After working in a company for 4 years,10 months and 11 days an employee is eligible for gratuity. Gratuity is a reward for working in the same company. This article explains what is Gratuity? How many years of service is considered to be eligible for Gratuity? How is Gratuity amount calculated? What is tax and Tax exemption on Gratuity? The difference between Gratuity and Pension? How to show Gratuity in ITR?
On 21 Mar 2018, Parliament has passed Payment of Gratuity(Amendment) Bill 2017 paving the way for doubling the limit of tax-free gratuity to Rs 20 lakh. It will also fix the maternity leave period to 26 weeks for the purpose of computation of continuous period. Before 24 May 2010, limit was 3.5 lakh.
Accordingly, the gratuity withdrawal limits for staff in private companies and public-sector units have been doubled to Rs 20 lakh. At present, even if a worker accumulates more than Rs10 lakh as gratuity contribution, the withdrawal is capped at Rs10 lakh and the rest is paid out after deduction of taxes. This will only come into effect once the Payment of Gratuity Act is amended. The cabinet has approved the introduction of the amendment bill in Parliament.
The government had increased the gratuity ceiling limit from Rs 10 lakh to Rs 20 lakh for government employees with effect from January 1, 2016
Table of Contents
Understanding Gratuity
What is Gratuity?
Gratuity is the amount an employee may receive in gratitude for his services. Job-hopping can increase your pay, but good old loyalty also has its perks.
- Gratuity is a lump sum payment made by an employer to the employee based on the duration of his total service when the employee leaves the job. The reason for leaving the job can be either by resignation, death, retirement or termination, etc.
- The amount you get as gratuity depends on the number of years you have served and the last drawn monthly salary. Roughly, you get half a month’s Basic and Dearness Allowance(DA) for every completed year of service.
- Gratuity amount = (Number of years of service rounded off) * (Last drawn monthly Basic and DA) *15/26.
- Gratuity up to 20 lakh is tax-free.
- Gratuity can be claimed multiple times. Gratuity is purely a function of the number of years (minimum 5 years) an employee is in continuous service with a company. So it can be claimed any number of times, provided that he has been in the service of each of the companies for more than 5 years.
- The ceiling of tax-free exemption ie 20 lakhs is applied to the sum of the gratuities whether it is received from one or more than one employer in different years.
- The Gratuity whether taxable or tax-free has to be shown in ITR as Income from Salaries. In the year you have resigned from one company where you got Gratuity and joined another company, in ITR2 you would have 2 rows for Salaries for each of the employer.
What does continuous service mean?
It simply means no break by the employee from the date of joining to be eligible for the sum.
Gratuity and the Law
Gratuity comes under the Payment of Gratuity Act of 1972. Most establishments including Charitable institutes, hospitals, educational institutes employing 10 or more workers are covered by the Act.Even employees not covered under the Payment of Gratuity Act are entitled to gratuity. The document (pdf) related to act is at labour.gov.in/upload/uploadfiles/files/ActsandRules/SocitySecurity/ThePaymentofGratuityAct1972.pdf
How many years of service is considered to be eligible for Gratuity?
Gratuity is payable only if an employee has been with the employer for five years or more. But this rule is waived if an employee dies or is disabled. In such cases, even if the tenure is less than 5 years gratuity is paid to the nominees or to the employee. After 5 years of service, if you serve more than six months in the last year of employment, it is considered as a full year of service for calculation of gratuity amount. As per the judgement of the Supreme Court, an employee is eligible for gratuity if he has completed 4 years of continuous service and 240 days continuous working in the 5th year.Since the gratuity is a statutory service condition, the Act provides for the punishment of the employer who fails to pay it to an employee.
- To calculate the number of years of employment, employee’s date of joining and date of leaving is considered and date of resignation is not taken into consideration.
- The probation period is included while calculating eligibility for gratuity.
- If you have worked for MNC and join the parent company as a permanent employee in foreign location, you will no longer be the employee of the company registered in India and hence if you have completed 5 years in India office you will be eligible for gratuity.
- If the company changes its name but management remains the same, there is no resignation from one company and joining a new company then years in both the companies will be counted.
