is the basis for the leave policy of your company. In this article find out information about privilege leaves, rules for casual leave, compensatory off, leave carried forward, paid casual leave etc. in India?
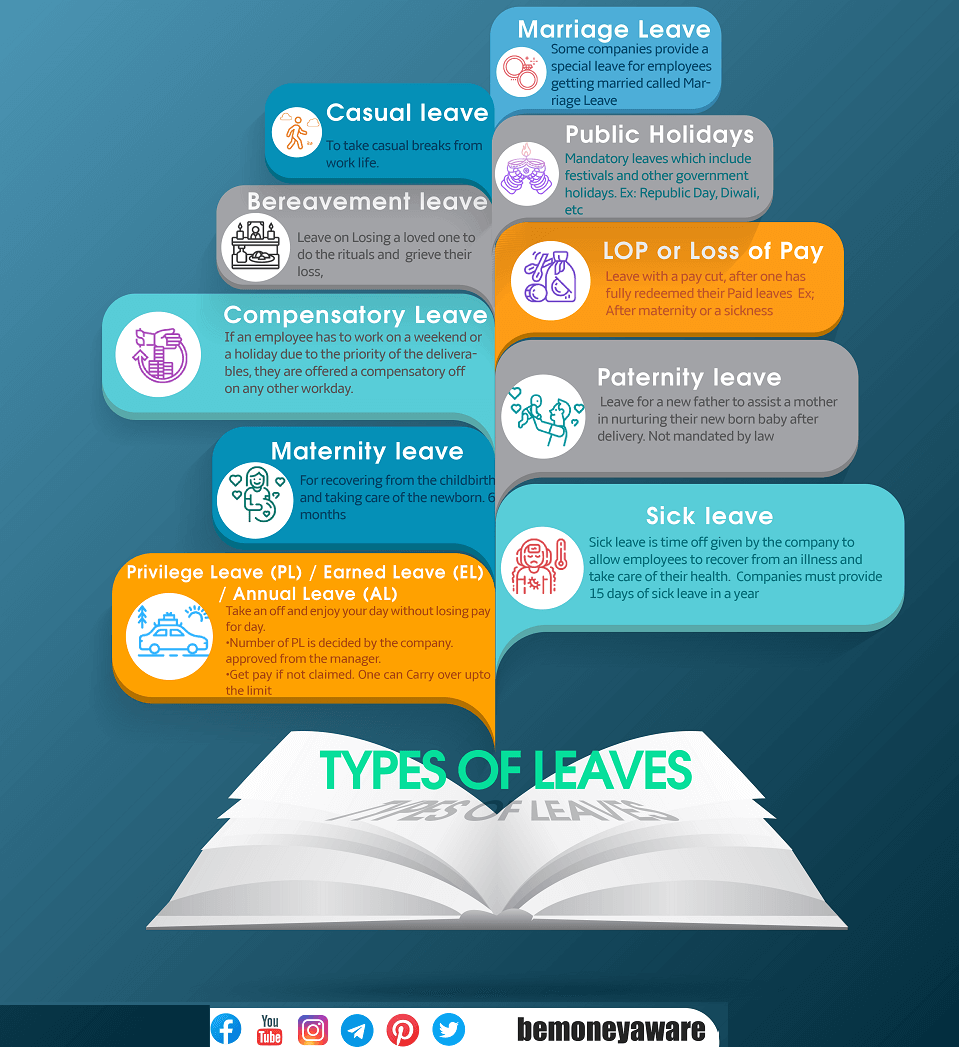
Table of Contents
General Overview of Leaves
Commencement of Leave Period is calendar year i.e 1st January to 31st December every year. All regular employees are entitled to around 27 days’ leave in a year. Holiday List is provided at the beginning of the calendar year. Generally, all State Legislations have a common provision for leaves usually at least seven holidays for national and other festivals. Republic Day, Independence Day, and Mahatma Gandhi’s birthday are compulsory holidays. Employer and Employees can decide on remaining national and festival holidays. Hence Diwali holiday in Karnataka is usually on Narak-Chaturdashi(second day) while in Delhi it is on Laxmi Pooja day. Minimum 7 days casual leave and 14 days sick leave are provided to employees.
Employees need to apply for each leave and take approval except in cases where approval could not be taken in advance usually for casual or sick leaves. Grant of leave shall depend upon the policies of the workplace and is at the discretion of the manager/management. There is no set rule for which leave to be approved and not approved. An employer can refuse the leave application, if not satisfied with the reason of leave. It depends from reason to reason, manager to manager.
Prorate means in proportion. For new joinee & resigned employees one gets pro rated leaves. So if one works half a year, one is entitled to just half of leaves.
Usually All leaves with pay are excluding weekly off and holidays. For example if an employee take leave from Saturday to Monday where Sunday is weekly off then Sunday should not be counted as leave. Hence only 2 leaves should be counted. If an employee is on leave for whole month (30 days) which includes 4 weekly off and 1 holiday then employee should be considered on leave for 25 days only. But then it depends on the Shop and Establishment Act of the state.
From Paycheck.in Earned & Casual Leave in India Shop and Establishment Act of 2 states is given below
DELHI SHOPS AND ESTABLISHMENTS ACT, 1954
|
Type of Leave |
Privileged Leave/ Earned Leave |
Casual Leave |
Sick Leave |
Maternity Leave |
|
Quantum per year |
15 days |
12 days casual-cum-sick leave |
No provisions |
|
|
Entitlement |
5 days after 3 months on completion of 60 days working in that period |
Not less than 1 day for every completed period of 1 month (casual-cum-sick leave) |
||
|
Accumulation |
45 days maximum of 3 years |
Not allowed |
Not allowed
|
|
KARNATAKA SHOPS AND COMMERCIAL ESTABLISHMENTS ACT, 1961
|
Type of Leave |
Privileged Leave/ Earned Leave |
Casual Leave |
Sick Leave |
Maternity Leave |
|
Quantum per year |
20 days (1 leave for every 20 days) on working 240 days in a year |
– |
12 days on Medical grounds |
Provisions of Maternity Benefits Act, 1961 to apply |
|
Entitlement |
On working 240 days in a year. On joining mid year, he will be entitled to 2/3rdof the remaining period during the year |
– |
– |
|
|
Accumulation |
Maximum of 30 days |
Not allowed |
Not allowed |
Types of leaves
Sick Leave/Medical Leave
Sick leave is the leave that an employee can avail when he is out of work due to illness.
