The Indian banking sector is fragmented, with 46 commercial banks including 27 public sector banks, jostling for business with dozens of foreign banks as well as rural and co-operative lenders. This article talks about Banks in India, Types of Banks, What are Public Sector and Private Sector banks, About Nationalization of Banks, List of Banks with their Chairman, Head office, and Slogan History of Banking in India
Table of Contents
Schedule Banks, Commercial Banks, Cooperative Banks in India
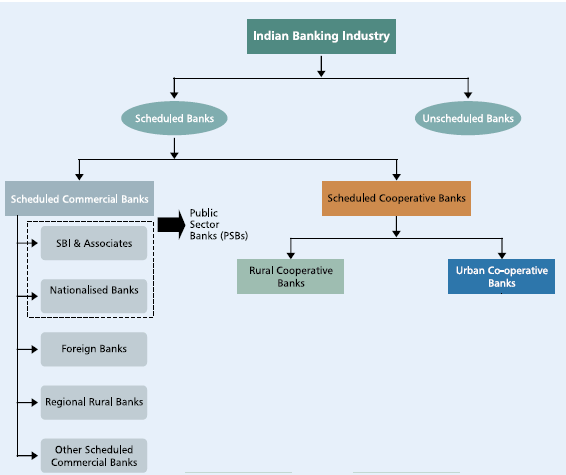
The Indian banking sector is broadly classified into scheduled banks and non-scheduled banks. For List of Banks under various categories refer to RBI Banks in India and Wikipedia List of Banks in India
- The Scheduled banks are those which are included under the 2nd Schedule of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. In order to be included under this schedule of the RBI Act, banks have to fulfill certain conditions such as having a paid up capital and reserves and satisfying the Reserve Bank that its affairs are not being conducted in a manner prejudicial to the interests of its depositors.A scheduled bank is eligible for loans from the Reserve Bank of India at bank rate. They are also given membership to clearing houses.
- Commercial banks refers to both scheduled and non-scheduled which are regulated under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949. Commercial banks operates on the commercial principles. They operate to earn a profit, accept deposits from public for the purpose of lending to industry and commerce.
- Co-operative Bank : The main objective of a Co-operative Bank is to accept deposits from the members and the public for the purpose of providing loans to farmers and small businessmen with a motto of service. The main objective of a Co-operative Bank is to accept deposits from the members and the public for the purpose of providing loans to farmers and small businessmen with a motto of service. In India, the Co-operative Banks are required to be registered under the Co-operative Societies Act, of the concerned state. In India Co-operative Banks are not nationalised.The basis of operations is on co-operative lines, i.e. service to its members and the society.
- Payment banks are banks which will offer selected services as compared to full fledged banks. A payment bank can only receive deposits and provide remittances. It cannot carry out lending activities. This type of bank is targeted at migrant labourers, low income households, small businesses, and other unorganised sector entities to to help India reach its financial inclusion targets. These banks have to use the word Payment Bank in its name which will differentiate it from other banks. Our article Payment Banks discusses it in detail.
Scheduled Banks in India
The scheduled banks are further classified into:
- Scheduled Commercial banks
- Nationalised banks
- State Bank of India and its associates
- Regional Rural Bank (RRBs)
- Foreign banks
- Other Indian private sector banks
Scheduled cooperative banks
- Scheduled State Co-operative Banks
- Scheduled Urban Co-operative Banks
Public Sector Banks: are banks whose majority of stakes hold by central government. During 1969 major Nationisation process started and 14 banks were nationalised and later in 1980 5 other banks were nationalised. Nationalisation made Banks public limited and are controlled by central government. In 2011 IDBI was nationalised with 500 cr capital and then on 8 March 2014, Bharatiya Mahela Bank was nationalised with 500cr capital. Example of Public Sector Banks are State Bank of India (SBI), Punjab National Bank (PNB) etc.
Nationalization is a process whereby a national government or State takes over the private industry, organisation or assets into public ownership by an Act or ordinance or some other kind of orders. This strategy has been frequently adopted by socialist governments for transition from capitalism to socialism. Examples of nationalizations In India . In 1949 , RBI was nationalized (RBI was state owned at the time of Indian independence). In 1953 : Air India was nationalised under the Air Corporations Act 1953. In 1972, 106 insurance companies were nationalised into four insurance companies. In 1973 Coal Industry and Oil companies were nationalised. Article What is is the difference between nationalized banks and public sector banks explains it in detail.