Gratuity shall be paid to
- The Employee
- Employee’s Nominee (if deceased employee had made a nomination)
- Employee’s Legal heir (if deceased employee had not made any nomination)
- If case of minor legal heir or nominee, the amount of gratuity shall be deposited with controlling authority. Controlling authority deposit/invest the gratuity amount in a financial institution or bank for benefit of minor, as may be prescribed, until such minor attains majority.
When will the employee not get Gratuity even after completing minimum 5 years of service? The employer can forfeit gratuity even if an employee has completed 5 years when the employee is fired for Disorderly or riotous conduct or any other act of violence or moral offence during the course of his employment. A proper enquiry should be held and employee should have been found guilty and termination letter should mention that. Other than that even on being fired an employee is eligible for Gratuity.
What if you work in multiple companies? Can Gratuity be claimed multiple times?
Gratuity is purely a function of the number of years (minimum 5 years) an employee is in continuous service with a company. So it can be claimed any number of times, provided that he has been in the service of each of the companies for more than 5 years.
But The ceiling of exemption ie 20 lakhs is applied to the sum of the gratuities whether it is received from one or more than one employer in different years.
Where an employee had received the gratuity in an earlier year(s) and had claimed exemption u/s 10(10) in respect of gratuity received earlier also, he will still be entitled to this exemption but the limit which at present is Rs. 20,00,000 shall be reduced by the amount of exemption(s) availed in the earlier year(s).
- If Shyam worked in ABC for 6 years, then when he leaves the company, he is entitled to gratuity which is calculated as (Last Basic/26) x 15 x 6
- Then if he joins DEF Limited and works for 11 years, then he can claim gratuity for the 11 years which is calculated as (Last Basic/26) x 15 x 11
What is the difference between Gratuity and Pension?
Gratuity is a one-time payment made to an employee who has completed 5 years of service in an organisation. Gratuity is the amount an employee may receive in gratitude for his services. Technically it is same as a TIP(TO INSURE PROMPTNESS), given to a waiter, taxi driver, or hairdresser. Gratuity will be mainly calculated on employee’s basic salary (last month salary). Gratuity is not calculated on any fixed rates, but by the formula, discussed below. There is no contribution from the employee. The percentage of basic salary which you may get as a Gratuity may be roughly around 6-7%.
The pension is the monthly payment made to retiring employees. Though most retiring employees get the gratuity, the pension is given only by some organisations, mostly government ones.
Is Gratuity part of CTC (Cost of Company)?
It’s a company discretion whether they want to make Gratuity part in employee’s CTC or not. The argument of not including Gratuity in CTC is that employee becomes eligible for gratuity only after completion of 5 years so how come a company can make it part of employee CTC. What if an employee leaves the company before completing 5 years? But employer sees Gratuity as a liability. So most of the employers include Gratuity in CTC because they believe Cost to the Company (CTC) is cash out go today + cash outgo in the future, which means, Basic + perquisites + Company’s contribution to your PF + today’s valuation of the gratuity element, especially when employer has taken insurance policy to cover gratuity liability. Our article Salary, Net Salary, Gross Salary, Cost to Company: What is the difference discusses CTC in detail.
Calculation of Gratuity Amount
How is Gratuity amount calculated?
The formula to calculate gratuity amount for a government employee/non government employee covered under the act is given below. Your employer can choose to pay you more but the maximum amount of gratuity according to the Act cannot exceed Rs. 10 lakh. Amount paid more than the formula is something voluntary and not mandated according to law(called ex-gratia)
Gratuity amount = (Number of years of service rounded off) * (Last drawn monthly Basic and DA) *15/26.
Ex: if an employee has served 20 years and in last year he drew monthly Basic and DA of Rs. 40,000, he would get a gratuity of Rs. 4,61,538 calculated as (20 * 40,000 *15/26).
If an employee has completed 20 years of service earning a monthly salary of Rs 2 lakh, will now be eligible to receive Rs 20 Lakhs (15/26 x 2,00,000 x 20 years) as tax-free gratuity, though the actual amount works out to Rs 23 lakh. And remaining 3 lakh would be taxable.
