Inflation means a certain amount of money buys you much less today than it did years ago. Inflation is one of the most important concepts in economics. Central banks throughout the world use monetary policy to control inflation. In India Inflation is measured through two major indices: Consumer Price Index(CPI) and Wholesale Price Index (WPI). What is Inflation? Why should you worry about the Inflation? How is Inflation measured? What Causes Inflation? Is Inflation Good or Bad? HypeInflation and What happened in Zimbabwe? And Venezula.
Table of Contents
What is Inflation?
Inflation is defined as an increase in the level of prices for goods and services in a country and is measured as an annual percentage change. Say you buy a veg thali today for INR 100. The yearly inflation is 10%. Next year, the same veg thali will cost you INR 110.
You would have heard your grandparents, parents talk about how expensive things have become now, Kalyug ka zamana hai. Humaare zamane mein toh itne kaam paise mein mil jata that. In your grandparents time they used to get a thali for Rs 1. But these days you just get a candy for 1 rupee.
The reason for spending more to buy the same thing is due to Inflation as Inflation reduces how much you can buy. The image shows how much buying power of money will reduce over years.
But one also needs to remember that the wages or salaries have also increased.
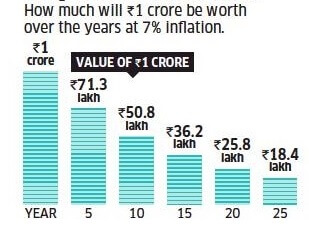
After the study of data of different years, it has been observed that the moderate rate of inflation motivates the investors or producers for more production in the economy because they got more return as compared to their cost. This scenario generates employment and purchasing power in the economy hence a holistic development of the economy take place.
Central banks along with Government track Inflation and try to keep it within acceptable limits.
In India, RBI wants a healthy inflation rate of 5 per cent.
If inflation reaches the double-digits, that’s hyperinflation. If it happens, you will need a wheelbarrow of money to buy a loaf of bread. Hyperinflation only occurs when the government is so irresponsible that it prints money without regard to the inflation rate. It happened in Germany in the 1920s and Zimbabwe in the 2000s. And in 2018 it is happening in Venezuela!
Overview of How is Inflation measured?
The inflation is measured using the Price Index, where the change in prices of goods, such as milk, footwear, clothing, wheat, rice, hospitalization, education and many such products and services are measured. Based on types of goods selected and where they are selected from we have different kinds of price indices.
In India, two kinds of indices are used to measure inflation: Wholesale Price Index (WPI) and Consumer Price Index (CPI).
Consumer Price Index (CPI) calculates the average price paid by the consumer to the shopkeepers. Education, communication, transportation, recreation, apparel, foods and beverages, housing and medical care are the 8 groups in India for which the CPI is measured.
Wholesale Price Index (WPI) is an indicator of price changes in the wholesale market. WPI calculates the price paid by the manufacturers and wholesalers in the market. WPI measure the changes in commodity price at selected stages before goods reach to the retail level.
WPI was used by the Reserve Bank of India till 2014 to make its monetary policy, The main reason RBI, under ex-governor Raghuram Rajan, shifted to the Consumer Price Index is because it neglects services and the bottlenecks between a wholesaler and a retailer
To give a simple example, let’s assume that the typical consumers in an economy buy a basket of only two goods; rice and chocolates. By conducting surveys, we find out that on average every consumer buys 3 kgs of rice and 8 chocolates. So we can now fix our market basket to 3 kgs of rice and 8 chocolates. But the effect of the rise in the price of rice is different from that of chocolates. So more importance is given to the price of rice than chocolates. This is called the weighted average.
Calculating Consumer Price Index, Inflation rate follows a four-step process which is explained here.
- Fixing the market basket,
- calculating the basket’s cost
- Computing the index
- Computing the inflation rate.
What Causes Inflation?
There are three main causes of inflation.