- Sick Leave can be taken for a minimum 0.5 to maximum 7 days (paid).
- There are no sick leave carry-forwards or encashment. At the end of the calendar year, any available sick leave will lapse automatically.
- For all absences exceeding 2 or 3 days, depending on company policy, usually, a medical certificate needs to be enclosed.
- Sick Leave can be appended with Earned Leave.
- For new joinee & resigned employees, one gets pro-rated sick leave.
Casual Leave
Casual Leave(CL) are granted for a certain unforeseen situation or where you are required to go for one or two days leaves to attend to personal matters and not for vacation. In case of casual leave normally company’s strict maximum to 3 days in a month. In such cases, the person has to take the permission in advance.
- Casual Leave can be taken for a minimum 0.5 to maximum 3 days. In case of more than 3 days leave, it should be taken as Earned/Privileged Leave. If taking 3 leaves together Need to apply before.
- As per the rules under The Shops and Establishment Act, you are entitled to 6 days of Casual Leave
- There are no casual leave carry-forwards. On the closing day of the year, any unused Casual Leaves will lapse automatically.
- Casual leave is not encashable. At the end of the year, unused Casual Leaves lapse automatically.
- Can not be appended with Earned/Privileged Leave or Sick Leave
- For new joinees or person who has resigned Casual leaves are on a Pro-rata basis. If you have joined during the middle of the year say Jul 1, your casual leave will half ( pro-rated) from the date you start employment through December 31 of that calendar year.
Earned Leave or Privilege leave
Privilege leave or Earned Leave is provided for planned long leaves for the purpose of travel, vacation etc
- Earned Leave is calculated on a month-on-month basis for the calendar year. Earned Leave is credited at the beginning of Calender Year to every employee’s account, but the entitlement will be proportional to the number of months worked. For example Based on company policy, for every month completed in the company 1.25 days will be credited to the employee’s entitlement.
- If you have joined during the middle of the year, your earned leave will be pro-rated from the date you start employment through December 31 of that calendar year.
- For employees who resign, their leaves entitlement would be calculated pro-rata i.e. till their last day of work. Any excess leaves taken would be adjusted in Full & Final Settlement.
- If you are unable to use all of your accrued Earned Leave during a calendar year, you may elect to carry forward any accrued but unused Earned leave into the next calendar year, subject to the maximum accrual level. A maximum number of earned leaves is based on State your company is in, which typically is 30 working days but in some states can go up to 45 or 60 days.
- Accumulated leaves can be encashed at the time of working or leaving the company based on the company’s policy. The formula used for the calculation of Encashable Leaves is : Encashable Amount = Monthly Gross / 22* Encashable Leave.
- Leave Encashment during service is fully taxable in all cases.
- Any payment by way of leave encashment received by Central & State Govt. employees at the time of retirement in respect of the period of earned leave at credit is fully exempt. In case of other employees, the exemption is to be limited
What is the difference between Earned Leave and Privileged Leave: Although the nature and purpose of both Privilege Leave(PL) and Earned Leaved(EL) are the same, however, applicability differs in terms of minimum allotment and act which covers them.
- Under Factories Act such leaves are called Earned Leave (EL) and under Shops & Estb. Act the same is called Privilege Leave (PL).
- Another difference is how many leaves are allotted under this category. Under Factories Act, 1 EL for every 20 days of work (18 per year)and on the other hand under S&E Act 5 PL for every 4 months work (15 per year).
Other leaves
Apart from these, there are other paid, unpaid, or half-paid leaves like Study Leave, Bereavement Leave, and Leave for Voting. These although are left at the organization’s discretion.
National Holidays and Festival Holidays
Republic Day (January 26), Independence Day (August 15), and Gandhi Jayanti (October 2) are the three national holidays observed in India. On these days all institutions, irrespective of under which law they are covered, or whether they are public or private organizations or MNCs should necessarily remain closed.
The festival holiday is decided based on the local festival of that locality and is granted to the employees in accordance with the company policies.
Maternity Leave
Maternity Leave is covered by Maternity Benefits Act, 1961
- Female employees are entitled to a maximum of 12 weeks (84 days) paid maternity leave. Six weeks leave has to be taken after the actual date of delivery
- A woman worker is entitled to maternity benefit only if she has worked at least 80 days in an establishment in the 12 months prior to her expected date of delivery
- In case of miscarriage or medical termination of pregnancy, an employee is entitled to six weeks of paid maternity leave.
- Employees are also entitled to one additional month of paid leave in case of complications arising related to pregnancy, delivery, premature birth, miscarriage, medical termination or a tubectomy operation (two weeks in this case)
- No pregnant woman can, on a request made by her in this behalf, be required by her employer to do any work (during 10 weeks before her expected delivery) which is of an arduous nature or which involves long hours of standing, or which in any way is likely to interfere with her pregnancy or the normal development of the fetus, or is likely to cause her miscarriage or otherwise to adversely affect her health.
Paternity leave
Paternity leave is paid or unpaid leave given to a male employee when a child is born. While paternity leave is authorised for government employees there is no law that instructs the private sector to make it obligatory. Hence, paternity leave is open to interpretation by individual companies. Thus, on the one hand, you have Cisco Systems (India) which grants its employees 12 weeks paternity leave and on the other, you have Infosys which offers 5 days of paid leave
Individual organizations decide whether or not they would like to extend the facility of Paternity Leave. There is no legal requirement in regards to granting Paternity Leave to anyone.
Leave without pay
If a person does not have any unused leave and the situation warrants him to take the leave, the leave is granted by the Company as loss of pay or which may be adjusted against the future leave or as a special case depending on management discretion.