The number of years of service rounded off: If an employee has served more than 5 years and in last year of employment he served more than 6 months then for gratuity calculation it is considered as a full year of service. For instance, if his tenure is 20 years and 7 months, the years of service for gratuity calculation will be rounded off to 21. But if he has served 20 years and 5 or 6 months, then the number of years of service will be considered as 20.
For an employee not covered under the Gratuity Act
Gratuity amount = (Whole Number of completed years of service) * (Last drawn monthly Basic and DA) *15/30
Ex: if an employee has served in an organization not covered under the act for 20 years and 7 months, then in calculation 7 months are ignored and only 20 years are used for calculation. If in last year he drew monthly Basic and DA of Rs. 40,000, he would get a gratuity of Rs. 4,00,000 calculated as (20 * 40,000 *15/26).
How do companies plan to pay Gratuity amount?
Some organisations set up a gratuity fund as a part of their financial planning. Some companies take the Gratuity schemes of insurance companies like LIC’s, Group Gratuity(Cash Accumulation) Scheme where the employer pays a premium and gets a tax rebate on the premium.
Tax on Gratuity Amount
What about Tax on the Gratuity amount?
The gratuity received by an employee is NOT taxable if it is received on his retirement, his becoming incapacitated prior to retirement or if such gratuity is received by his widow, children or dependants on his death. So if one doesn’t retire and is below the retirement age then Gratuity is not tax-free. Gratuity is taxed under the head Income from Salaries. Gratuity received by the legal heir is taxable under the head Income from Other Sources. Some portion of gratuity received is exempt from tax as per Section 10(10) of the Income Tax Act which is explained below.
For a government employee, the entire gratuity amount is exempt from tax.
For a non-government employee covered under the Act or not covered by Act, he would get tax deduction for an amount which is the minimum of the following. Note that the ceiling of Rs. 20 lakh applies to the sum of all the gratuity received from one or more employers in the same or different years. Before 24 May 2010, limit was 3.5 lakh.
- Actual gratuity received
- 15 days Basic and DA for each completed year of service (according to calculations in the example above)
- Rs. 20 lakh
For example, after 20 years of service, the employer paid a gratuity of Rs. 5,00,000, gratuity amount by calculation is 4,61,538 to employee. Minimum of 5 lakh, 4,61,538 and 10 lakh is 4,61,538. The employee, nongovernment will enjoy tax deduction on Rs 4,61,538 and Rs 38,462(5 lakh – 4,61,538) will be subject to tax.
How to show Gratuity in ITR?
Calculate the gratuity amount exempted using the formula given
- Actual gratuity received
- 15 days Basic and DA for each completed year of service (according to calculations in the example above)
- Rs. 10 lakh
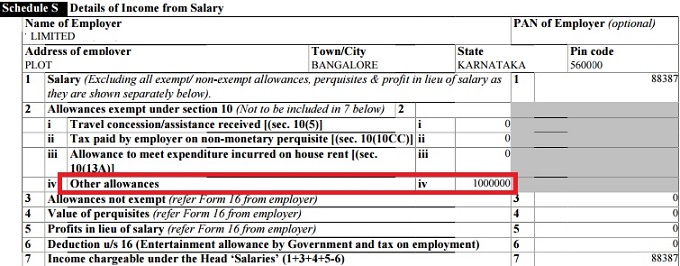
If you have joined another job, make 2 separate Schedule S i.e Details of Income from Salary.
- Enter details about the previous employer such as salary.
- Claim the exempted amount in ITR Other allowances
- If some amount of gratuity is not exempted then add it to salary amount.
In the image below, one got 10,88,387 as the gratuity amount. As only 10 lakh is exempt 88,387 becomes income from Salary.
Related Articles:
All articles related to Salary, EPF, Job , Income Tax in one place
- Interest on Saving Bank Account : Tax, 80TTA
- Exempt Income and Income Tax Return
- How to Calculate Income Tax
- What are Employee Stock Options (ESOP)
- Employee Stock Purchase Plan or ESPP
Job-hopping can increase your pay, but good old loyalty also has its perks.