Demand-Pull inflation: When the demand for something is far greater than the supply or availability of it. This theory can be summarized as “too much money chasing too few goods“. In other words, if demand is growing faster than supply, prices will increase. This usually occurs in rapidly growing economies. This theory is often promoted by the Keynesian school of economics.
Cost-Pull inflation: When companies are faced with increased input costs like raw goods and materials or wages, they will preserve their profitability by passing this increased cost of production onto the consumer in the form of higher prices. For Example, if there is an increase in milk prices, it would increase the price of a tea or coffee cappuccino. Though companies often try to limit the cost increases they pass on to customers by finding ways to make their operations more efficient and their workers more productive
Too much money: The third reason that inflation occurs is when the country prints money excessively. If there’s too much printed money in circulation, it reduces the value of money, and as a result, prices are hiked.
Types of Inflation
There are several variations of inflation:
- Deflation is when the general level of prices is falling. This is the opposite of inflation.
- Hyperinflation is unusually rapid inflation. In extreme cases, this can lead to the breakdown of a nation’s monetary system. One of the most notable examples of hyperinflation occurred in Germany in 1923, when prices rose 2,500% in one month!
- Stagflation is the combination of high unemployment and economic stagnation with inflation. This happened in industrialized countries during the 1970s, when a bad economy was combined with OPEC raising oil prices.
If inflation reaches the double-digits, that’s hyperinflation. If it happens, you will need a wheelbarrow of money to buy a loaf of bread. Hyperinflation only occurs when the government is so irresponsible that it prints money without regard to the inflation rate. It happened in Germany in the 1920s and Zimbabwe in the 2000s. And in 2018 it is happening in Venezuela!
Is Inflation Good or Bad?
Inflation hurts your buying power. It means you have to pay more for the same goods and services. But if your income doesn’t keep up with inflation, your buying power declines. Over time, inflation increases your cost of living. If the inflation rate is high enough, it hurts the economy.
Inflation affects your savings. So Rs. 25 lakhs might be enough for a higher education degree today, but will it be enough in 10 years time? Rs. 2 lakhs might be enough for an emergency hospitalization today, but will it be enough in 5 years’ time? ? It is extremely important to think about your savings with respect to inflation and see if you’re saving enough to cover for your future goals inflation will eat into the value of your savings. It is better to include inflation while you are saving than to ignore it and find yourself coming short when it’s too late.
After the study of data of different years, it has been observed that the moderate rate of inflation motivates the investors or producers for more production in the economy because they got more return as compared to their cost. This scenario generates employment and purchasing power in the economy hence a holistic development of the economy take place.
But if the industries, people do not re-invest this benefit and spend on luxurious life or not invested in the productive activities then the economy will not be benefitted. Because in the absence of new investment new jobs will not be created which will further reduce the purchasing power of the consumers.
So let’s look at Impact of Inflation on different peoples:
Loss for Consumer, Lender, Public saving, Export, Pensioners, Fixed Income Group(such as daily wage earners, pensioners, salaried etc.)
Gain for Borrower, Public Expenditure, Taxation, Producers, Farmers, Entrepreneurs
Inflation in India
If we talk in the reference of the Indian economy; it is observed that if the rate of inflation is between 3 to 5%; it is beneficial for the economy and if it is beyond this range it adversely affects the manufacturing sector in the country which further squeezes the job opportunities and other opportunities.
The images show India’s inflation rate from 1961 to 2013 (Ref IBN Live) and from 2012 and expected till 2022
The lowest inflation rate, technically deflation, was recorded in May 1976 at (-)11.31 per cent. On the other hand, the highest inflation rate observed was 34.68 per cent in September 1974.