Articles for Employees: Job: Salary, EPF, Income Tax
- Salary, Net Salary, Gross Salary, Cost to Company: What is the difference
- Four Corner Stones: Income, Expense, Assets, Liabilities
- What are Employee Stock Options (ESOP)
- Understanding Variable Pay
- Basics of Employee Provident Fund: EPF, EPS, EDLIS
Hope this gave you an overview of various leaves that one is entitled to in India. Why holidays in different places differ? Why all companies do not give Paternity leave? Do you think men should get Paternity Leave and if yes how many days?

144 responses to “What are Casual Leave, Earned Leave, Sick Leave etc?”
This was my first blog on your website. I would like to say that the quality of the content is up to mark. Thanks a lot for sharing this. I will surely read all the blogs from now.
Please claim Rs.2,00,000/- under PM Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojna. If applicable to anyone.
Please click the link below for further information
https://youtu.be/FrPl5n16qfk
Hai,
Thanks for sharing in detail information fo leave benefit our company provide GST and company Registration and Auditing ,Taxation
Tax consultants in delhiand
new company registration delhi,
GST consultants in delhi
If any require plz visit our site
[…] Many people remain divided on the issue. Across India, employees are entitled to a certain number of leaves, apart from days off and holiday leave, which is provided at the beginning of the year. The number […]
Hi Google,
I don’t have any balance of sick leave in my account, is it allow to apply Earned Leave as Sick basis.
Thanks for sharing our valuable information with us. It is really a helpful article!
Casual leave and sick leave are mandatory under which act..?
Sir, please reply two questions for me
1) casual leaves taken on either days of declared holidays by comapny i.e. on thursday and monday ( friday to sunday being holiday) then all five days will be calculated as leave or not
2) I am working in madhya pradesh but my company is from gujrat then which State’s shop and establishment act or factory act will be applicable to it.
Invest something to buy properties is very risky. Hence, I want to know complete information about the properties before buying it. I am searching for properties in Bhopal and I want to know the ideas.
I have on leave for 3 days from tuesday to thursday and my employer is saying that your sunday is going to add up in leave that is they are going to deduct 4 days from my salary..
Need some clarification or they are doing right thing.
Often employers do that.
This is very useful post for me. This will absolutely going to help me in my project.I am looking for and I love to post a comment that “The content of your post is awesome” Great work!
how to write a maternity leave application
dear sir
i have 68 paid leaves and working in jindalx for 4 years and my process is going to shift in gurgaon and i am not able to continue due to very far away from my home and plz tell me that will i get encash all leaves in Full and Final or leaves will be lapse, our hr is not responding well. plz tell me eary
sir i am working with mnc and process is going to shift soon and i have 32 paid leaves and will i get encash or will deduct those leave in full and final, plz tell me early or should i claim in consumer court for same.
sahil george
Useless cos no reply
If an employee was on leave, but forgot to apply for it in the hrms for some reason. The employee has adequate leave balance. In this case, company chooses to deduct the pay instead of debiting the leave balance. Is that fair and a general practice?
HI,
In my previous company i had been for emergency surgery for 20 days including saturday and sunday. Just wanted to know the procedure it will be deducted from my sick leave or it will be seperate from company side.
Interesting question. You need to ask your company.
The practice of calculating leave varies from company to company and sectors to sectors. The differences are due to the following factors: –
Leave with wages and type of leaves, as well as their numbers varying in legislations; like Factories Act, Shops & Establishment Acts of various states etc.
– Concept of calculation of “Wages” and “Salaries” and the consequent calculations based on “daily rate” or “monthly rate”
The daily rate calculations of Wages are based on 26 working days in a month; as rightly reflected even in the Payment of Gratuity Act; whereas the monthly rates are based on 30 days or the number of days in that particular month.
– Philosophy of the employer : Govt. or PSUs have employee-friendly policies which do not penalizes the employees whereas private companies seek to reduce the number of leave balance of employees to reduce payment in lieu of Earned or Privilege leaves.
“Usually All leaves with pay are excluding weekly off and holidays.”
…….. But, In our company this rule is not applicable. My company’s head office is in Maharashtra State. If I take leave on Friday and by any chance I could not come to office on Monday. I have to apply for a leave of 4 days. Is this injustice?
Can I show your blog as a rule?
Regards,
Jyoti
Me ek para medilcal employ hu govt hospital me. Hme koi govt holiday ki leave nhi hoti h. Par iske badle me hmre yha kuchh staff ko 19cl ke sath 8 leaves extra di jati h. Or vhi same work hamara bhi h or timing and duty hours bhi same hone ke bad hme only 19CL and 3 OL di ja rhi h. Eski comlent hm kssi kr skte h pls help..
Hi,
This Blog was great. I am read this. I am a real easted owner please visite my site.
[…] of Leave of absence is an application written when you’re about taking a leave from work. Leave of absence can be different forms which may […]
This paragraph provides clear idea in favor of the new viewers of
blogging, that in fact how to do blogging and site-building.
I am working in Pvt. Printing press just like Factory in chennai but any Leave is refused salary is cut off. Is there any labour act for this.
And that very last thing is the vital thing, because regardless how good an event is,
nothing makes a party great much like the perfect, personal party
decorations you choose. Flowers appear in a variuety of colors, and when you add stems
and vines, you can geet an incredible custom tattoo design.
Hilary Duff also became a singer froom being merfely a star
of her Disney Channel show, Lizzie Maguire.
I am working pvt.ltd. in maharastra vasai company.iam 2 year complete this company .please provide my cl.pl.leave & send calculation last 1 years dippend new years leave given me.
Hi if an employee joined in 18/02/2019 and he is eligible for two days casual leaves
Yes, he can. By joining in Feb he would get less number of casual leaves in a year.
His leaves would be calculated on a pro-rata basis.
Pro-rata means, calculation on the basis of the number of days worked.
i.e if one has joined on 5th of March and the full number of leaves are 20.
Total Leaves he can claim in the year = 20/365*302 (Rest of the calendar year) = 16.54 Leaves.
I have worked for 25 years, and earned 300 encase leave. I leave this service and joined New Fresh service with New terms and condition.Where I got benefit of Earned lave. But previous Employer does not ready to give benefit of 300 encase leave, stating that you have get with second Employer. It is true ? How past Employer can issue the benefit of Future Employer ?