35 responses to “What is Gratuity? Formula for calculating Gratuity? How much of Gratuity is Tax free? Tax,ITR”
Thank you for sharing your info. I really appreciate your efforts and I will be waiting for your next content.
I have completed 30 years in a pvt ltd, they r not giving wages ad per law, my final salary is 11250pm, pf amount calculating only for 5500, they r not following rules, what is my facilities, what is the procedure to get my benefits kindly reply
There are different ways of calculating PF.
Its better to ask your employer about the facilities it offers.
I worked in a Pharma company as medical rep for 6 years & 10 years. I resigned in December 2012. I submitted company properties & applied for settlement of my dues. Company HR is not replying to any of my request for settlement. I have not received Gratuity. Please suggest what to do?
Hi,
Please confirm the tenure to be considered for gratuity calculation if a person has completed 10 years, 5 months and 28 days of service.
Regards,
Anupriya
It will be consider for 10 years only…
i worked with most well known Tyre company,but duo to bed working condition
i resignation and at that time my working year is 4 years and 3 months.at time of joining company add Gratuity in C T C BUT WHEN I LIVE THE COMPANY IN FINAL STATEMENT THERE IS NO AMOUNT OF GRATUITY WAS ADDED.IF COMPANY GIVEN IN RETURN THAT YOUR C T C AMOUNT INCLUDING GRATUITY IS SO AND SO.SO COMPANY HAVE TO PAY IS THIS NOT BEACH OF CONTRACT,IF WE SIGN THE DOCUMENTS
WITH ALL CONDITION COMPANY APPLYING TO OUR SELF.AND WHAT WILL COMPANY DO TO THAT VERY AMOUNT WITCH BELONG TO US.IF THERE ANY REMEDY.KINDLY LET US KNOW.
Hi,
I joined an Indian company in 15th Feb’2010 and I left (according to my release letter) on 27th Nov’2014. I completed 4 years and 286 days of continuous service. When I asked them for Gratuity, they said that I am not eligible for Payment of Gratuity as I didn’t complete 5 years.
I would like to know the exact law and if I am eligible then what should I do.
Thanks.
As per the judgement of the Supreme Court an employee is eligible for gratuity if he has completed 4 years of continuous service and 240 days continuous working in 5th year. (Ref lawyersclubIndia ). Since the gratuity is a statutory service condition,the Act provides for the punishment of the employer who fails to pay it to an employee.
Law:
Section: 2A
Continuous service.
For the purposes of this Act, –
(1) an employee shall be said to be in continuous service for a period if he has, for that period, been in uninterrupted service, including service which may be interrupted on account of sickness,
accident, leave, absence from duty without leave….
(2) where an employee (not being an employee employed in a seasonal establishment) is not in continuous service within the meaning of clause (1), for any period of one year or six months, he shall be deemed to be in continuous service under the employer –
(a) for the said period of one year, if the employee during the period of twelve calendar months preceding the date with reference to which calculation is to be made, has actually worked under the employer for not less than –
(i) one hundred and ninety days, in the case of an employee employed below the ground in a mine or in an establishment which works for less than six days in a week; and
(ii) two hundred and forty days, in any other case;
So you can try to talk it with your company and understand the reasons why company is not giving you gratuity
Can you please provide me the copy of the “supreme court” judgment.
I need the judgment urgently because I had filled a case to my company, and the labour officer is asking for the “supreme court” judgment copy.
regards
Partha
m_partha12@rocketmail.com
Hello,
We could find this. Hope it helps
Supreme Court Judgement
Can a Private Organisation decide make their own rules that they will pay Gratuity to Teaching Staff only if they have completed 10 years in service and pay the Non Teaching Staff is they have completed only 5 years of service?
I fall in teaching staff category..They are refusing orally citing the above rule. What should I do? Thanks in advance…Your reply awaited.
Sir, theoretically No
Gratuity Act is applicable to all establishments, where number of employees, are 10 or more in any day of the preceding 12 months.
Charitable institutes and hospital are also covered under the act.
It includes both commercial and non commercial establishment like educational institutes etc.