Private sector banks: Majority of share capital of the bank is held by non Government i.e private individuals. These banks are registered as companies with limited liability. · Examples of private sector banks are: Axis bank, HDFC Banks,ICICI Bank.

Foreign Banks: These banks are registered and have their headquarters in a foreign country but operate their branches in our country. Examples of foreign banks in India are: HSBC, Citibank, Standard Chartered Bank.

Regional Rural Banks,(RRBs) were established on October 2, 1975, to provide credit to the rural people who are not economically strong enough, especially the small and marginal farmers, agricultural labours, and even small entrepreneurs. Example Allahabad UP Gramin Bank, Kerala Gramin Bank.
List of Banks with their Chairman, Head office, and Slogan
| Bank Name | Chairman | Head Office | Tagline/ Slogan |
| State Bank of India | Smt. Arundhati Bhattacharya | Mumbai | The Banker to Every Indian |
| State Bank of Bikaner And Jaipur | Smt. Arundhati Bhattacharya | Jaipur | The nation banks on us |
| State Bank of Hyderabad | Smt. Arundhati Bhattacharya | Hyderabad | Modern.Innovative.Dependable |
| State Bank of Mysore | Smt. Arundhati Bhattacharya | Bengaluru | Working for a better Tomorrow |
| State Bank of Patiala | Smt. Arundhati Bhattacharya | Patiala | The nation banks on us |
| State Bank of Travancore | Smt. Arundhati Bhattacharya | Thiruvananthapuram | Long Tradition of Trust |
| Allahabad Bank | Rakesh Sethi | Kolkata | A Tradition of Trust |
| Andhra Bank | Satish Kumar Kalra | Hyderabad | Where India Banks |
| Bank of Baroda | P S Jayakumar | Vadodara (Baroda) | India’s International Bank |
| Bank of India | Vijayalakshmi R. Iyer | Mumbai | Relationship beyond banking |
| Bank of Maharashtra | Sushil Muhnot | Pune | One Family One Bank Mahabank |
| Bharatiya Mahila Bank | Usha Ananthasubramanian | New Delhi | Empowering Women, Empowering India |
| Canara Bank | Rakesh Sharma | Bangalore | Together we can, serving to grow, growing to serve |
| Central Bank of India | Shri. Rajeev Rishi | Mumbai | Build a better life around us |
| Corporation Bank | Shri Sadhu ram Bansal | Mangalore | A Premier Government of India Enterprise |
| Dena Bank | Shri Ashwani Kumar | Mumbai | Trusted Family Bank |
| IDBI Bank Ltd | Mr. Kishor Kharat | Mumbai | Bank aisa dost jaisa |
| Indian Bank | Mahesh Kumar Jain | Chennai | Your Tech-Friendly Bank |
| Indian Overseas Bank | R. Koteeswaran | Chennai | Good people to grow with |
| Oriental Bank of Commerce | Shri Animesh Chauhan | Gurgaon | Where every individual is committed |
| Punjab And Sind Bank | S.Jatinder Bir Singh | New Delhi | Where service is a way of life |
| Punjab National Bank | Usha Ananthasubramanian | New Delhi | The name you can BANK upon! |
| Syndicate Bank | Arun Shrivastava | Manipal | Faithful and Friendly |
| UCO Bank | Arun Kaul | Kolkata | Honours Your Trust |
| Union Bank of India | Arun Tiwari | Mumbai | Good people to bank with |
| United Bank of India | P.srinivas | Kolkata | The Bank that begins with “U” |
| Vijaya Bank | Shri.Kishore Kumar Sansi | Bengaluru | A friend you can bank upon |
| Axis Bank | Shikha Sharma | Mumbai | Badhti ka nam zindagi |
| Catholic Syrian Bank | Anand Krishnamurthy | Thrissur, Kerala | … support all the way |
| City Union Bank | Dr. N. Kamakodi | Kumbakonam | Trust and Excellence since 1904 |
| Development Credit Bank | Nasser Munjee | Mumbai | We value you |
| Dhanalakshmi Bank | Shri. G. Sreeram | Thrissur, Kerala | Tann. Mann. Dhan. |
| Federal Bank | Shyam Srinivasan | Kerala | Your Perfect Banking Partner |
| HDFC Bank | Aditya Puri | Mumbai | We understand your world |
| ICICI Bank | Ms.Chanda Kochhar | Vadodara | Hum Hai Na, Khyal Apka |
| Indusind Bank | Romesh Sobti | Mumbai | We Make You Feel Richer |
| ING Vysya Bank | Shailendra Bhandari | Bangalore | Jiyo easy |
| Jammu and Kashmir Bank | Mushtaq Ahmad | Srinagar | Serving To Empower |
| Karnataka Bank | P Jayarama Bhat | Mangaluru | Your family bank. Across India |