We have a NBFC business . Our employees are eligible for 7 CL , 7 SL and 21 PL apart from 12 holidays in a year . Pls clarify if our following leave policies are correct:
1) CL are credited in April every year
2) PL after 11 months of service
3) SL after 12 months of service .
4)We do not permit encashment of PL
5)We lapse 7 PL every year
6)If some one takes holiday on Sat and Monday we defect sandwich leave on Sunday also
Numbers of leaves entitlement in a company depends upon state you are in.
Every state has different leave entitlement and leave policies which should be seen before one defines leave policy of your company. Leave policy of a company cannot be less than that mentioned by the State’s shop and establishment act.
Generally all State Legislations has common provision for major matters. They provide at least seven holidays for national and other festivals. Republic day, Independence Day and Mahatma Gandhi’s birthday are compulsory holidays. Employer and Employees had given right to decide remaining national and festival holidays.
Commencement of Leave Period is calendar year i.e 1st January to 31st December every year.
Where are you located?
And what Act do you follow ? Ex: THE FACTORIES ACT,SHOPS AND ESTABLIHMENTS ACT
if 30th december is sunday & 1st January is holiday, then if we too leave on 31st December, how many days should be deducted
I HAVE AN ACCIEDENT ON OUR COMPANY WORKING DAYS AND HOUR AND I GOT AN FACTURE ON BACK I REST FOR 60 DAYS AS PRICRIBE BY DOCTOR
I WANT TO KNOW I EGIBLE FOR RECEIVED MY SALARY FROM THE COMPANY OR NOT ON THIS 60 DAYS ?? IF YES, HOW MUCH SALARY RECEIVABLE …
THANKS
I am working in government deptt.i want to know about my casual leaves and earned leaves,i joined in the department on November 1st 2018.plz tell how many E.L and C.L i can take till December.
Hi,
Please send me the rules and leave policy for employee and employer applicable in India country. Please send me in the mail id.
i m a shift engineer i applied privilege leave from 9.5.19 to 28.5.19. Can i avail prefix on 8.5.19 as weekly rest and sufix on 29.5.19 as weekly rest.
You need to ask your supervisor.
Great post on the leaves granted to Indian employees. Today, more men would like to and are beginning to participate in child-care actively hence I believe that paternity leaves also very essential for men. Thanks for sharing the info.
Yes, Paternity leaves are also essential.
sir one Small requested Spilled leave in C.L &S.L Can be quietly Granted Than No Leave So Automatically Lapsed in (S.L&C.L) .This rules can be in followed Goverment
which Rules can act follwed
Pl give your e mail address
I am working in one company in karnatak.there are giving only one leave per month.if you dont take then that leave will be laps.we are more than 70 members.
when i want to resign that time can question my earned leave.
why they are not giving
Did you try speaking to your management as to why it is so?
What kind of leave is monthly leave – Earned Leave?
Hi
Yes this is monthly earned leave @ 2.5 days per month. It got transferred from old bank to the new bank. They are not encashing it. I spoke to management, saying only encashment on retirement and not on resignation. Can you please advise?
I have been working for a Foreign Bank in Mumbai since 2002, this bank then was taken over by another foreign bank in 2009. All Accumulated leaves were transferred and available. Over and above, we were provided the new Foreign Banks leaves of 30 days per year which is used. Now i have resigned in Sep 2017. I am only given the option to adjust my Accumulated Leaves (Accrued leaves) against the Notice period which cannot be done due to operational reasons..as a result i am serving the whole notice period of 90 days.
The management is not providing encashment of this accumulated Privilege Leave since i have resigned. As far as i know, RBI and even the S&E Act has provisions around Encashment of Leaves on resignation.
Can you please advise whats to be done? What act or law i can cite to get encashment or do i have to contest this in a Labour Court?
What if a company is not having Maternity leave in their leave policy?
Every shop or establishment, in which ten or more persons are employed, comes under the purview of law to grant a paid maternity leave.
startups with less than 10 people are not obligated to follow this policy.
Onemay approach the law enforcing agency i.e. the area labour office of your area in case the employer fails to comply.
I have been working for a Foreign Bank in Mumbai since 2002, this bank then was taken over by another foreign bank in 2009. All Accumulated leaves were transferred and available. Over and above, we were provided the new Foreign Banks leaves of 30 days per year which is used. Now i have resigned in Sep 2017. I am only given the option to adjust my Accumulated Leaves (Accrued leaves) against the Notice period which cannot be done due to operational reasons..as a result i am serving the whole notice period of 90 days.
The management is not providing encashment of this accumulated Privilege Leave since i have resigned. As far as i know, RBI and even the S&E Act has provisions around Encashment of Leaves on resignation.
Can you please advise
My name is Prabhakar (Age 56 years) working in public company as manager. I had taken one day pre-sanctioned casual leave on 19th September 2017 and unfortunately I had infection and flue from the same day next two days (i.e. 20th and 21st September 2017) was on leave due to sickness. I had applied for two days SL and our senior has sanctioned the leave, but our HR is not allowing me to take SL after one day CL. Is it as per the rule?
yes, you cannot append leaves thats what it says above.
I have worked in pvt company and left after 7 months ,i had 8 Cl and 9 El ,but they are not encashing my el ,kindly suggest?
Why are they not cashing your EL? Did you get your Full and Final Settlement?
sir
i have been working in contract basis in ONGC since 2002. Sir In PSU company is Saturday and GH off . i am a contractual worker.my contractor has told that i must complete attendance ,if any GH (apart from:-26 JAN,15Aug,2OCT and Saturday) come and 26 attendance not complete. my salary will be deducted.
Dear Team,
I joined in private firm on 2nd jan 2017 and after six month i got confirmation letter when i asked to my manager about my CL & PL then she told me that CL & PL will be started from after 1 year of completion , so Is this Correct ?
Regards,
Ronak.
Which company do you work for? In which state?
Did you check with your colleagues?
Leave rules are generally governed by the Standing Orders of the company and relevant provisions in the Factories Act, Plantations Labour Act or the Shops and Commercial Establishments Act as the case may be.