Only Basic and Dearness allowance should be considered as wages for the purpose of Gratuity.
No, even if company is not doing financial well, company is bound to pay gratuity amount.
Company should ensure that it pays gratuity within 30 days from the date when gratuity become payable to an employee. Also it is responsibility of employer to notify employee about his gratuity payment even if employee do not apply for same. It is employer duty to pay the gratuity.
He should send letter to company asking for his rights and in case of no action possibility of approaching court.
If no result, then take help of any advocate and approach court. He will surely get his rights.
Thanks…..Thou maketh my Day!
Be Blessed!
Best of Luck. Keep us posted on whether your institution gives the Gratuity.
Can a Private Organisation decide make their own rules that they will pay Gratuity to Teaching Staff only if they have completed 10 years in service and pay the Non Teaching Staff is they have completed only 5 years of service?
I fall in teaching staff category..They are refusing orally citing the above rule. What should I do? Thanks in advance…Your reply awaited.
Sir, theoretically No
Gratuity Act is applicable to all establishments, where number of employees, are 10 or more in any day of the preceding 12 months.
Charitable institutes and hospital are also covered under the act.
It includes both commercial and non commercial establishment like educational institutes etc.
Only Basic and Dearness allowance should be considered as wages for the purpose of Gratuity.
No, even if company is not doing financial well, company is bound to pay gratuity amount.
Company should ensure that it pays gratuity within 30 days from the date when gratuity become payable to an employee. Also it is responsibility of employer to notify employee about his gratuity payment even if employee do not apply for same. It is employer duty to pay the gratuity.
He should send letter to company asking for his rights and in case of no action possibility of approaching court.
If no result, then take help of any advocate and approach court. He will surely get his rights.
Thanks…..Thou maketh my Day!
Be Blessed!
Best of Luck. Keep us posted on whether your institution gives the Gratuity.
Hi!
My resignation has been accepted by my company. Accordingly 26 th April will be my last working day. 26 april is sunday- weekly holiday. This was supposed to be the day on which I would be completing my 5 years bond period with the company- as I had joined there for 5 years on 27/4/2010.
So, 1] Do qualify for getting gratuity in above scenario?
2] And if suppose, I have to put in a leave from 25-29 April i.e. before
my supposed to be last working day and finish my left over 2 days on 30/4/15
or 2/5/2015 as First May shall be a government holiday; Will i get gratuity?
If answer to above 1] or 2] is NO—-What measures should I adopt to make it a Big Yes?
Thanks
Hello Sir,
Gratuity is payable only if an employee has been with the employer for five years or more. As per the judgement of the Supreme Court an employee is eligible for gratuity if he has completed 4 years of continuous service and 240 days continuous working in 5th year. (Ref lawyersclubIndia. )
To be on the safe side ,Technically it would make sense to leave after 26 Apr.
I would suggest talking it with your manager or your finance or payroll department as each company interprets the law in their own way.
Best of Luck and Do keep us updated.
Thanks for the Info!
I enquired with them…..the management says that as per the rules of their trust, they will give gratuity to a worker [Non Teaching] staff if he has completed 5 years and to Teaching Staff only if he has completed 10 years of service. I fall in Teaching category…So does that mean that I won`t be getting Gratuity? Are they allowed to make rules as per their choice like that? Its a Private Health Educational trust. Any Comments!
Thanks..
Hi!
My resignation has been accepted by my company. Accordingly 26 th April will be my last working day. 26 april is sunday- weekly holiday. This was supposed to be the day on which I would be completing my 5 years bond period with the company- as I had joined there for 5 years on 27/4/2010.
So, 1] Do qualify for getting gratuity in above scenario?
2] And if suppose, I have to put in a leave from 25-29 April i.e. before
my supposed to be last working day and finish my left over 2 days on 30/4/15
or 2/5/2015 as First May shall be a government holiday; Will i get gratuity?
If answer to above 1] or 2] is NO—-What measures should I adopt to make it a Big Yes?