| Karur Vysya Bank | Katta Pradyumna Kumar | Karur, Tamil Nadu | Smart way to bank |
| Kotak Mahindra Bank | Uday Kotak | Mumbai | Let’s Make Money Simple |
| Lakshmi Vilas Bank | Mr. Rakesh Sharma | Karur, Tamil Nadu | Life smiles where LVB serves |
| Nainital Bank | S.K.Gupta | Nainital | Banking with personal touch |
| South Indian Bank | Sri. V.G. Mathew | Thrissur City, Kerala | Experience next generation banking |
| Tamilnad Mercantile Bank | HS Upendra Kamath | Tuticorin | Be a step ahead of life |
| Yes Bank’s Ltd | Rana Kapoor | Mumbai | Experience our expertise |
| Standard Chartered Bank | Sir John Peace | London | Your Right Partner. |
| Bandhan Bank | Ashok Lahiri | Kolkata | Aapka Bhala, Sabki Bhalai |
History of Banking in India
The Banking industry in India goes back to the 18th century when two banks the General Bank of India and Bank of Hindustan operated under the British rule. These banks are no longer operational. Around 1796, three important presidency banks were established. The government owned its first bank the State Bank of India (SBI). It was formed after the merger of Bank of Bengal. SBI is still functional today.
- The Reserve Bank of India, India’s central banking authority, was established in April 1935, but was nationalised on 1 January 1949 under the terms of the Reserve Bank of India (Transfer to Public Ownership) Act, 1948 (RBI, 2005b).
- Government implemented insurance cover for people who deposited money in banks in 1961.
- The Indian government passed the Banking Regulation (Amendment) Act 1965 where RBI was given immense power to handle financial services.
- The Government of India issued an ordinance, Banking Companies (Acquisition and Transfer of Undertakings) Ordinance, 1969, and nationalised the 14 largest commercial banks with effect from the midnight of 19 July 1969. These banks contained 85 percent of bank deposits in the country.
- Rural banks were created in 1975.
- A second dose of nationalisation of 6 more commercial banks followed in 1980 and Government of India controlled around 91% of the banking business of India.
- In the early 1990s, the then government embarked on a policy of liberalization, licensing a small number of private banks. These came to be known as New Generation tech-savvy banks, and included Global Trust Bank (the first of such new generation banks to be set up), which later amalgamated with Oriental Bank of Commerce, UTI Bank (since renamed Axis Bank), ICICI Bank and HDFC Bank
- Bharatiya Mahila Bank (BMB), the country’s first all-women lender November 2013, the bank started with a seed capital of R s1,000 crore. One of the key objectives of the lender is to focus on the banking needs of women and promote economic empowerment.
- The next stage for the Indian banking has been set up with the proposed relaxation in the norms for foreign direct investment, where all foreign investors in banks may be given voting rights which could exceed the present cap of 10% at present. It has gone up to 74% with some restrictions.
- On 28 Aug, 2014, Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana, a scheme for comprehensive financial inclusion was launched by the Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi. Run by Department of Financial Services, Ministry of Finance, on the inauguration day, 1.5 Crore (15 million) bank accounts were opened under this scheme
YouTube Video below shows the history of Banking in India
Related Articles:
- Payment Banks
- What are Mobile Wallets or Digital Wallets
- Different ways of Banking:Internet,Mobile
- Interest on Saving Bank Account : Tax, 80TTA
- What do we want from Bank : Is Social Banking the way to go?
- What is Auto Sweep Bank Account?
- JAM Trinity: Jan Dhan Yojana, Aadhaar and Mobile number

3 responses to “Banks In India: Logos,Tagline, History of Banking in India”
Thank you to give a some information
Thank you for sharing this valuable information.
Hey,
Wonderful collection! You have listed all the details about all the banks of India. Kudos to your great work mann! Keep going.