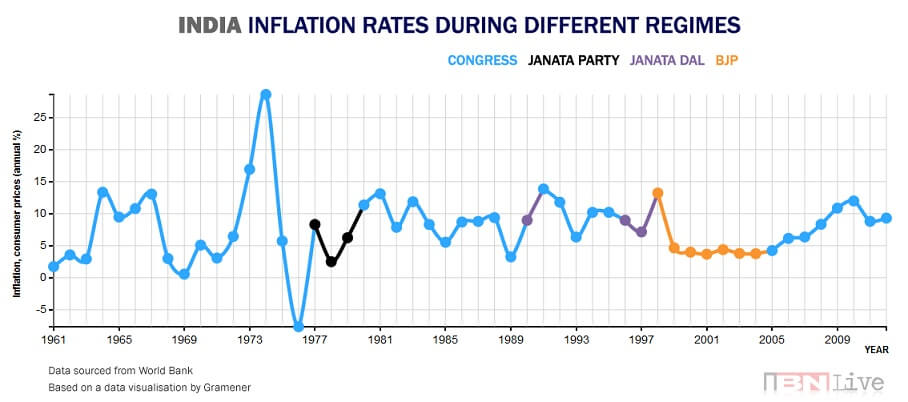
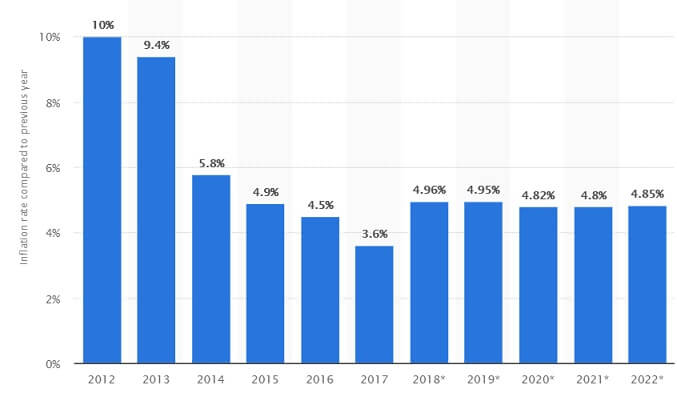
Who tracks and controls the Inflation and How?
Central banks along with Government track Inflation and try to keep it within acceptable limits.
In India, RBI wants a healthy inflation rate of 5 per cent.
In the United States, the FED aims for a target inflation rate of 2 per cent year-over-year.
The main policy tools to control inflation include:
- Monetary policy – Setting interest rates. Higher interest rates reduce demand, leading to lower economic growth and lower inflation
- Control of money supply – There is a close link between the money supply and inflation, therefore controlling money supply can control inflation. Two examples of this include calling in debts that are owed to the government and increasing the interest paid on bonds so that more investors will buy them. The latter policy raises the exchange rate of the currency due to higher demand and, in turn, increases imports and decreases exports.
- Supply-side policies – policies to increase competitiveness and efficiency of the economy, putting downward pressure on long-term costs.
- Fiscal policy – a higher rate of income tax could reduce spending and inflationary pressures.
- Wage controls. Trying to control wages could help to reduce inflationary pressures.
How to protect from Inflation?
Inflation tells people how much they need to make for them to maintain their current standard of living. For example, their income increases by 4% and inflation was 5%, then the real increase would be -1% (5%-4%).
The most powerful way to protect yourself from inflation is to increase your earning ability and income.
If you work and get a 5 per cent annual raise or a promotion with a 20 per cent gain, you have a net increase.
To grow your wealth, as you will not be working throughout your life, You also need to make your money work harder by investing in something which gives more returns than inflation.
Investing in the stock market is suggested as it gives more return than inflation. In India stock market has given around 10 per cent over time. Whether it will do so in the future is unknown, and there’s the risk. One needs to understand the risk and consult a financial planner.
How to Calculate Inflation
Calculating Consumer Price Index, Inflation rate follows a four-step process which is explained here.
- Fixing the market basket,
- calculating the basket’s cost
- Computing the index
- Computing the inflation rate.
Fixing the market basket
To give a simple example, let’s assume that the typical consumers in an economy buy a basket of only two goods; rice and chocolates. By conducting surveys, we find out that on average every consumer buys 3 kgs of rice and 8 chocolates. So we can now fix our market basket to 3 kgs of rice and 8 chocolates. But the effect of the rise in the price of rice is different from that of chocolates. So more importance is given to the price of rice than chocolates. This is called the weighted average.