Under the Factories Act an employee is not entitled to any leave during his first year of service but will get leave with pay in the succeeding year provided he has worked at least for 240 days in the preceding year. Leave will be at the rate of one leave for every twenty days worked.
For example, a bank officer in SBI for the first 11 months is only be eligible for availing Casual Leaves and after that he will be on par with the other officers.
I am working in private ltd. company . how many days will be deducted if I take leave on 15 th august 2017, Tuseday .
Im working Helath care company since 5years,
I have 65 earned leves, can i claimed my leves? Pls help me what i have to do.
My name Muniraj from Bangalore
what is ES
Can IT sector employer (MNC) allow only Privilege leave and not give sick or casual leave? There are 22 days Privilege leave and 10 days public holidays, but there are no Sick or Casual leave in this company.
giving CL/SL is not mandatory however a certain amount of leave needs to be given by all corporates as per Shops and Establishments Act. You need to check the same for your state and demand the same accordingly from the management. Cl/SL etc are just classifications of leave done by HR. Mostly the leaves are given on prorata basis i.e. one leave for every 20 days of work.
Leave rules are set by the individual company and it varies from company to company. You have to follow your company’s set rule. There is no law prevailing in the country where you can approach for any clarification. Purely on company to company. You can see there is lot of difference in the leave structures also. Some company gives 10 day CL 10 day Sick Leave and 30 days PL. Whereas the pattern is different in other companies
Thank you so much for taking the time to respond to all my queries.
You inputs and article is very helpful to all the employees and provides much guidance on leave policies in various companies from legal and implementation perspective. Keep up this great work in spreading awareness!!!
Leave without pay query: Can IT sector (MNC) employer count all weekend and public holidays which are before, during and after a leave without pay to deduct pay? For example, if employee takes leave without pay from 24 April 2017 till 05 May 2017, the weekend of 22 and 23 April (before LWP) is counted as leave without pay, the weekend 29 and 30 April and public holiday of 01 May (during) is counted as leave without pay and the weekend 06 and 07 May (after) is counted as leave without pay, even though employee took leave without pay from 24 Apr till 05 May. Here the total leave without pay is for 16 days. Is this legal? Can the employer keep changing the leave without pay and other leave policies every year by adding and removing these types of clauses?
leave policy is a discretion of a company’s management and framing of leave policy is as per the needs and requirements of the company.
As per Factories act leave is to be given for one day for every 20 days worked by a workman. Nothing else. No rule/law says how this is to be given or whether Sundays/Saturdays or intermittent holidays are to be considered as leave/holiday.
There are Casual Leaves and Earned Leaves. In the case of casual leaves, an employee can apply leave on Saturday and Monday, with permission to avail public holiday on Sunday. In such case, casual leave will be deducted for two days only and Sunday cannot be considered as casual leave.
In the case of Earned leaves, if the employee applies leave from Saturday to Monday including Sunday, the entire three days will be considered as earned leave for granted.
This is the general rule in all firms. However, leave rules are subject to the guidelines and norms and standards prescribed by the concerned companies and firms according to their policies.
Same applies for LWP.
Hello, My query is, can a IT sector employer (MNC) deduct leave if employee does not complete 9.5 hours on daily basis? Employee agreement has been signed by all employees mandatorily when the daily working hours were changed from 9 hours per day to 9.5 hours. If employee has shortfall of 4 hours for any week, can employer deduct 1/2 day leave from the employee’s leave balance?
Yes, sadly this practice is followed in many companies.
Technology firms are increasing working hours and monitoring the hours worked far more rigorously than ever before in a bid to squeeze more out of employees in these difficult times.
By increasing work hours by an hour a day an employee works an additional 22 hours a month. If an hour of his/her work is billed at $20, the company makes an additional billing of $440 per employee. That means, in rupee terms, a single employee can bring in additional revenues of Rs 22,000 a month for the company.
Such work time extension works well for projects that are on what is called the ‘time & material’ model. Most of tech projects are currently under this model, while the rest are fixed price projects where the service providers may resort to pruning the size of teams to bringing cost down.
Sir,
My works in pvt mining sector company in which all the rules are under mines act.My father have 85 earn leave over six year service. Now at present company tender has completed . So all the workers have retired .
Now company say u can avail only 30 days earn leave payment according to gov. Rules of mines.
So sir please tell me its true or not….. please soon…
Thanking you…
Typically Section 79 of The Factories Act, 1948 says that every employee who works for 240 days in the previous year is entitled to Earned leave @ 1 leave per 20 days of working.
When the worker is discharged or dismissed or quits employment, the unused earned leave at his credit has to be paid.
A worker is entitled to accumulate upto 30 days of earned leave and over and above 30 days will lapse.
Which mining company does your father worked in? Can you ask for its leave rule book?
When we searched for mining act (pdf). we found the following information.
Encashment of Earned Leave: The workmen will be entitled to get encashment of earned leave @ of 50% of leave due to his account subject to the maximum of 15 days in a calendar year subject to the minimum of 7 days/per year. In the event of death or superannuation or VRS etc. the balance leave or 140 days whichever is less will be allowed for encashment.
Thanks for this sir .
My father works inTCL MMPL PVT LTD UNDER HINDUSTAN COPPER MINES (GOVT SECTOT) .
MY FATHER WORKS IN PVT COMPANY IN WHICH ALL RULES LED BY COPPER MINES
Another document that we found was for Bharat coal cooking ltd at http://www.secl.gov.in/writereaddata/section_4(b)/leave0001.pdf
i am central govt.employee. i has applied earned leave one month before to avail leave after 32 days which is very essential for me.but after 28 days i do not got any reply from my higher authority. can i able to avail my earned leave from the date which is mention in my leave application.please suggest me.
This is the perfect site for anybody who would like to understand this topic. You realize so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I personally will need to…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a subject that’s been written about for a long time. Excellent stuff, just great!
Dear Sir,
Can a pvt. ltd company mandate approval for Sick leave? Even for one day SL? What happens if Employee is not well, cannot come to office, and manager reject the leave?
