For the product to reach from the producer to the consumer, lots of people are involved. Goods or service can travel through the Producer to Consumer in many different ways, through a wholesaler, retailer, middleman, direct. We shall explore these different ways in detail.
To produce good, different things or people are needed. Let’s say we want to build a table. What would we need?
- First of all, we would need wood, i.e. the raw material. For making dress we need cloth.
- Once we have the wood then we need to have a carpenter to make the table i.e. we need people or human resources.
For buying wood and to pay the carpenter to make the table, we need money. Or, we can go to the shop and buy the table. But even then, it’s the carpenter who would have to make the table and supply it to the shop to sell it.
For the product to reach from the producer to the consumer, lots of people are involved. Let’s take an example.
Table of Contents
The journey of Product from Producer to Consumer
Goods or service can travel through the Producer to Consumer in many different ways. Why can’t a producer sell directly?
Can a small farmer not go directly to the market and sell directly?
The farmer not only has to take care of the growing of fruits and vegetables but he also has to sell them. Using a middleman may mean lower price but usually, all the wares are sold which means the farmer can spend more time on the farm. In fact, nowadays in fact companies like Reliance (under the name’Reliance Fresh’) are buying directly from the farmers and selling through their shops, so the farmer benefits.
- A farmer in Nagpur has an orange orchard. Once the oranges are ripened, he sells the oranges to an agent in Bangalore.
- The agent collects oranges from the farmer, packs them, and sells them to a wholesaler at Bangalore subzi-mandi.
- The wholesaler then distributes them to various retail fruit vendors throughout Bangalore by selling smaller quantities.
- Finally, we purchase from those vendors, shops or the cart selling oranges, as per our requirement
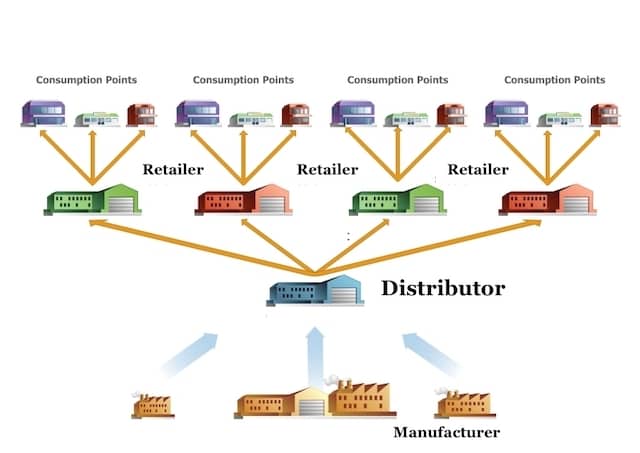
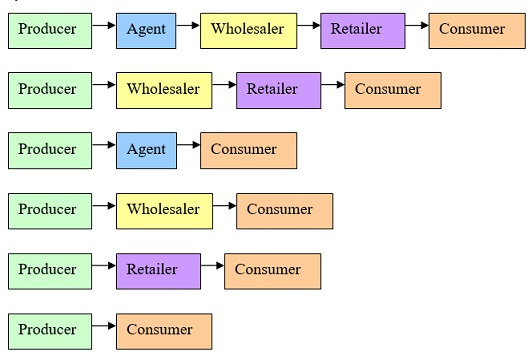
Thus, oranges grown in Nagpur reach the consumer by passing through several hands like an agent, wholesaler and a retailer. These are called middlemen. These middlemen become a route or path along which goods move from producer to consumers. They make a chain, each passing the product down the chain to the next organization before it finally reaches the consumer or the end-user. This process is known as the ‘distribution chain’ or the ‘channel’.

Producers sell directly to consumers without involving any middlemen. They may sell directly through their salesmen going door to door or opening their own shops. Example: Bata Shoes, Sony have opened their own shops to sell their products directly to consumers. Banks, Airlines also sell their services directly to consumers.
More middlemen involved mean more cost to be added to the product. Every middleman would like to earn money for providing his services. No one is doing it for free! So 1 kg of potatoes which a farmer sold at Rs 5 per kg becomes Rs 12 by the time your mother picks it up from the shop because the middlemen take their share!
Retailer, Whole Saler, Distributor
A retailer is one who sells directly to the end customer. A retailer is the one who is involved Business to customer sale(B2C). He sells to customers and buys from businesses.
Wholesalers have a huge quantity of the same product. For example, a marble shop which is a wholesaler and has a huge quantity of different marble floorings and tiles.
Distributors sell strictly from business to business. An example of distributors are the ones selling Apple Smartphones who visit all the shops within a region to ensure that the material is on display by the retailers. You will not find a wholesaler of Apple but you will find retailers and distributors.
Consumer durables, electronics, hardware or other equipments, medicines are perfect examples of sectors which use distributors and not wholesalers. A medicine retailer may have more than 1000 different type of medicines. He cannot afford to visit wholesalers who are stocking all these machines.
So the companies appoint a distributor who can distribute the various medicines to the retailer who in turn sells it to customers. Similarly, there are various distributors for washing machines, televisions and other goods who distribute products to retailers – small retailers or modern retailers.
The retailer himself buys products from wholesalers and distributors. If it is electronic goods, most likely a retailer will buy from a distributor. There is also a lot of logistics involved in the distribution of large items so generally distributors visit retailers.
If however, a retailer wants to sell food items, then it is likely that the retailer visits a wholesaler and buys the products in wholesale. This is because a single wholesaler generally deals with a limited number of goods and he has huge quantities of those goods. So a retailer might have to visit multiple wholesalers to complete his requirement.
A retailer stocks limited number of each item. So if you go to a stationery store, you will see only 50 units of the same pen being stocked. But if you go to a wholesaler, the quantity will be 500000 units in stock with the wholesaler. This is a major difference between wholesalers retailers and distributors – the number of units they have in stock at a time.
Different ways in which product reaches from Producer to Consumer
How to choose best distribution channel?
What factors are taken into account in choosing the best distribution channel? Here is a summary:
Nature of the product
- Perishable/fragile? Is the product with a short-life
- Technical/complex? Complex products are often sold by specialist distributors or agents
- Customised? A direct distribution approach often works best for a product that the end consumer wants providing to a distinct specification
- Type of product – e.g. convenience, shopping, speciality
- The desired image for the product – if intermediaries are to be used, then it is essential that those chosen are suitable and relevant for the product.
The market
- Is it geographically spread?
- Does it involve selling overseas (see further below)
- The extent and nature of the competition – which distribution channels and intermediaries do competitors use?
The business
- Size and scope – e.g. can it afford an in-house sales force?
- Marketing objectives – revenue or profit maximisation?
- Does it have established distribution network or does it need to extend its distribution option
- How much control does it want over distribution? The longer the channel, the less control is available
Legal issues
Are there limitations on sale?
What are the risks if an intermediary sells the product to an inappropriate customer?
What do sellers and buyers want? Those who want to sell, have aims different from those who want to buy. Seller wants to sell at the highest price he can get. A buyer wants to buy at the cheapest price.