Calculate Basket’s Cost
Once the basket is fixed, the next step in calculating the Price Index is to find the current and previous prices of all goods and services. This allows us to calculate the price of the entire basket at any point in time. The important thing to note here is that the market basket remains fixed, i.e. neither goods or services nor their quantity changes. Hence, the only variable is price, which allows us to isolate the effects of price changes over the years.
Revisiting our example, we now have to find the prices of ice cream and chocolates.
In 2017, a kg of rice costs Rs 20 and a chocolate sells at Rs 10.
Hence, the basket’s cost adds up to 140 (3 kgs rice x 20 + 8 chocolates x 10).
Back in 2016, consumers only had to pay 18 for an kg of rice and 9 for a chocolate, which results in a basket cost of 126(3 kgs rice x 18 + 8 chocolates x 9). We can already see that the price level has increased from 2016 to 2017.
Weighted Average
Price Index is a weighted average of prices of a market basket of goods and services. Weighted average means giving weight or percentage of importance to an item, for example, the rise in the price of houses has a different affect than the rise in the price of wheat or rice or toothbrush.
When we say Inflation rate is 4.28%, it does not mean milk prices and school fees will increase by the same 4% every year! Each category has its own rate of rise and fall, but it gives a trend of how expensive things are becoming.
Ex of Weighted Average:
Example 1: A student is enrolled in a course where the final grade is determined based on the following categories: tests 40%, final exam 25%, quizzes 25%, and homework 10%. The student has earned the following scores for each category: tests-83, final exam-75, quizzes-90, homework-100. What is the student’s overall grade?
To calculate a weighted average with percentages, each category value must first be multiplied by its percentage. Then all of these new values must be added together. In this example, we must multiply the student’s average on all tests (83) by the % that the tests are worth towards the final grade (40%). Thus, the overall calculation would be (83 * .40) + (75 * .25) + (90 * .25) + (100 * .10) = 33.2 + 18.75 + 22.5 + 10 = 84.45 or 84% if rounded down.
Base Year and Consumer Price Index
Next, to actually calculate the Consumer Price Index we need to define a base year. The base year serves as the benchmark against which all other years are compared. It can be designated freely, although for the sake of comparability it is common practice to keep the same base year for a few years before moving on to a new one.
The index is then calculated by dividing the price of the basket of goods and services in a given year (t) by the price of the same basket in the base year (b). This ratio is then multiplied by 100, which results in the Consumer Price Index.
The formula to calculate Consumer Price Index is =100 * ( Cost of Basket in Year / Cost of Basket in Base Year)
In the base year, CPI always adds up to 100.
If in the above example, CPI in 2016 is taken as a base year with Cost of Basket as 126.
The CPI in 2017 is 111.11 = (140/126)x100. Thus we can say that the Consumer Price Index has increased from 100 in 2016 to 111.1 in 2017.
The base year of CPI and WPI in India is 2012.
Inflation Rate
The inflation rate is the percentage change in the price index from one period to the preceding one. To calculate it, we can use the following formula = 100 * (Price Index in given Year – Price Index in Year before given year/ Price Index in the year before given year)
In our example, the inflation rate in 2017is 11.1% (i.e. ([111.1-100]/100)x100).
Measuring Inflation in India: WPI and CPI
In India, two kinds of indices are used to measure inflation: Wholesale Price Index (WPI) and Consumer Price Index (CPI).
WPI was used by the Reserve Bank of India till 2014 to make its monetary policy, The main reason RBI, under ex-governor Raghuram Rajan, shifted to the Consumer Price Index is because it neglects services and the bottlenecks between a wholesaler and a retailer
What is the Consumer Price Index (CPI)?
CPI takes into account the change in the average retail price of goods and services over a period of time. It includes:
- Food and beverages
- Tobacco, clothing and footwear
- Fuel and other items
CPI, based on 260 commodities including certain services, measures the change in prices at the retail level. Prices of sample goods and services are collected periodically (usually every month) by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation, and the change, if any, is noted
Through CPI, the RBI tried to increase the span of monetary control and monitor inflation better.