Yes, manager approval is required for leaves. Why is your manager rejecting your leave? Can you prove that you were sick?
CAN AN EMPLOYER DEPRIVE AN EMPLOYEE OF ENCASHMENT OF ACCUMULATED PRIVILEGE LEAVE AT THE TIME RETIREMENT WHICH IS A STATUTORY ENTITLEMENT. CAN THE EMPLOYER BE SUED FOR NOT COMPLYING TO THE RULES OF SHOPS & ESTABLISHMENT ACT.
Hi iam Working in Chennai one Pvt LTD company. Iam joined on april12. Till El/sl leave encashment not received. This year iam give my request of leave encashment. Now the management told sick leave not encashment. As our leave policy in our sick leave is encashment.
What is labor law leave cash encashment or no
Hi, Just want to understand whether a company can define or enforce policy on availing Earned Leave. I’m working with an retail organisation and they have policy stating EL cannot be avail if it’s less than 3 days leave. Please share if any government ruling is available.
This can be just the simplest and best advice I have ever come across about this topic. Thank you for this very useful blog post of yours. Additionally, I enjoy writing articles which has a personal tone incorporated. I feel it makes your reader feel more important and inclined to believe me more. Plus it sounds more real and never coming from a robot. I enjoy making my visitors feel important and special. I want to let them have the best tips on how to cope with important issues such as this.
Deference to article author , some superb selective information .
Can somebody tell me if I Joined a co.in the Feb and left in Nov (same yr.), then am i eligible for earned leave entitlement at the time of Full and final with Employer. if in the offer letter mentioned that eligible for earned leave for 15 days after completion of One year.
I had a Contract with a British company having an office in India since 01 Dec2012. The contract stated that I will be entitled one day leave for every twenty days worked.
I have left them on 30 Jun and had accumulated 34 days of Earned leave. The company is refusing to encash this leave, saying that employees on Contract are not entitled to carry forward their, something which they never mentioned in the contract.
Is the stand of the company legally correct?
Please advise.
Legally if its in contract company should honour it..either encash/carry forward to leave.
All workmen/employees engaged through any contractor are worker/workmen/employee under relevant provisions of labour legislation. They are governed by same rules as are applicable to other workers/workmen/employees in respective law. For example a worker in Factories act includes contract worker as well and they are eligible for one day paid leave for 20 days worked, They also must have completed 240 days or 2/3 rd of the working days.
Similarly the provisions in shops and Establishments act are applicable in such establishments where contract employees are engaged.
Contract workmen are eligible to all statutory benefits. The only difference between a contract workmen and regular employee is that the benefits over and above the statutory benefits extended to regular employees are not applicable to these employees.
Is it Mandatory for a company to allow accumulation of Earned Leaves/ or allow carry forward of accured but unused Earned leaves. Take Bombay S&E Act for instance, it mentions under section 35 (1) (b) every employee who has worked for not less than two hundred and forty days during a year 15[ irrespective of the date of commencement of his service,]15 shall be allowed leave, consecutive or otherwise, for a period of not less than twenty-one days:
Provided that such leave may be accumulated up to a maximum period of forty-two days.
It still doesnt mandate a company to allow carry forwards right?
i have joined govt recognized export house in aug 2016(IN DELHI) & same month i have taken one leave due to some urgent work .I just wanted to know that new joiner cannot take one day leave .actually they deduct my salary &told me that first two months i cannot avail any leaves.
CASUAL LEAVES WE GET AMOUNT
No you get amount only for paid/earned leaves(EL)
Casual Leave lapse if not taken during the year.
Current Year CL balance only for eligible get amount and below ways also get you CL amount.
1.your boss Approved (Informed)leave.
2.unfortunately factory close that time you get CL Amount.
3.your Resign the job that time also you get CL Amount.
I have workings in a Pvt Ltd company .I want to know how many CL , SL , EL minum I get
Hi, i was working in a pvt medical college and had resigned from my post. During my notice period I had to take leave twice each for three days due unforeseen conditions . My mother was diagnosed with some serious condition which needed to b attended on urgent basis. I applied for EL as I had my leaves pending.I also had few CLs pending however my HR refused to approve the leave citing that leave can not b granted during notice period. My argument was that it was completely unforeseen condition which needed me to go on leave but HR won’t accept my argument citing company policy. They won’t even encash my ELs due to company policy. What is way out in this situation? What policies govern private medical colleges in India? Can I contest their decision legally? I would appreciate help. Thanx
Our company is not following own, this is just doing what written here: http://www.citehr.com/426280-leave-policy-pvt-ltd-ltd-company.html
Only 30 days leave in a year.
9 CL, 9 SL and 12 gvt holiday leave.
60 days of Maternity Leave is allowed to females who have to deliver a child.
Very bad policy, I donot feel good there.
dear sir kindly inform to me how many leave in pvt.ltd. company in jharkhand
Ashok Das ji… If 30 days leave in a year are appearing less to you then you should get pre mature retirement and rest full time at home.
I joined a Pvt. Ltd. Company in Bangalore and there leave policy is weird. They have 14 ELs (which comes to 1.17 days per month) and 12 National Holidays. There is no SL or CL. This doesn’t sound right to me. Further, they told me first three months is probation period and you can avail any leaves. But in other places where I have worked, they have 1 privileged/Earned leave during the probation period. After confirmation, they grant 18 ELs and 12 SL/CLs for employees. There is no Comp off as well. The offer letter says Monday to Friday as working days. The HR tells me that Saturday is off but if you work, its not comp off (because you couldn’t finish your work over the week and so you have to work on saturday). This all deviates the Factory Act and Shop and Establishment Act. Can you please guide me what is the correct rule/ clauses here so that I am aware and if needed I can site them the link/ website which has the right info. Please help me.
Amrita
Sir,
Please advice me, one day i was not inform to boss, i want need to take leave , but my HR department deducted my salary, i have EL/CL, boss not signed my leave register reason behind you without any information take leave, therefore i could not signed lease register ny my boss.
please advice what action take by me.
Please reply me.
Can My Employer ask me to work on Independence Day 15th August.
Yes. You may be required to work on national holidays sometimes if required. It’s being compulsory holiday, you will get an additional leave along with the twice the salary of a day.