Thanks
Hello Sir,
Gratuity is payable only if an employee has been with the employer for five years or more. As per the judgement of the Supreme Court an employee is eligible for gratuity if he has completed 4 years of continuous service and 240 days continuous working in 5th year. (Ref lawyersclubIndia. )
To be on the safe side ,Technically it would make sense to leave after 26 Apr.
I would suggest talking it with your manager or your finance or payroll department as each company interprets the law in their own way.
Best of Luck and Do keep us updated.
Thanks for the Info!
I enquired with them…..the management says that as per the rules of their trust, they will give gratuity to a worker [Non Teaching] staff if he has completed 5 years and to Teaching Staff only if he has completed 10 years of service. I fall in Teaching category…So does that mean that I won`t be getting Gratuity? Are they allowed to make rules as per their choice like that? Its a Private Health Educational trust. Any Comments!
Thanks..
Hi!
My resignation has been accepted by my company. Accordingly 26 th April will be my last working day. 26 april is sunday- weekly holiday. This was supposed to be the day on which I would be completing my 5 years bond period with the company- as I had joined there for 5 years on 27/4/2010.
So, 1] Do qualify for getting gratuity in above scenario?
2] And if suppose, I have to put in a leave from 25-29 April i.e. before
my supposed to be last working day and finish my left over 2 days on 30/4/15
or 2/5/2015 as
Hi!
My resignation has been accepted by my company. Accordingly 26 th April will be my last working day. 26 april is sunday- weekly holiday. This was supposed to be the day on which I would be completing my 5 years bond period with the company- as I had joined there for 5 years on 27/4/2010.
So, 1] Do qualify for getting gratuity in above scenario?
2] And if suppose, I have to put in a leave from 25-29 April i.e. before
my supposed to be last working day and finish my left over 2 days on 30/4/15
or 2/5/2015 as
Thanks very much for the clarification and your input on gratuity being the least in my Checklist!! 🙂 🙂
You are welcome Prassri.
Thanks very much for the clarification and your input on gratuity being the least in my Checklist!! 🙂 🙂
You are welcome Prassri.
thanks for this article!! I have one query though…
My company’s particular ITO division is going to sold to another major MNC in another few months. The employees will be given a new offer letter by the new company. Current employer will be paying the leave encashment, if any for each employee. It will be as if the employee will be leaving this old employer and joining the new employer.
However, there is one thing which is not yet clear:
Gratuity .
There is a discussion amongst employees that gratuity amount will be paid to employees who have worked for more than 6 months. For example, if a person has been working for 8 months, he/she would be receiving 2 months of Gratuity amount from the old employer.
I request your views in this scenario because there is lot of confusion amongst various employees on whether to stay or leave with current employment thinking about these sort of benefits.
Hello Prassri,
I can understand the confusion. But Every company may have their own interpretation of the rule.
Typically only those who have worked for 5 years and more are eligible for gratuity. But as it taken over by another company they might pay gratuity for employees who have worked less number of years.
Best is to get clarification from your Payroll or IT department or Manager.
Decision to stay/leave should be based on future prospects of the job, whether you would like to go to work every day. As per me gratuity should be much down in your checklist.
Hope the answer helped
thanks for this article!! I have one query though…
My company’s particular ITO division is going to sold to another major MNC in another few months. The employees will be given a new offer letter by the new company. Current employer will be paying the leave encashment, if any for each employee. It will be as if the employee will be leaving this old employer and joining the new employer.
However, there is one thing which is not yet clear:
Gratuity .
There is a discussion amongst employees that gratuity amount will be paid to employees who have worked for more than 6 months. For example, if a person has been working for 8 months, he/she would be receiving 2 months of Gratuity amount from the old employer.
I request your views in this scenario because there is lot of confusion amongst various employees on whether to stay or leave with current employment thinking about these sort of benefits.
Hello Prassri,
I can understand the confusion. But Every company may have their own interpretation of the rule.
Typically only those who have worked for 5 years and more are eligible for gratuity. But as it taken over by another company they might pay gratuity for employees who have worked less number of years.
Best is to get clarification from your Payroll or IT department or Manager.
Decision to stay/leave should be based on future prospects of the job, whether you would like to go to work every day. As per me gratuity should be much down in your checklist.
Hope the answer helped