What is the Wholesale Price Index (WPI)?
WPI measures the prices at the wholesale level. WPI is the price of a representative basket of wholesale goods. It takes a basket of 697 items into account and shows the combined prices. An important feature of the WPI which separate it from the CPI is that prices are collected from wholesalers. The WPI inflation does not capture price changes of services but the CPI does.
The WPI is calculated by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry. It is in use since 1942 and is being published from 1947 regularly. It has a long history for serving as the nationwide inflation indicator till the emergence of the combined CPI in 2011.
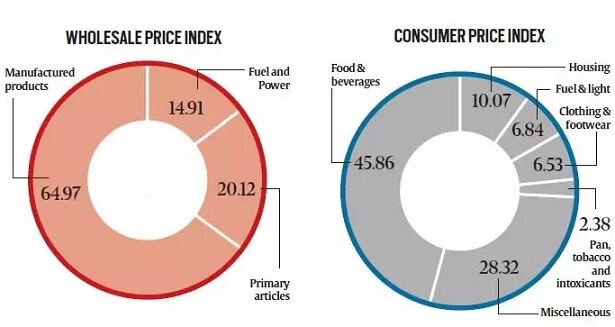
WPI reflects the inflation pertaining to the change in the average price of the goods that are transacted in the wholesale market. It includes:
- Primary articles consisting of the price of food, non-food and mineral items (20.1 per cent)
- Manufactured products consisting of food and non-food products (65 per cent of total weight),
- Fuel and power (14.9 per cent).
It is released on three duration basis.
- A) Weekly: on Every Thursday for Primary Articles and Fuel Group.
- B) Monthly : On 14th of Every month for all commodities.
- C) Final: the Final list is released every two months (~EIGHT weeks). When they get authentic price data for all commodities.
Difference between WPI and CPI
For common people, i.e. consumers, it is the CPI that is most relevant. CPI also covers the service sector. Therefore, the RBI linked CPI for fixing interest rates in India.
|
Basis For Comparison |
Wholesale Price Index (WPI) |
Consumer Price Index (CPI) |
| Meaning | WPI, amounts to the average change in prices of commodities at wholesale level | CPI, indicates the average change in the prices of commodities, at the retail level. |
| Published by | Office of Economic Advisor (Ministry of Commerce & Industry) | Central Statistics Office (Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation) |
| Measures prices of |
Goods only | Goods and Services both |
| Measurement of Inflation | First stage of transaction | Final stage of transaction |
| Prices paid by | Manufacturers and wholesalers | Consumers |
| How many items covered | 697 (Primary, fuel & power and manufactured products) | 448(Rural Basket)
460 (Urban Basket) |
| What type of items covered | Manufacturing inputs and intermediate goods like minerals, machinery basic metals etc. | Education, communication, transportation, recreation, apparel, foods and beverages, housing and medical care |
| Base year | 2011-12 | 2012 |
| Used by | Only a few countries including India | 157 countries |
| Data released on | Primary articles, fuel and power (Weekly basis) &
overall (monthly basis since 2012) |
Monthly basis |
HypeInflation and What happened in Zimbabwe?
How would you like to pay $417.00 per sheet of toilet paper?
Economic Crisis, Hyper Inflation, Venezuela
The International Monetary Fund says that Venezuela’s inflation is expected to hit 1,000,000% by the end of the year 2018.
It wasn’t so long ago that Venezuela was the wealthiest nation in the entire of South America. Today, half of their population lives in extreme poverty. So, the question is… How did they end up there? What did their government do so wrong to destroy an economy in so little time? Today, we are gonna tell you the story.


2 responses to “What is Inflation? How is it Calculated? WPI, CPI in India,HyperInflation”
Very comprehensive view of the inflation, and explained in a simple way. Must have taken a huge effort to put it all together!
interesting informative post thanks to sharing