I was in central bank of indiA. I worked there for an year till 2012. Being unaware and not properly guided by the staff, i didnot claim encashment of earned leave. I worked there from 2011-2012. As ofnow, i want to claim that… Please guide ob this matter
Sir, I need Indian leave calendar for a Year.
Also, can you please confirm me that an employee may get 30 days leaves in a year for i.e. –
1) – Earned leave 18 or 1.5 days in every month (Except National & Festival leave).
2) – Sick or casual leave 12 or 1 day leave in every month (Except National & Festival leave).
On medical reason, i have resigned from my organisation on 24th June,
i have got relieved early on July 22 (though the notice period was for 3 months). they said they do not have any project for relieving early.
i had 22 ELs, but they have not allowed for encashment as well, is this legal?, please clarify.
Dear Sir,
I am working in an airline, want to know if any employee taken the leave without pay on medical ground with permission of hod as he don’t have any kind of leave balanced. So is there any rule or policy that he will not get increment for that particular financial year.
Pls advise
No idea about it.
But its better to have good relationship with boss
I am working in a private company and as per our leave policy, and our company is opening the leaves on quarterly basis. For example – first qtr. we will get 4 PL and 2 CL. And we get 8 sick leave in a year alltogether. And if my all CL & PL deducted due to late comings adjusted, then at the last quarter, I will have only the SL leave available with and not CL and PL available, So, is there any policy to avoid the deduction from the salary, it can be adjusted from the SL available with me.
as per companies act salary to trainee,
calculation of days in moths in which was on leave without payed,
please give me reference of companies act
Casual leave and sick leave are mandatory under which act..?
Employees, across all industries in India, are entitled to a certain number of leaves per year aside from the holidays and days off. The number and type of leave depends on the industry,employer and state you are in under the Factories Act and State’s shop and establishment act. Every state has different leave entitlement and leave policies which is basis for leave policy of your company.
Casual & sick leaves are granted to the employees as per the applicability of the Act to the company. If your company is covered under any of the State Shops & Establishment then plz go through that Act for these leaves. If you are covered under the Factories Act then see whether the State NFH Act is applicable or not? If yes then go through that Act for grant of these Leaves.
Hello Sir / Madam,
I am currently employed with a Pvt. Ltd. company in Mumbai, India.
Work was all good for me until i met with an accident/incident inside the office premises (precisely inside the office washroom.)
I actually slipped and my left knee ACL + meniscus tore. I originally got this injury while playing a corporate tournament for the same company back in Dec 2015 or Feb 2016, however i pulled my days and finally my knee gave up and it got locked on 7th April, 2016 while i was at work.
People from office dropped me home. After which i went to the Doctor and got a surgery done for my left knee on 12th April, 2016.
After this i was advised a rest for 6 weeks. And then after the follow up of physiotherapy and all the Doctor told me i am fit to do sedentary work.
Now i reside at Borivali West and my workplace is at Ghatkopar West. So the travel in the train during peak hours is impossible for me with this unstable leg.
I tried negotiatiing the workings hours with my VP for a 1 month more as i wouldn’t be able to travel in the train during rush hours but he denied and told me to do a 10 am to 7 pm shift. Finally as this wouldn’t be possible i thought of putting down my papers and resign the company.
I tried convincing my concerned authority a lot for alternatives but all in vain.
I requested them to waive off the notice period of 30 days under medical grounds as i am not able to travel. But initially they refused and now finally they have agreed to it.
My question is now that i am finally leaving this company, what should be considered as my last working day with the company for my Full & Final Settlement and on my relieving letter/
Will it be the last day i worked in the office premises (7th April, 2016) or will it be the day i officially send them my resignation?
Also during this phase of Medical Rest, i had requested for work from home which was denied by my VP, even after knowing the fact that this injury had happened while i was playing for the company itself. And then i never asked for money without working i was ready to work from home and it was denied.
I even told him that you have witnessed it happened to me in front of you in office premises, but still he said no i am sorry we can give you LOSS OF PAY but not paid leave. so i continued to rest, but i still worked from home conducted interviews over the phone, coordinated with my team, etc.
Should i be getting paid for the Leaves i am totally lost on this one and dont know anything about it. Please guide me.
Also they promised me 14 days pay but that will be given to me when i come back to work after my recovery. So should i be getting that now that i am leaving the company?
And should be getting paid for the 2 months that i was home?
Please help me in getting answers to these questions.
Aldrin.
Mob : 7506864549
Dear Concern
I have an doubt on Maternity Leave Act .
Please Clear me that mater .
During the Maternity Leave , EL & CL credit in Employee account or Not .
Regards
Vikas
8010901012
working in pvt ltd.co,from 1991 to 2015 please informed me for give company benefit to me.Gratuity/earned leave benefit etc.
His joining date 01/01/2014, feb-10 days, March-10 days, Apri-10 worked his eligile for feb, march, april CL please clarity immediately
Hi
Can anyone give me a clarity on my following doubt?
Last year 2015, I have worked 238 days obviously become disqualified for getting EL for this year.
Total company working days are 286
My total working days are 238
Means 48 days I’d availed during 2015.
But till end of November 2015, I availed only 30 days. On December 7th, I put up my paper requesting to release me from all the official responsibilities.
End of it, i was compromised by management and agreed to call back my resignation.
Finally it reflects that I’ve availed 18 days leaves. So that add big change in my total leave went from 30 to 48 days.
Now, do I have any legal point to demand EL by adjusting 2 absent or let give up by loosing EL for this year with just 2 days gap.
Sir why go into legality. You have to work in that organisation. So try to find middle path.
You can argue that 18 days should not be taken as EL. Try to negotiate with a cool mind
if one employees 200working days in the calendar year he is entitled el 10 days or no as per leave rules entitlement complete 240working days in the year
i am karnataka state govt emloyee . i want to put leave without pay for 2 years for the sake of my daughter education .is there any provison for this type of leaves
Dear Sir,
I’m working in pvt. ltd. company our office timing is 9 am to 5.30 pm.I were late in some days around half an hour to 1 hour.Company marked my leave for full day for whole day.
Can you please tell what is rule of company law with section details.
Regards
Ajay Sethi
Consult with your management regarding it.
Can i join on sunday after my earned leave if i am a factory worker?
Check with your organization/factory
I have submitted my resignation and according to which, my last date is 17th FEB.
My leave balance summary:
20 days of paid leaves (Earned & Privileged)
4 Floating leaves (For holidays)
Management has declined my leaves and have ordered me to encash them while I leave. If leaves are encashed, I will just get 60% of the amount.
So this will incur a loss of 6000 rupees approximately.
My question is:
Am I not entitled to avail my paid leaves as per my needs?
What can be done in order to take these leaves and avoid money loss? Can I face sick leaves?
Oops that’s bad. Well sometimes you have such employers.
You can take sick leave..if you can get a medical certificate made. Company can’t force you to work if you are sick.
You can argue with company ..
please advice me can i tack causal leave( 2 days ) after medical leave or p/l leave within a week.
exam: Friday, sat , Sunday = medical leave, can i tack c/l on Monday ?
thanks & regards,
abhijit
Many companies follow the concept of sandwich leaves wherein in case between two of your CL/SL if there is a weekly off or a gazetted holiday, then the holiday / off is also counted as a leave. Please seek clarification from your HRD before applying for leaves.
please send me how many types of leaves in pvt company and total leaves in a year.
please uptade all type of upgrades related to leaves
I take leave 5 days before of diwali vaccation 15 days but joined diwali vaccation completed days. can 20 days consider as a diwali holiday?
It is best to clarify with your manager and HR
I was working in private firm. I went to medical leave for operation. I don’t have leaves left.
I got hospitalized suddenly, so informed my office people through phone about the same and in hospital my doctor suggested for operation.
I wrote this to office and asked for 15 days leave but didn’t got reply from them. As situation is not under my control so I went for operation. Again I extended the leave for 15 days. I received confirmation for the office for the leaves. I extended the leaves for the third time for 10-15 days. I already intimated my office initially that as I don’t know how much time the medical treatment so I will intimate about the leaves accordingly. For any operation 1-1.5 months treatment is normal.
I was about to join the office next day, the send me termination letter that “yesterday” was your last day. Your leaves are considered as notice period.Reason given that you took unapproved leaves. They haven’t send any such warning for the same.
Is it legal. Can something be done under labor law.
Is this correct. Can I got to legal under labour law
Hi iam working for pvt co.1 month back met with bike accident, Doctor says min 3months bed rest so i request you to suggests me company can approve the leave with salary
I am college lecturer in Govt. of Rajasthan. How many casual leaves will be allowed on completion of the service of complete six months?
any resign employee should apply for prevellige leave?
Sir you could take the Privilege leave but please remember that Accumulated Privilege leaves can be encashed at time of working or leaving the company based on company’s policy. The formula used for calculation of Encashable Leaves is :Encashable Amount = Monthly Gross / 22* Encashable Leave.
Check out the taxation part of the leave encashment and decide if you want to take Privilege leave or not.
When any employee does not avail his/her leaves as per terms of employment then he/she gets the salary in lieu of non-availed leaves. This type of payment is called leave encashment. As per Indian Income Tax Act, the leave encashment is exempt from income tax subject to the following conditions:-
In case of Central Government or State Government employees, whole amount of leave encashment is exempted from income tax.
In case of any other employee, the least of the following amount shall be exempted from income tax:-
Actual amount of leave encashment received
Cash equivalent of earned leave (not exceeding 30 days for each year of service) at his credit on retirement.
Ten months average salary i.e. ten times the average of salary drawn during ten months preceding his/her retirement or
Rs.3,00,000/= (Rupees three lacs).
Leave encashment is exempt from income tax only if it is received at the time of retirement only.
Leave availed during the service period is taxable whether it is availed at the time of LTC or otherwise.
Receipt of leave encashment of privilege leave standing to the credit of the employees received by the legal heirs of a deceased employee is exempt from income tax.
When the employees receives the leave encashment from more than one employer in previous year or more previous years, the maximum amount of exemption will not exceed the monetary limit as specified above i.e. three lacs as reduced by the amount which has already been exempted from income tax in the same previous year or earlier previous year or years.
Salary for this purpose includes Dearness Allowance but excludes other allowances and perquisites.
can i avail 2 EL at a time?
can CL & EL are merged?
can i avail 2 EL at a time?
can CL & EL are merged?
2 EL yes
CL and EL yes they can be merged.
uan number
I want 8, 9 & 10 july thats the three days earn leave, more 11 & 12 date is sencond Saturday and Sunday is already holly day, pl. me a information incluld the holly days two days in earn live , thats a five day earn leave
I am officer in allahabad bank,can i availed sick leave on half pay and half allowance during my last 10 months of sevice, can it affect my pension,teminal benefits.
can employee avail half day pl.?
How many sl can avail at a time?
Can employee avail sl for family sickness?
i am working a Game Developing company as a hr executive please provide information about all leaves rules and how to give in monthly salary?
And What are the main Roles and Responsibility of the HR……..
i want to know number of casual leave’s in one calender year.
i was appointed in july-2014 in that year i have taken per month one leave.
now i want to know in 2015 number of casual leave’s for in this calender year.
i want to know number of casual leave’s in one calender year.
i was appointed in july-2014 in that year i have taken per month one leave.
now i want to know in 2015 number of casual leave’s for me in this calender year.
i am working a manufacturing company as a hr executive please provide information about all leaves rules and how to give in monthly salary?
plesae mail me the entire rules & regulations of employement like., salary, deductions, sick leaves, casual leaves, paid leaves.
I have joined from MNC to local company and here they told no cl SL , EL untill 6 months and later one month one leave only avilable.
i did not under stand .can any one send mail clearly
The number and type of leave depends on the industry,employer and state you are in under the Factories Act and State’s shop and establishment act.
So which industry do you work in?
Is it a startup? usually in startups people work a lot without holidays though officially holidays are defined.
Hai,
Thanks for sharing in detail information fo leave benefit, And i gave few valuable information in this article.